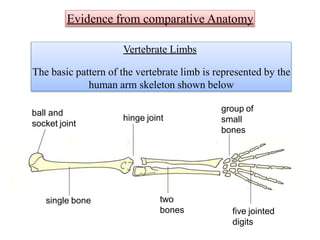
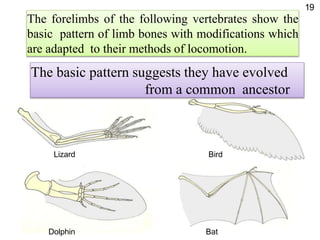
This document discusses several key concepts and theories related to evolution:
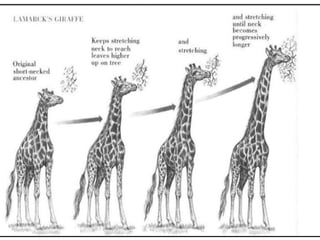
1. It describes Lamarck's theory of evolution which proposed that acquired traits could be inherited. It notes this theory is no longer supported.
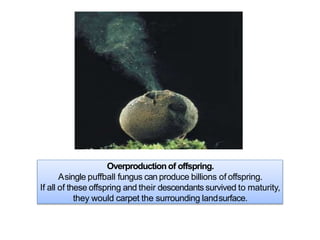
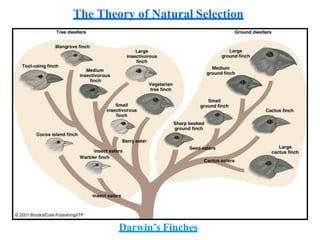
2. It summarizes Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection, noting the key principles of overproduction, variation, adaptation, and natural selection.
3. It discusses Hugo de Vries' mutation theory which proposed evolution occurs through accumulation of mutations in genes.
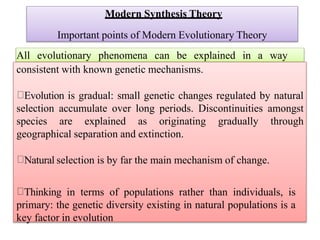
4. It notes the modern synthesis combines Darwinian evolution through natural selection with Mendelian genetics.