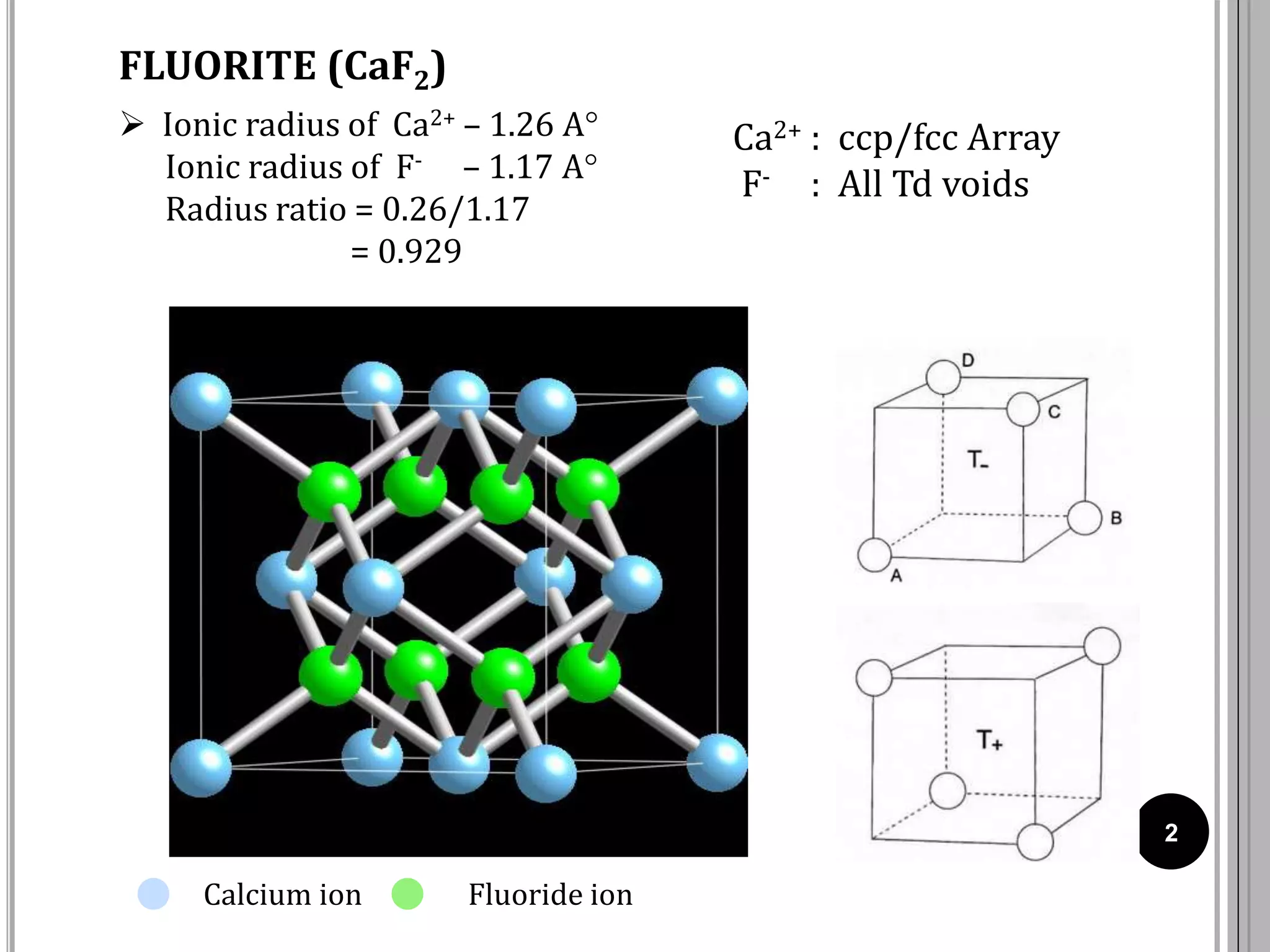
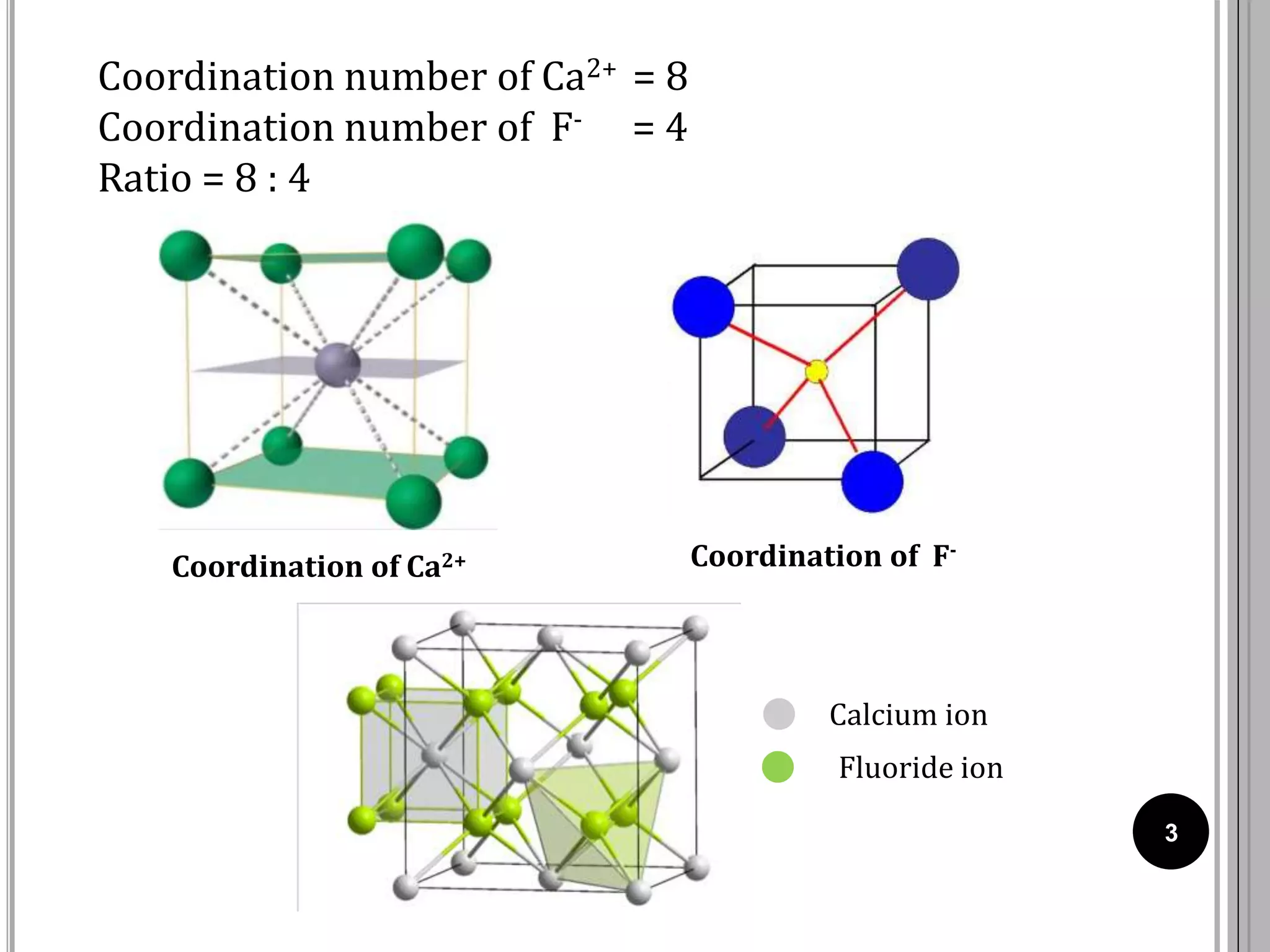
