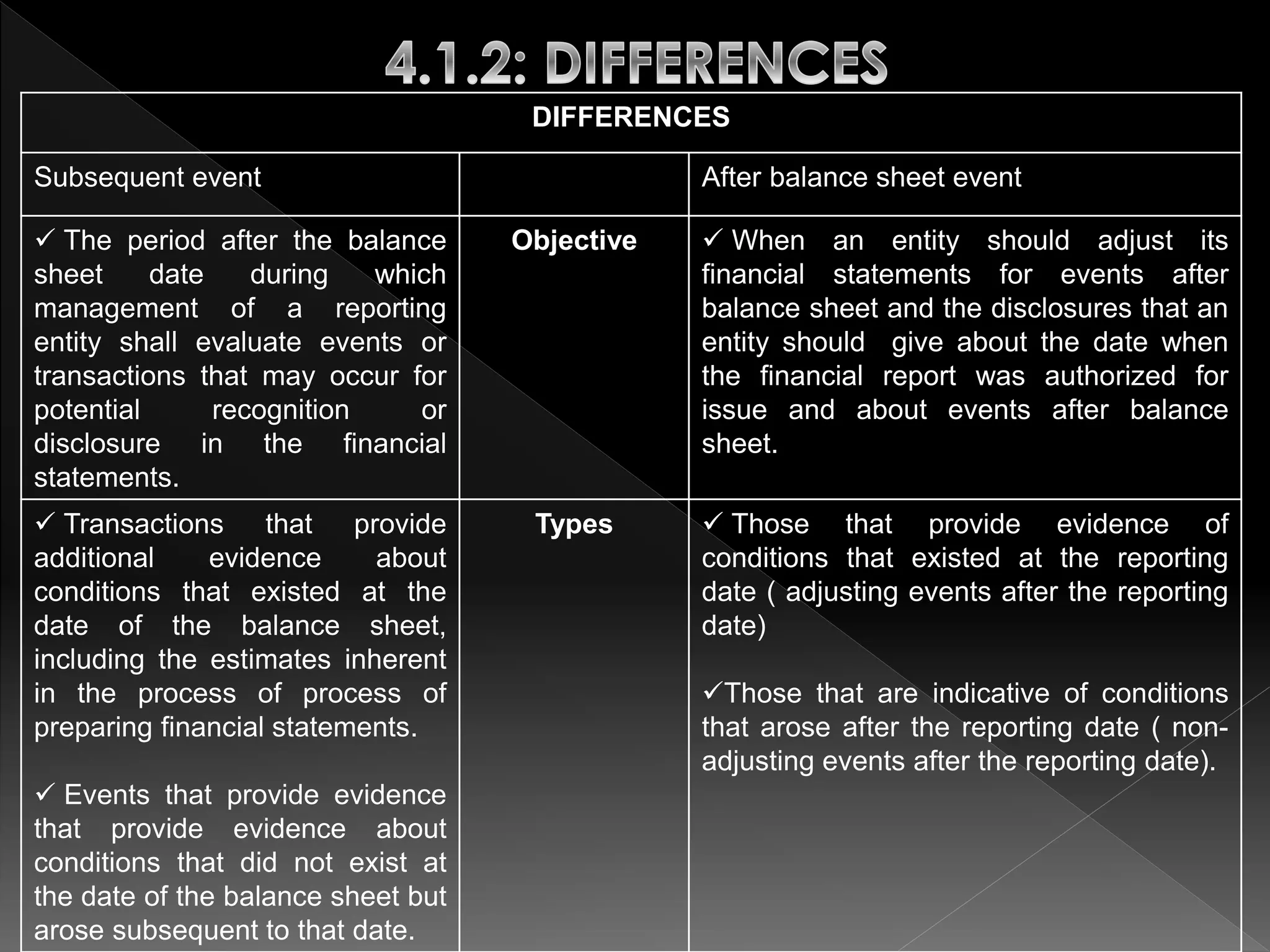
