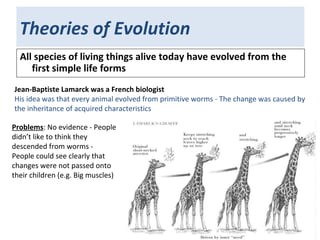
1. Theories of evolution progressed from Jean-Baptiste Lamarck's idea that acquired traits could be inherited, to Darwin's theory of natural selection and evolution of all life from simpler forms.
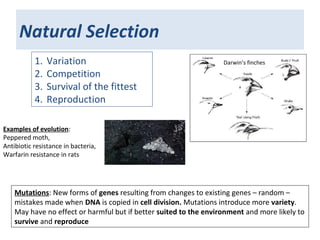
2. Darwin observed adaptations in animals on the Galapagos Islands, leading him to propose natural selection and survival of the fittest as mechanisms for evolution, though his ideas faced initial religious and evidentiary objections.
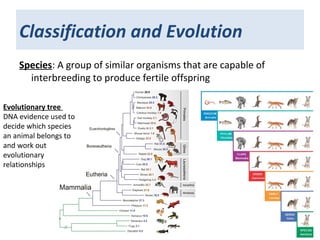
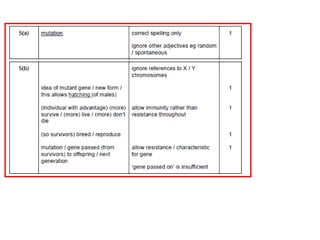
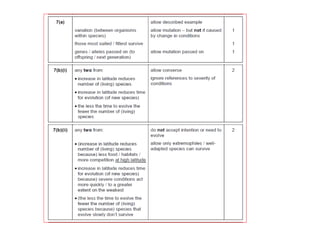
3. Evidence for evolution has accumulated from breeding experiments, fossil records, anatomical comparisons, and now DNA analysis, showing how species are related on an evolutionary tree and how traits have evolved over time through natural selection.