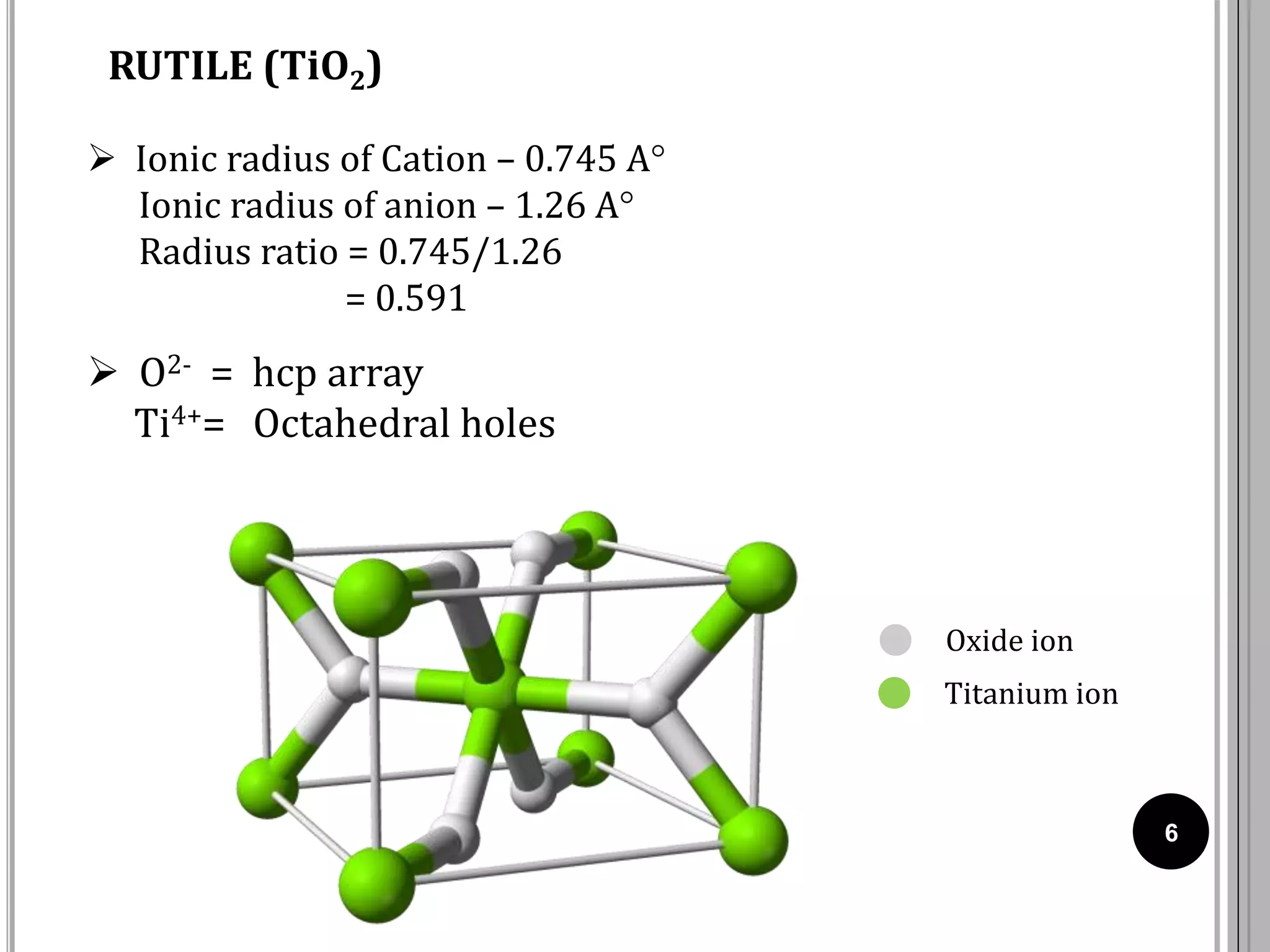
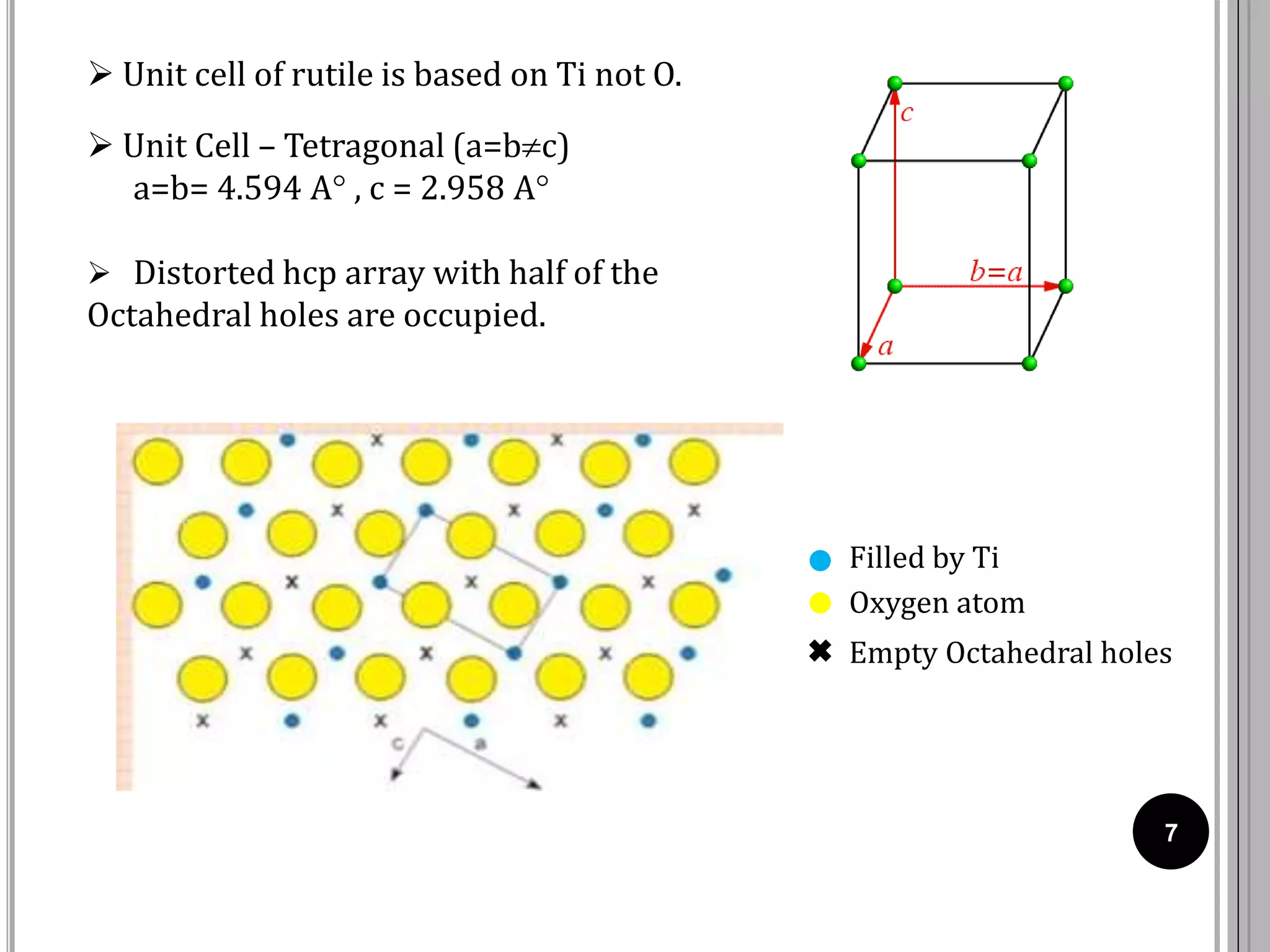
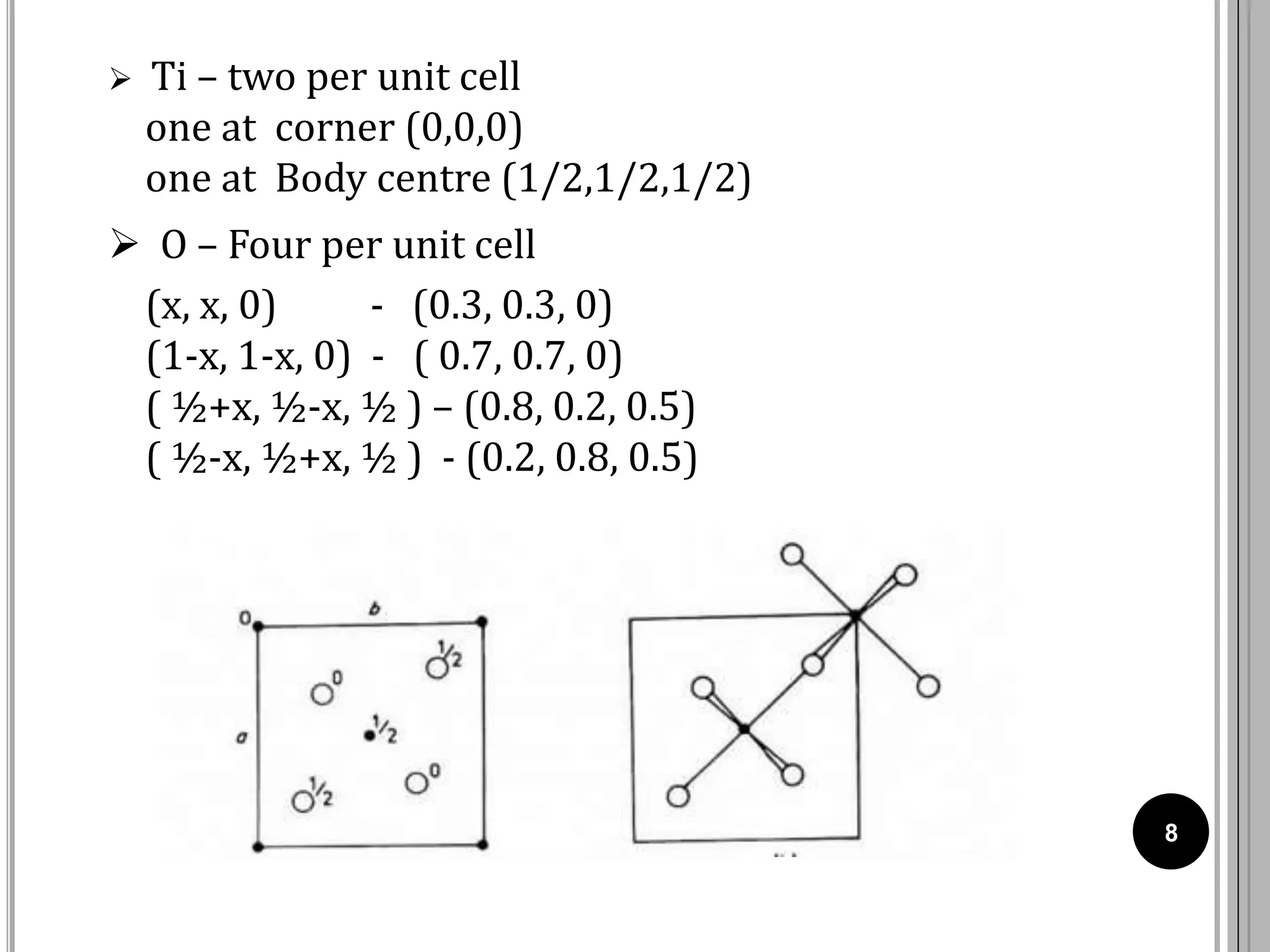