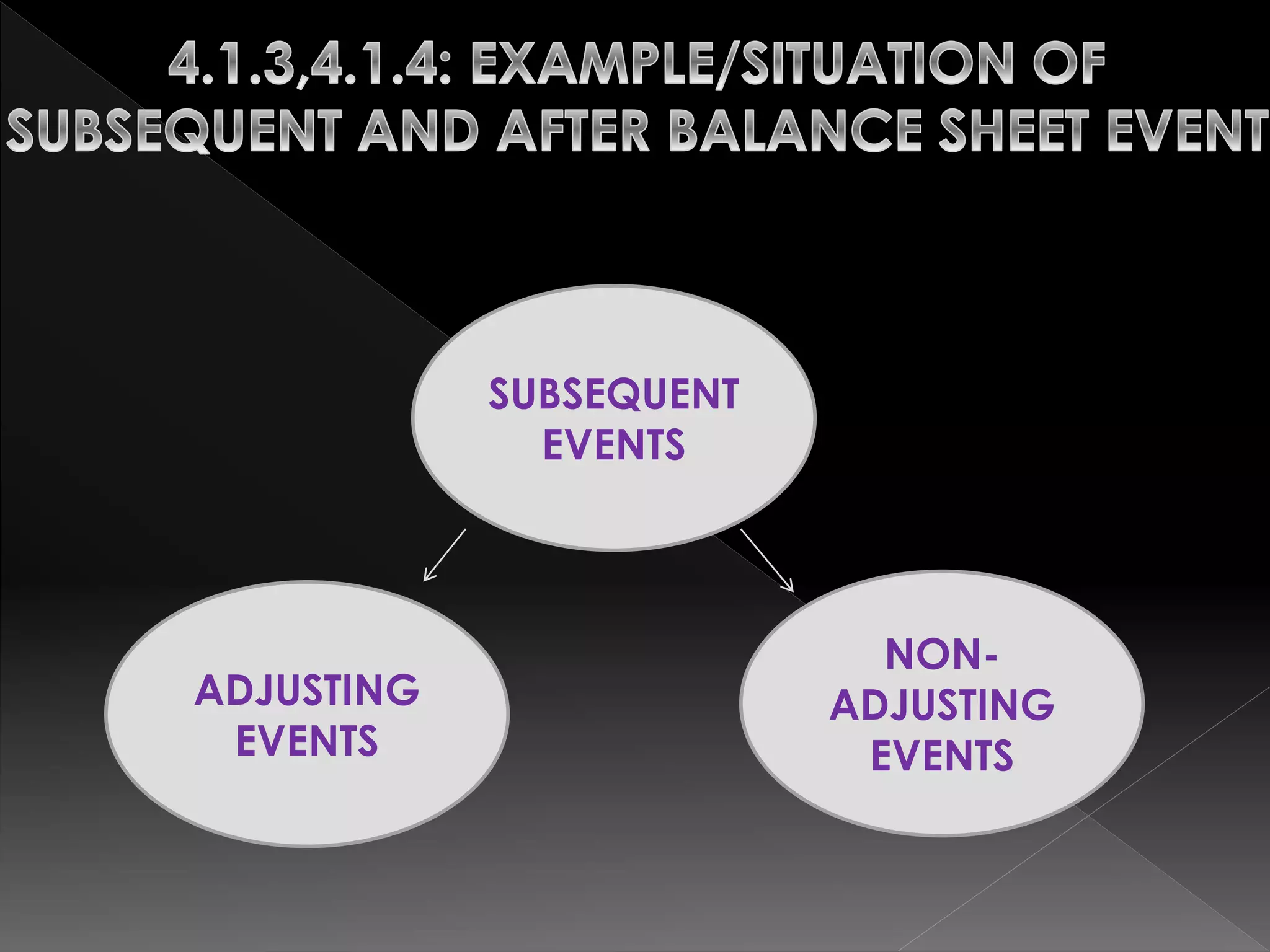
