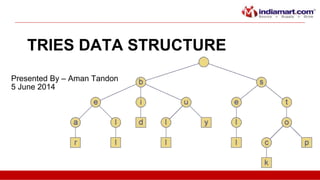
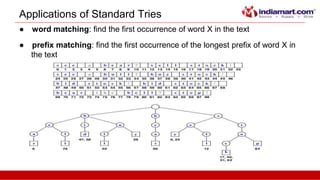
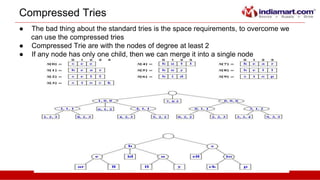
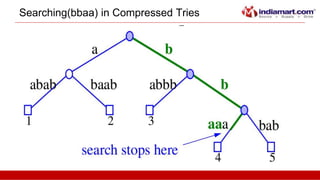
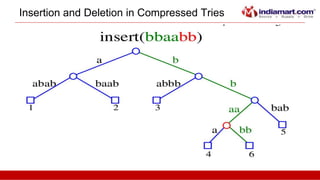
This document discusses tries, a data structure used to store strings. It begins by outlining the advantages of tries over hash tables, including faster insertion and lookup. It then defines a trie as a tree that stores strings where all descendants of a node have a common prefix. The document describes standard tries and compressed tries, noting compressed tries save space by merging nodes with only one child. It provides examples and discusses time/space complexity. Applications mentioned include word matching, prefix matching, and use in web search engines to index words and associated URLs.