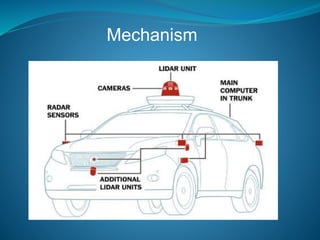
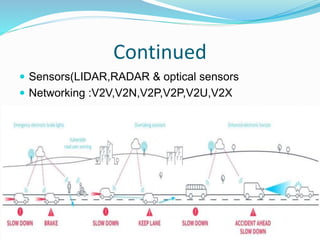
The document discusses the history and development of autonomous vehicles. It notes that experiments began in the 1920s and the first semi-automated car was developed in 1977 in Japan. Waymo began the first commercial self-driving service in Phoenix in 2018. An autonomous car can sense its environment and operate with little human input using sensors, software, and 5G networks. Challenges for autonomous cars include perception of the environment and predicting behaviors of other vehicles and actors on the road.