The document defines risk and issue, outlines the risk lifecycle and management cycle, and provides details on risk identification, analysis, assessment, and management. Key points include:
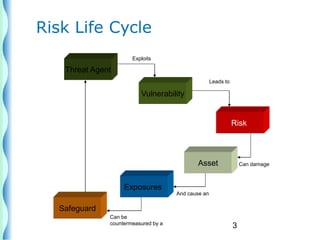
- A risk is a potential future event that could negatively impact objectives, while an issue is a current problem.
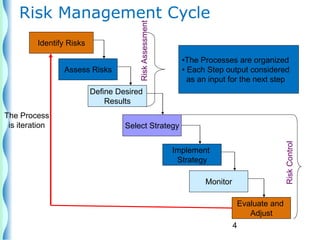
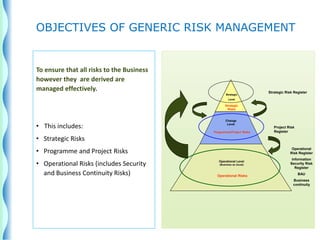
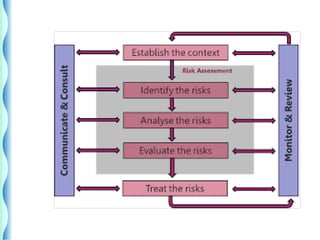
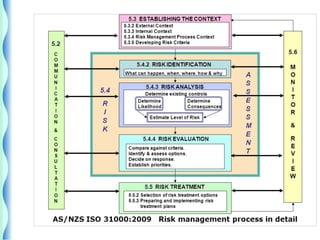
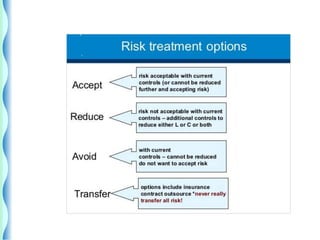
- The risk management cycle includes identifying risks, assessing them, selecting strategies, implementing controls, and monitoring/evaluating.
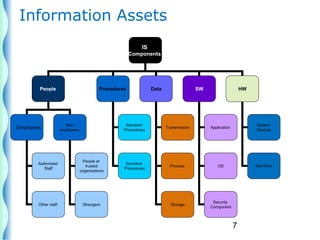
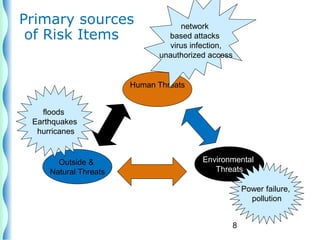
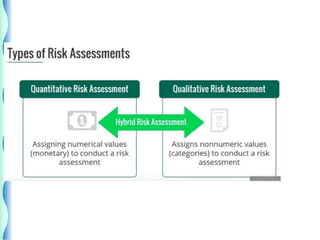
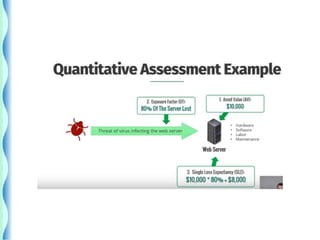
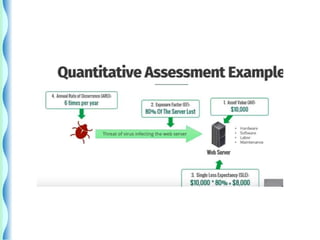
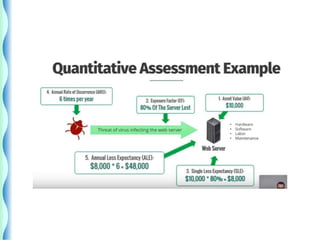
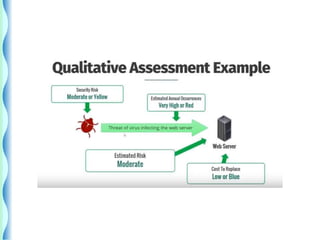
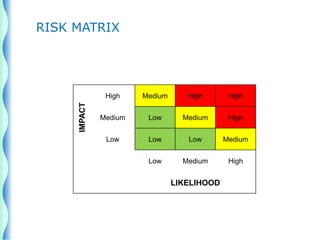
- Risk identification involves knowing the organization's assets and sources of risk. Risk analysis assesses the likelihood and impact of risks.