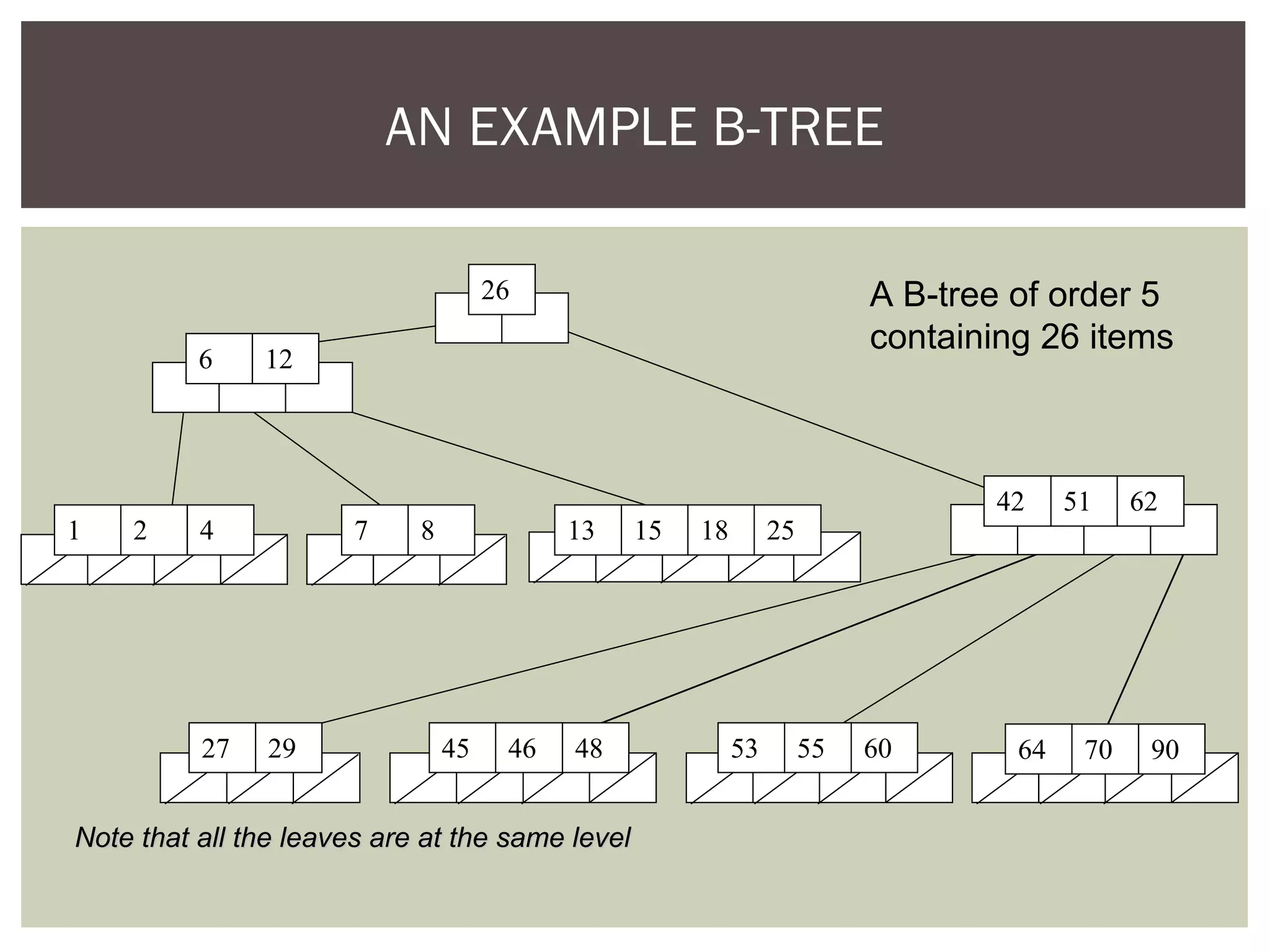
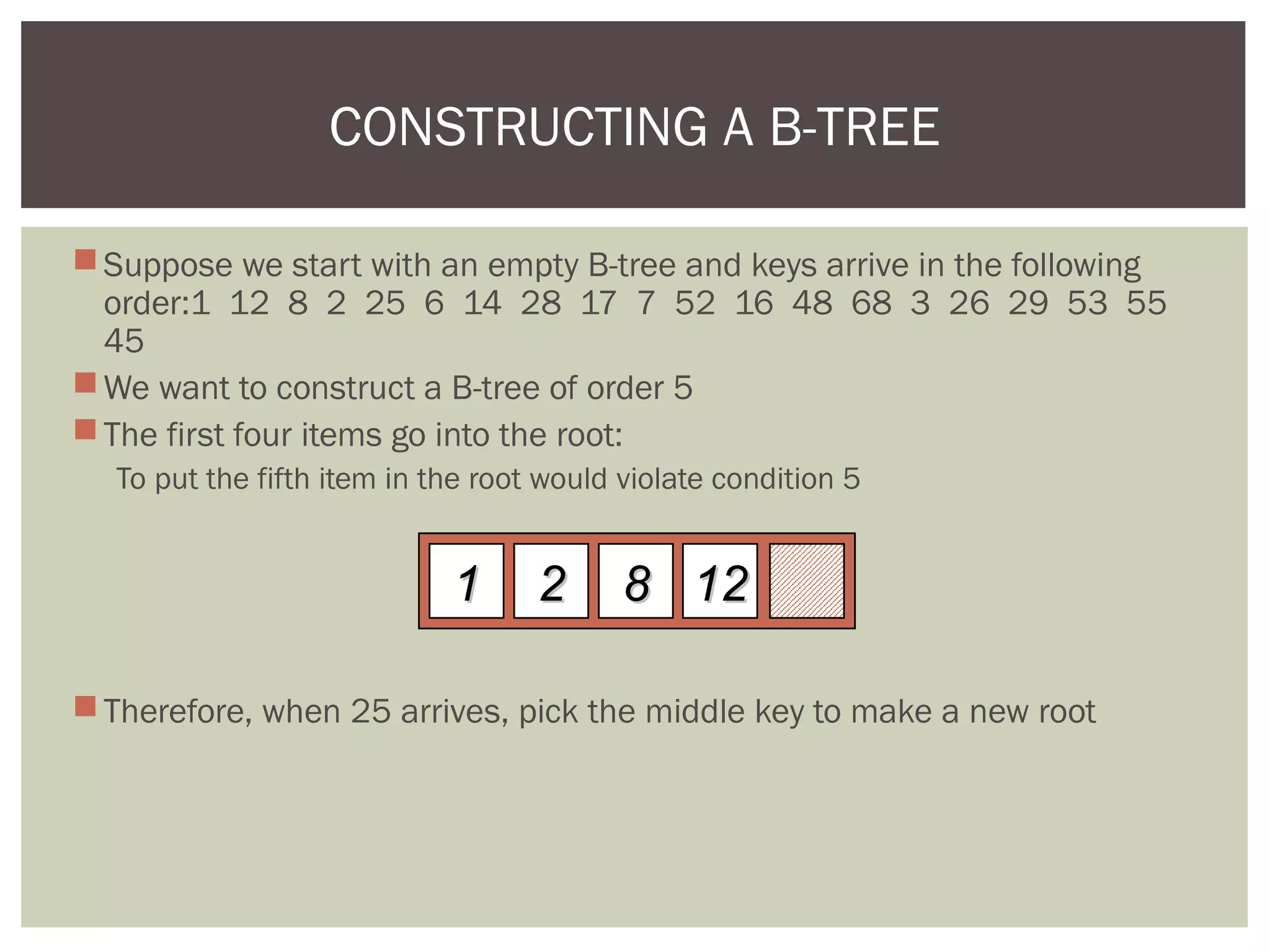
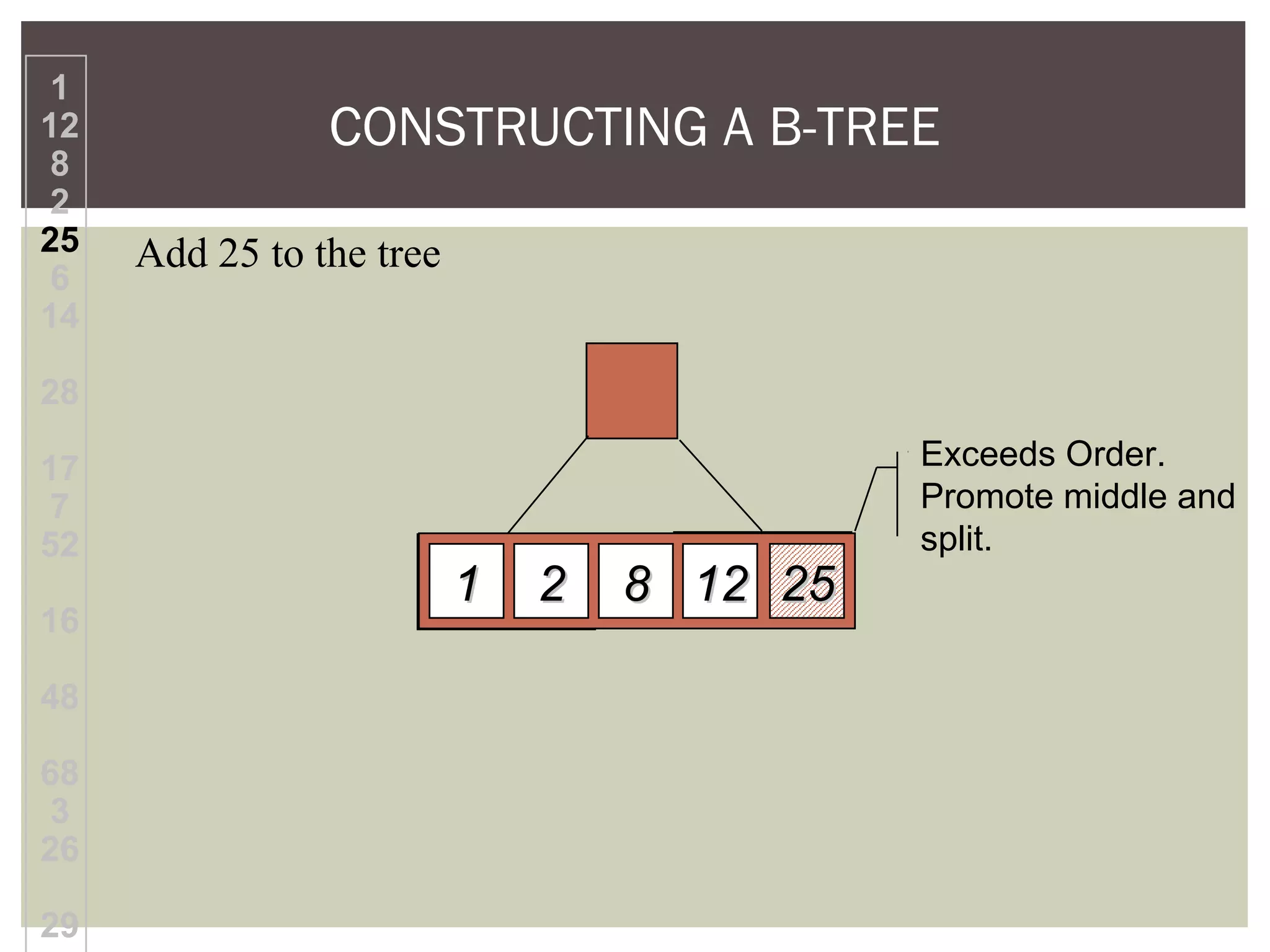
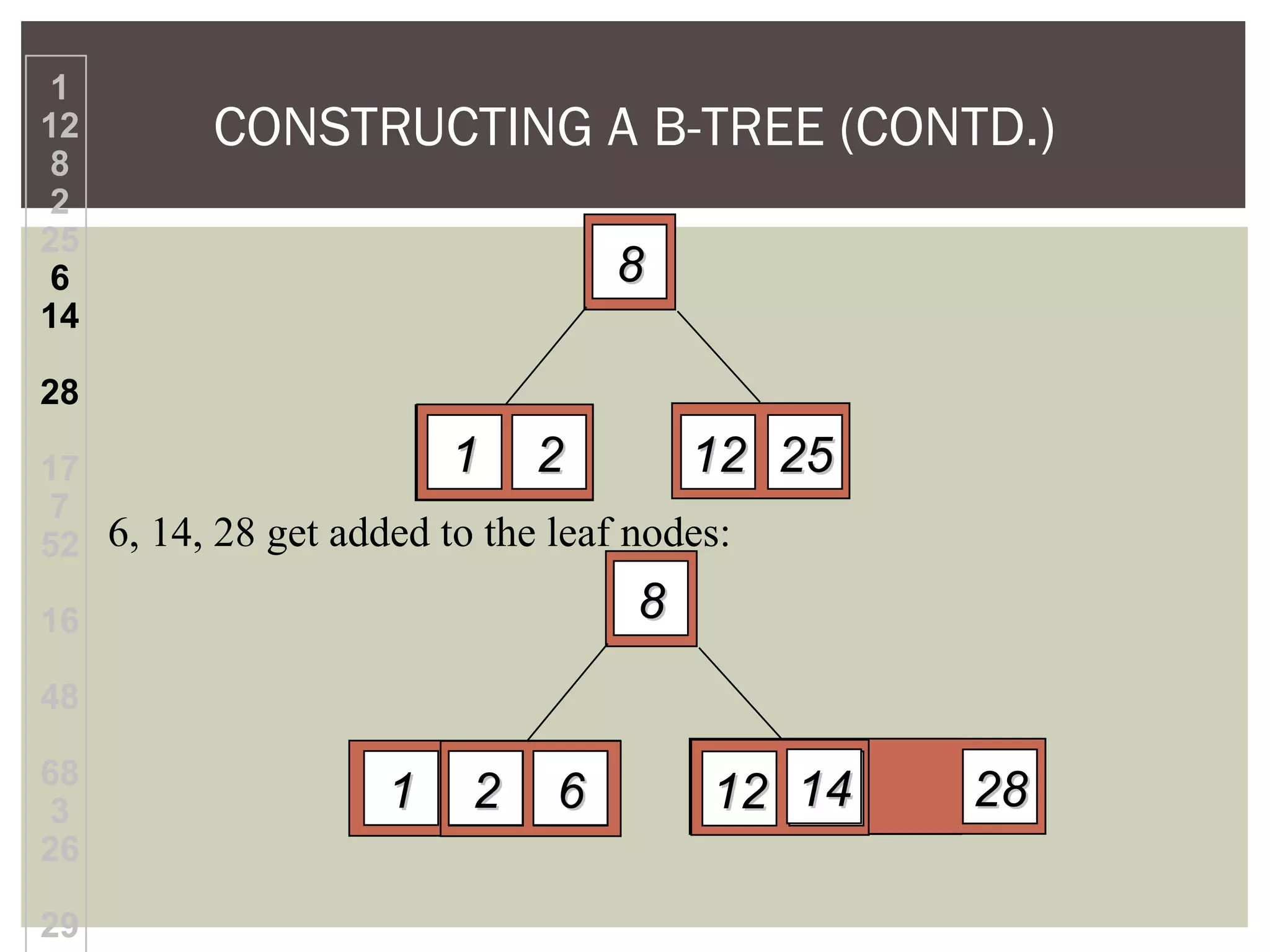