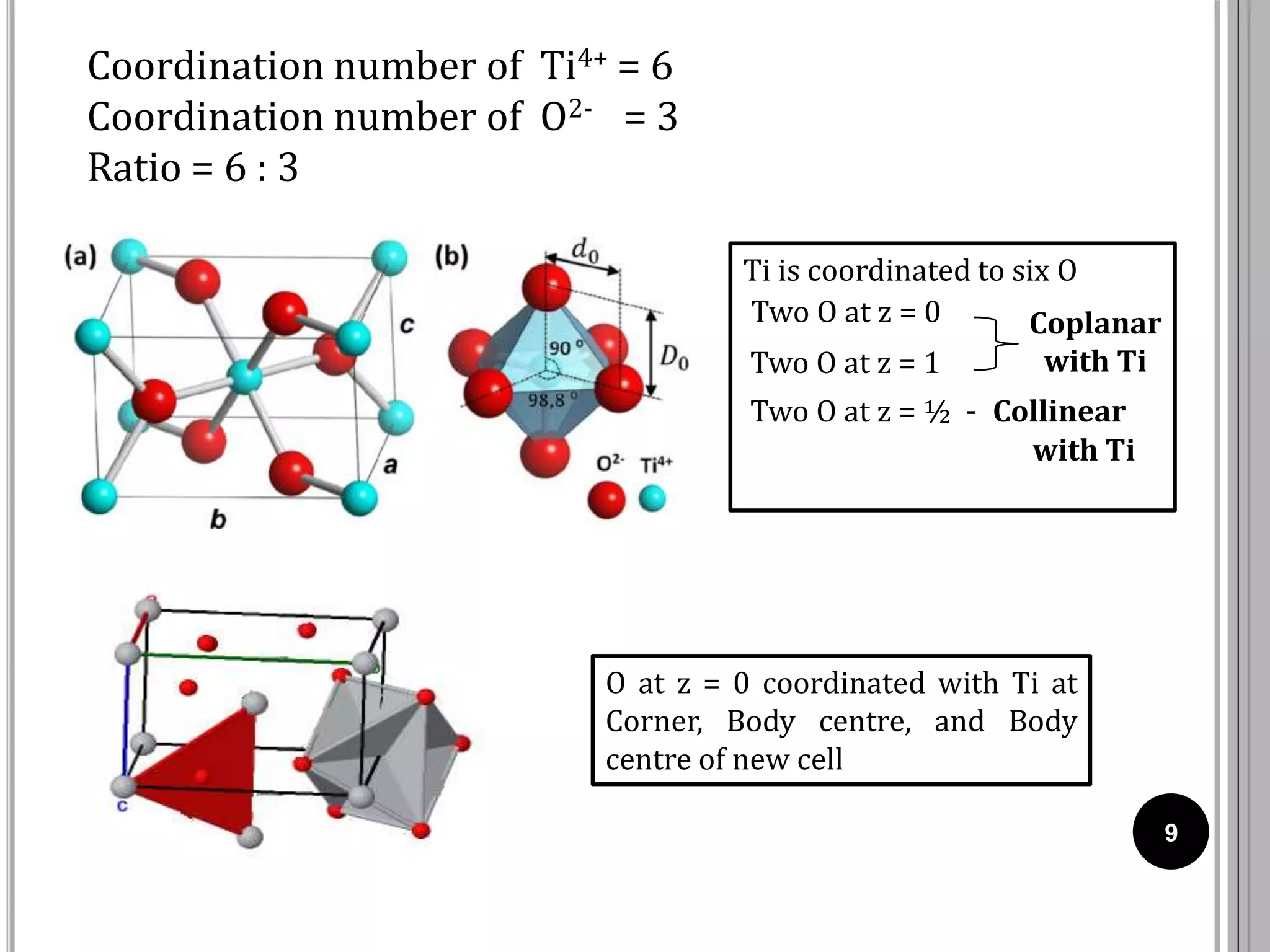
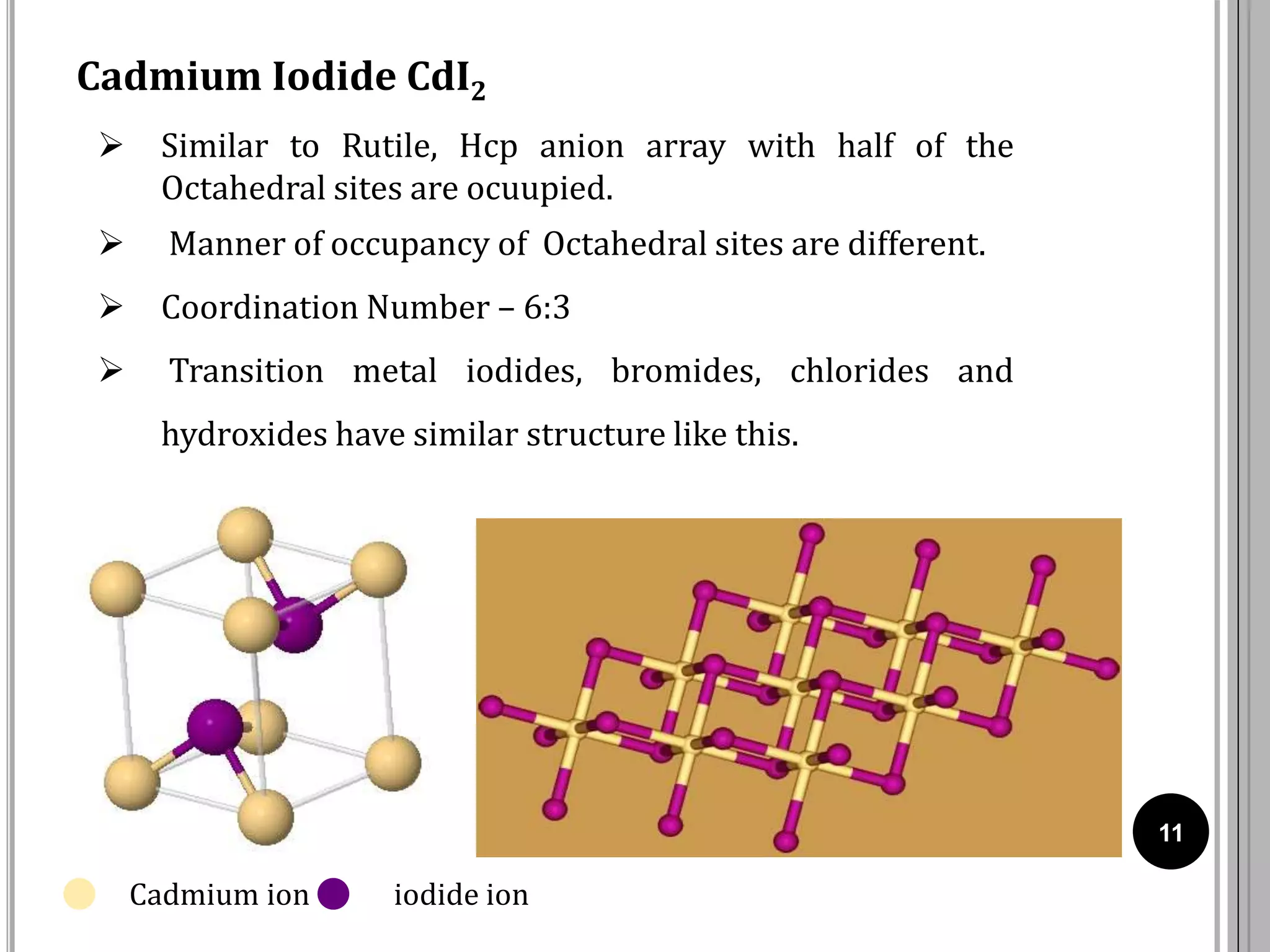
