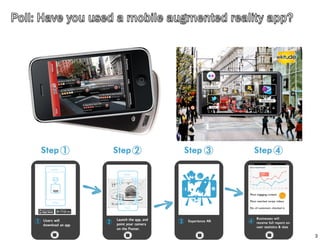
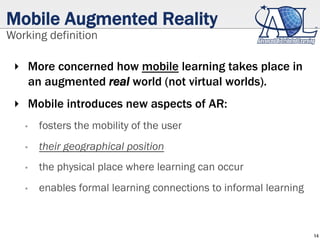
The document discusses the potential of augmented reality (AR) in mobile learning, highlighting its ability to provide tailored, accessible education and training. It outlines the definitions, technical and pedagogical challenges, benefits, and examples of mobile AR applications, indicating significant interest among users and developers. Additionally, it addresses the evolving landscape of AR technologies and communities supporting their development.