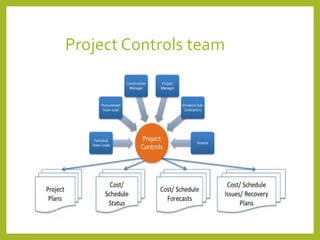
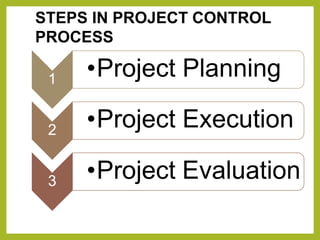
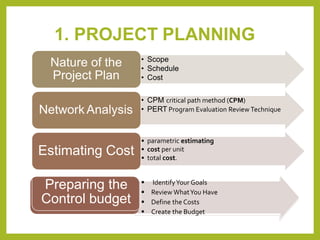
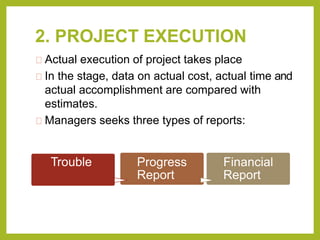
Project controls involves managing the metrics of a project such as time, cost, quantities and resources. The project controller generates cost and schedule information for the project manager. Project controls analyzes data from the technical team, procurement, construction and other stakeholders to develop the project plan, cost estimate, budget, resource plan and schedule. The project controls process involves three steps - project planning, project execution, and project evaluation.