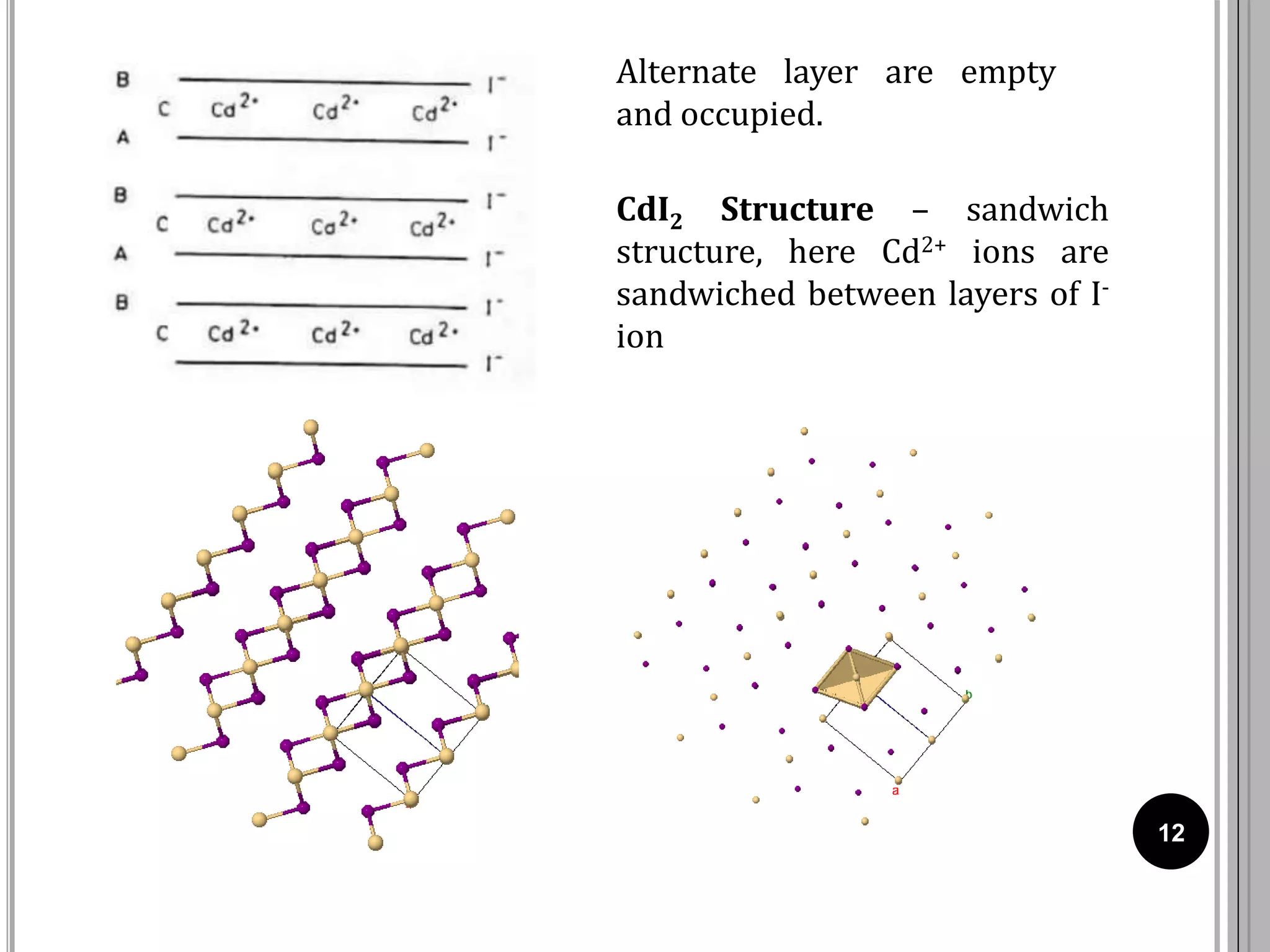
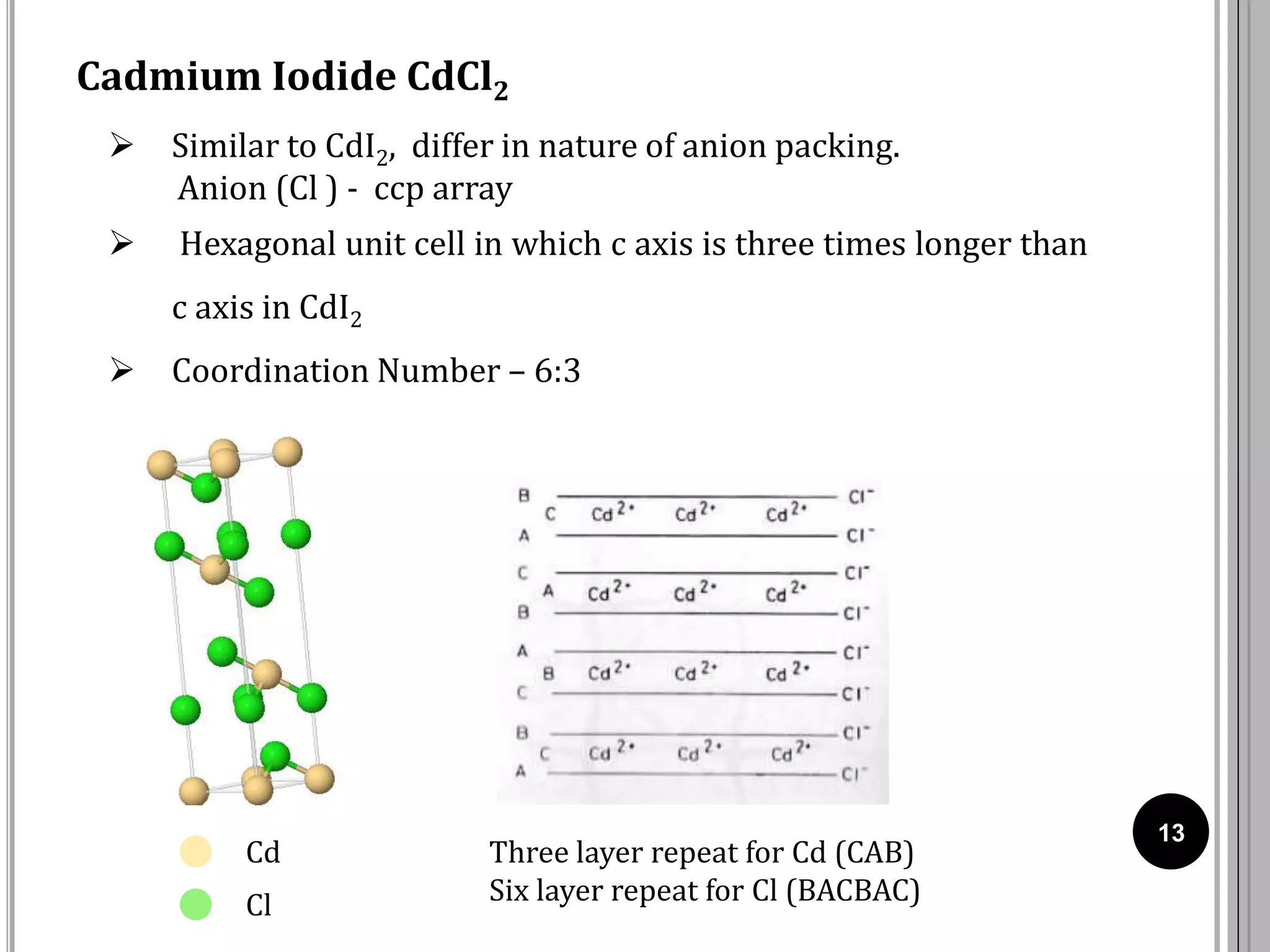
The document discusses various crystal structures including fluorite (CaF2), rutile (TiO2), and cadmium iodide (CdI2), detailing their ionic radii, coordination numbers, and unit cell configurations. Examples of similar compounds and applications in jewelry and other areas are mentioned, along with historical context. It also includes references for further reading on solid-state and inorganic chemistry.