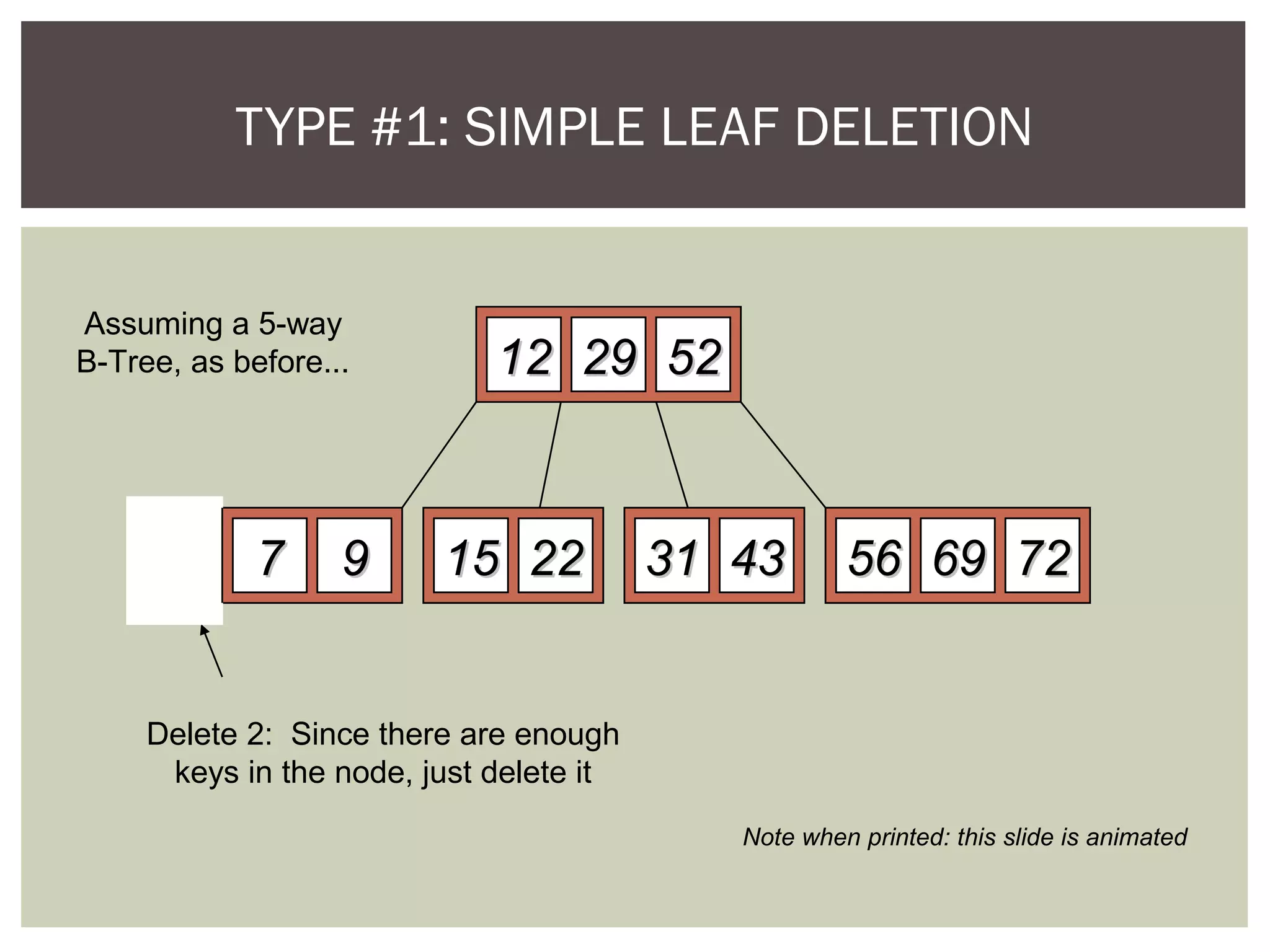
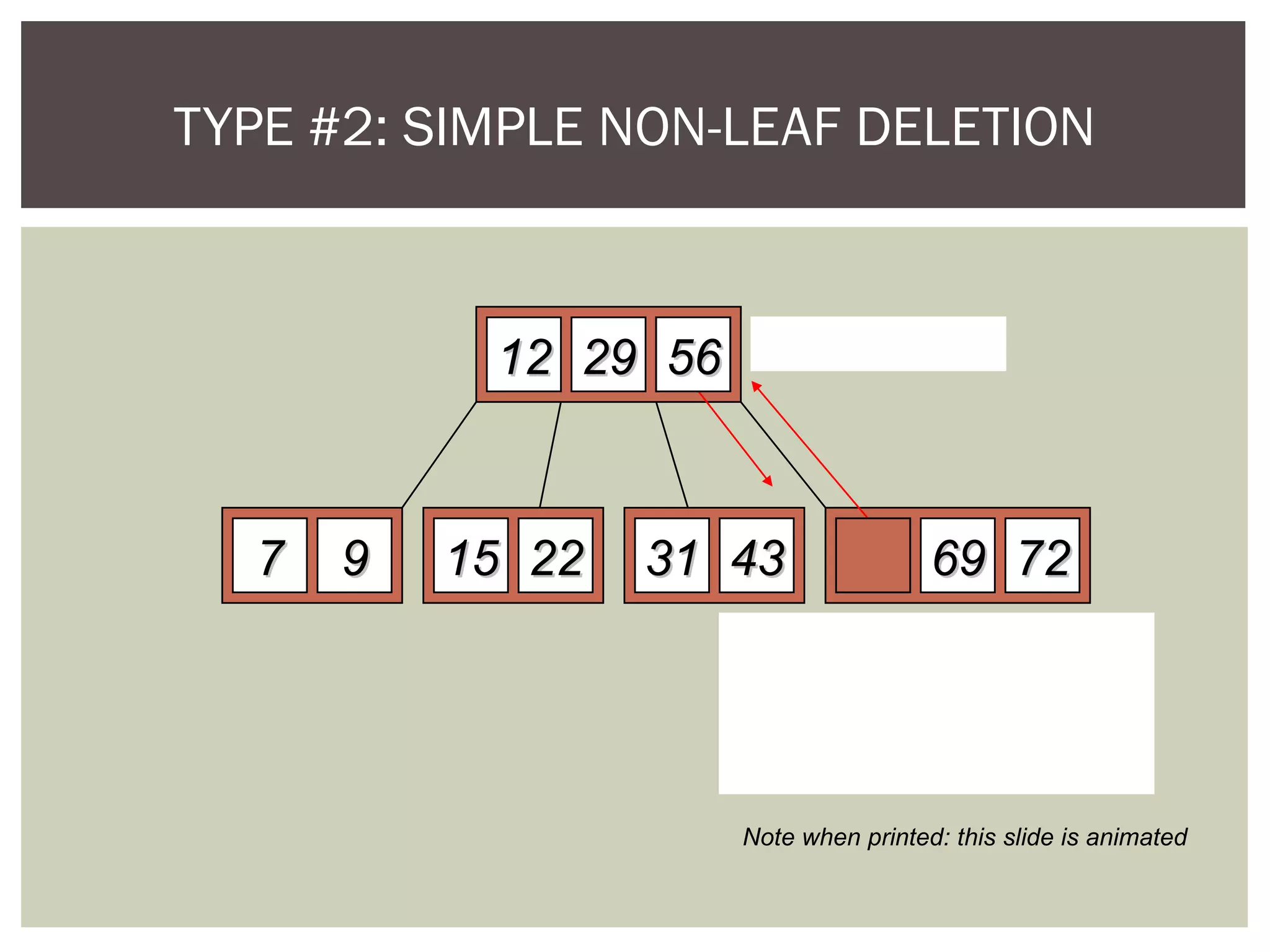
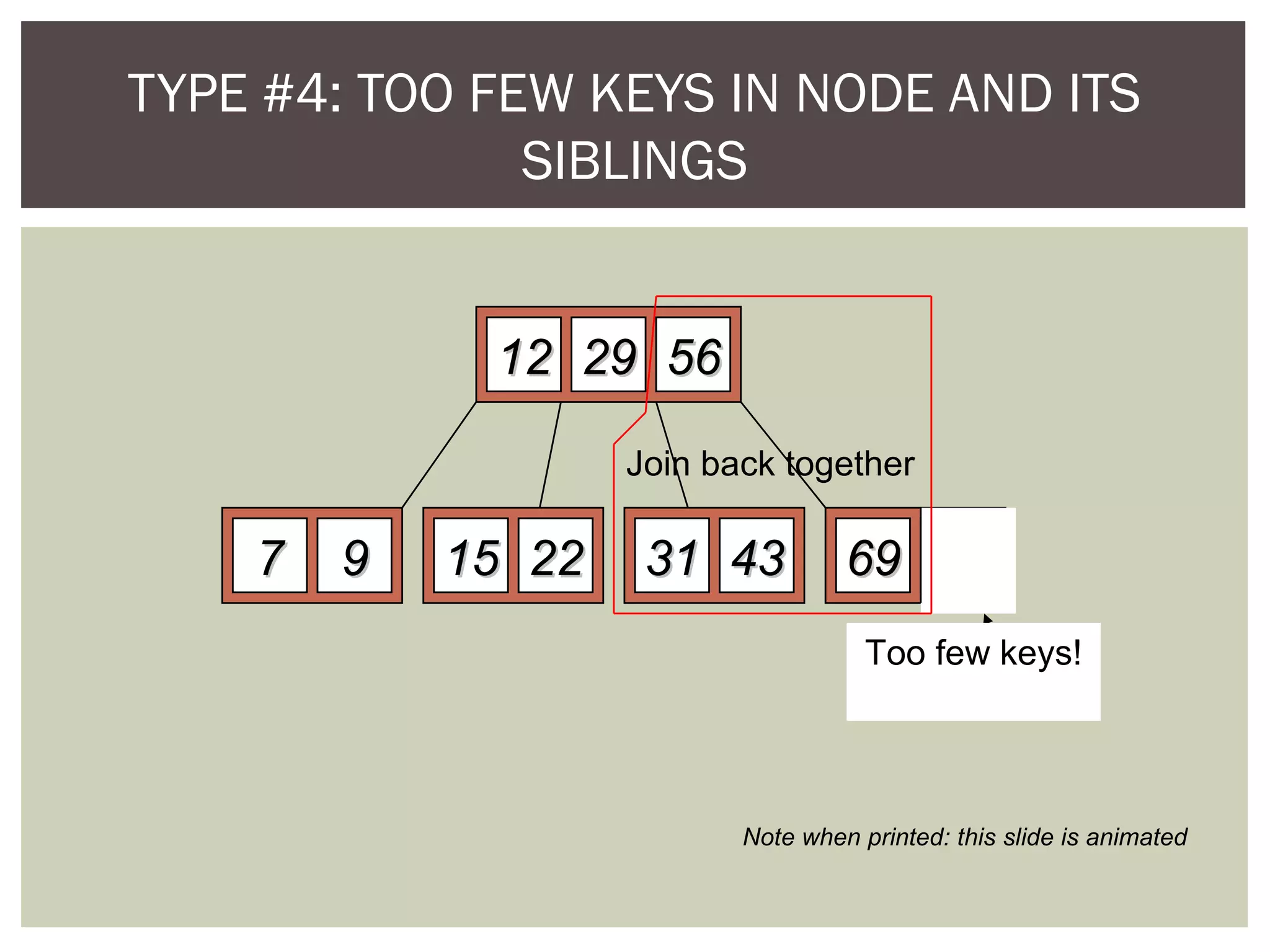
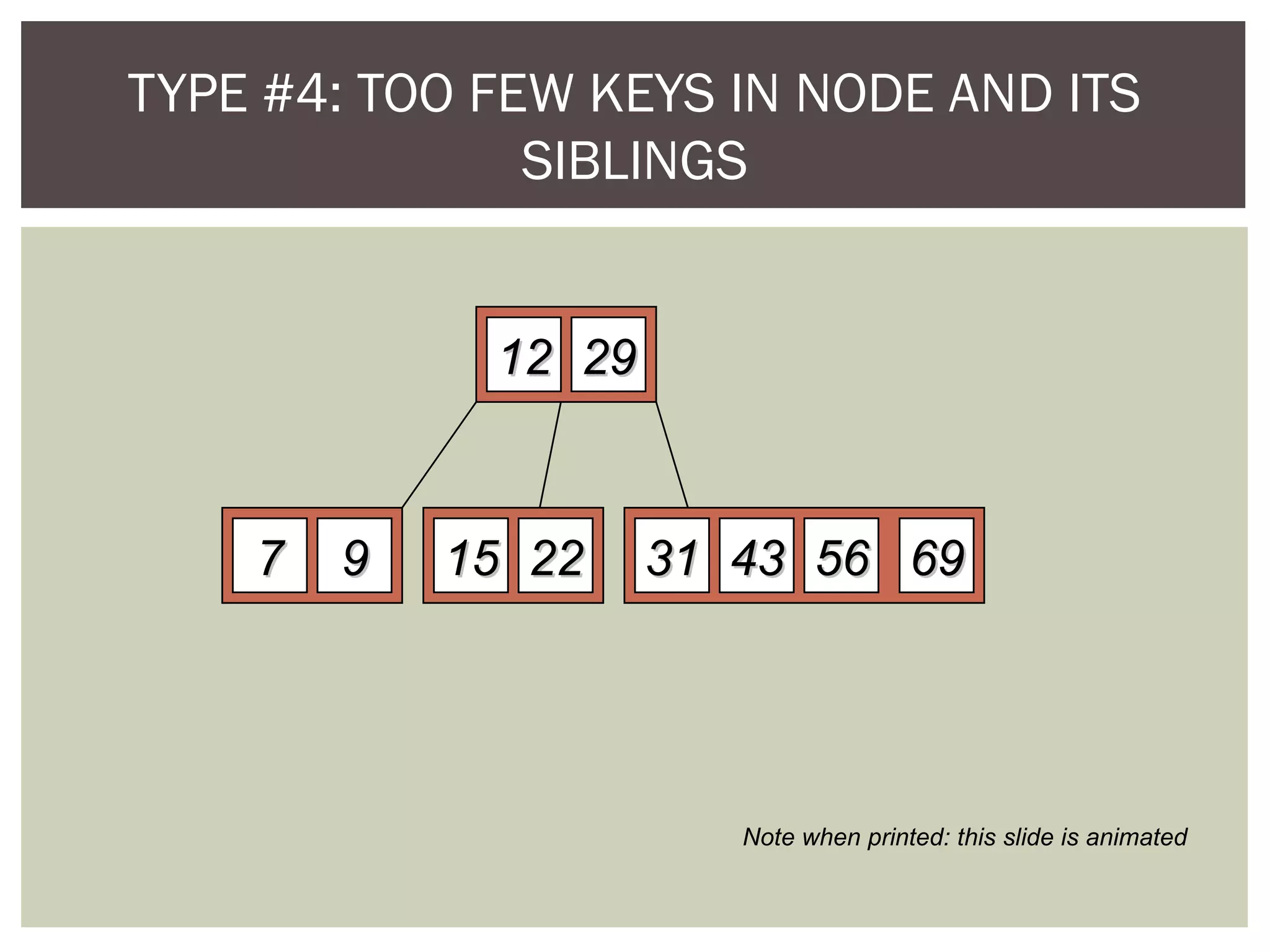
The document discusses the motivation for using B-trees to store large datasets that do not fit into main memory. It notes that while binary search trees provide logarithmic-time performance, disk access times are significantly slower than memory. B-trees are designed to group related data together to minimize disk I/O and improve performance. The document defines B-trees as m-way search trees where nodes can have up to m children, leaves are on the same level, and operations like insertion and deletion involve splitting or merging nodes to balance the tree.








![The maximum number of items in a B-tree of order m and height h:
root m – 1
level 1 m(m – 1)
level 2 m2
(m – 1)
. . .
level h mh
(m – 1)
So, the total number of items is
(1 + m + m2
+ m3
+ … + mh
)(m – 1) =
[(mh+1
– 1)/ (m – 1)] (m – 1) = mmhh+1+1
– 1– 1
When m = 5 and h = 2 this gives 53
– 1 = 124
ANALYSIS OF B-TREES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b-treeby-jashacharya-151203133019-lva1-app6892/75/B-tree-by-jash-acharya-28-2048.jpg)

