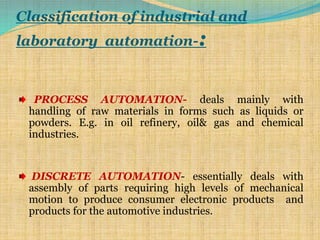
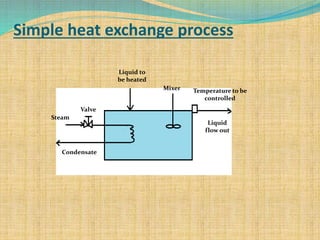
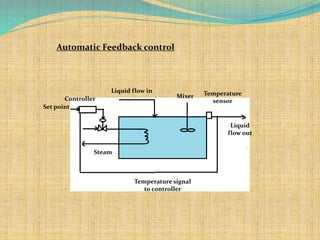
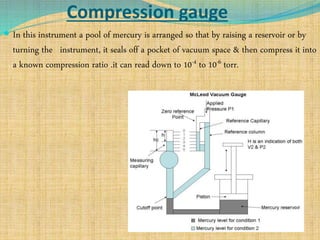
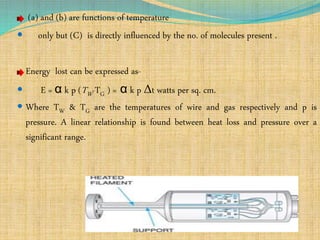
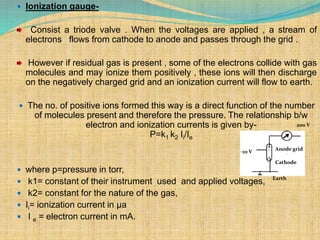
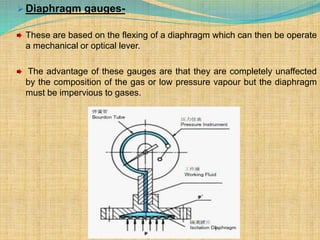
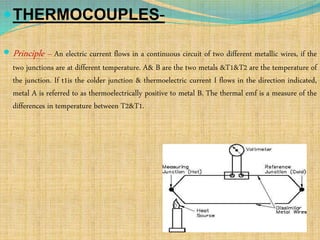
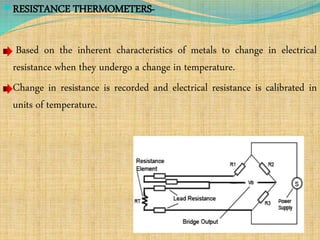
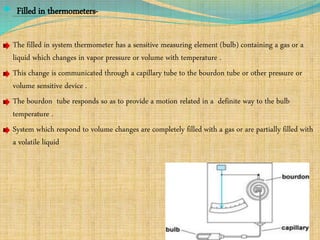
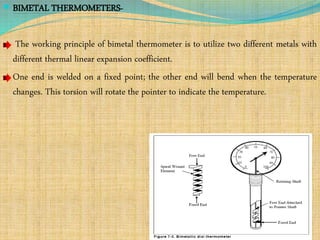
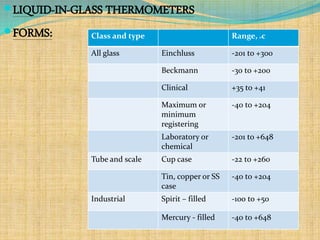
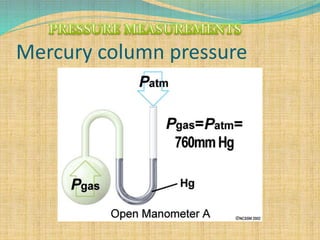
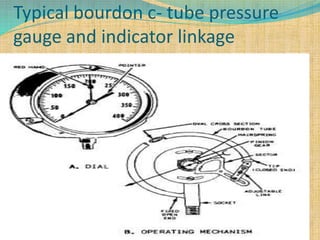
Automation refers to the use of machines and equipment to perform tasks that were previously done by humans. It is used in manufacturing to increase productivity, quality, and reduce costs. Some key benefits of automation include improved quality, reduced labor costs, increased speed and accuracy, and improved worker safety. Potential downsides include high upfront capital costs, high maintenance costs, risk of job losses, and reliance on continuous power supply. Automation can be applied at different stages of production like material handling, production processes, and quality inspection. The pharmaceutical industry uses automation for purposes like ensuring batch quality, consistency, compliance with standards, and handling of hazardous substances.