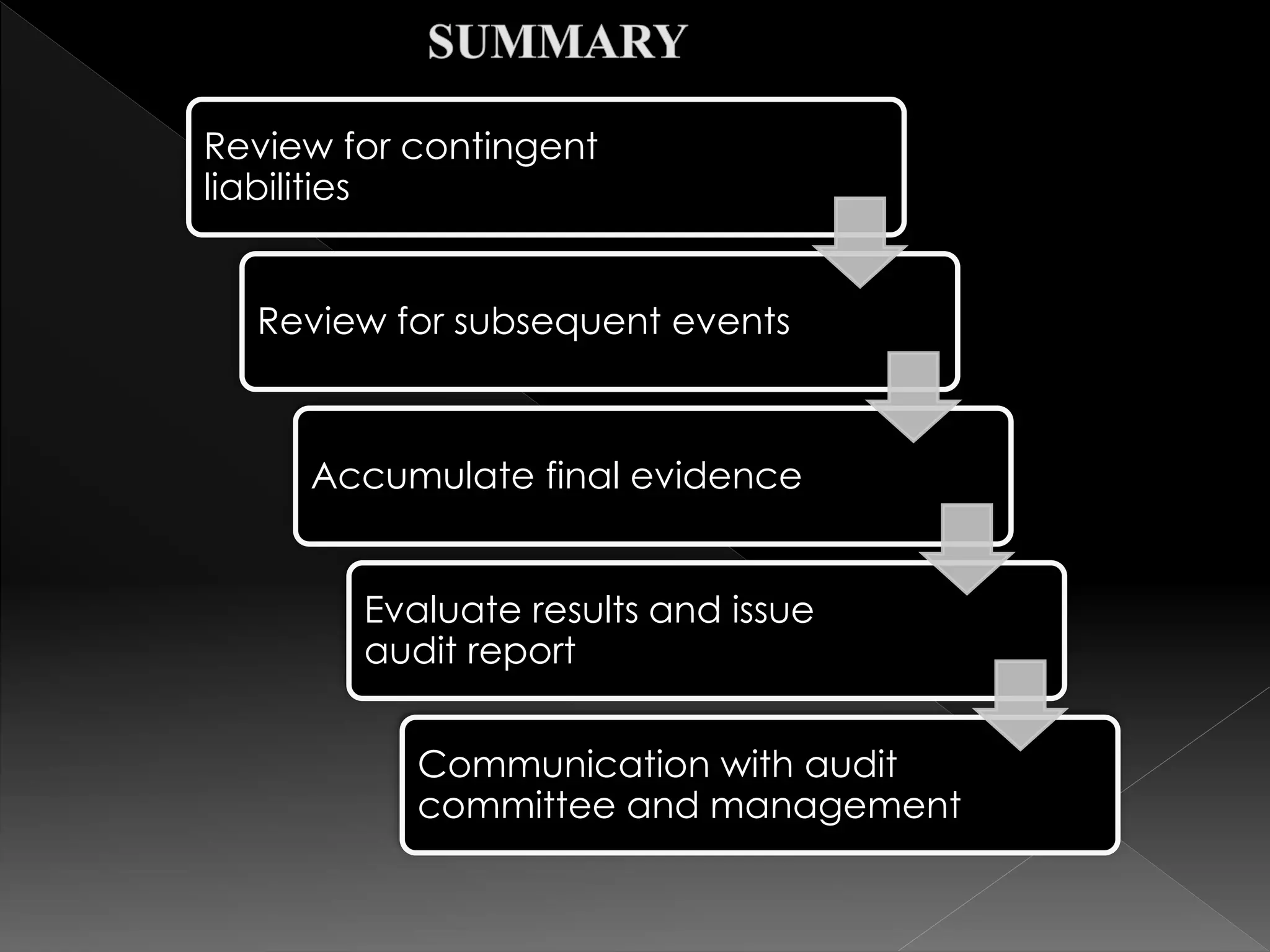
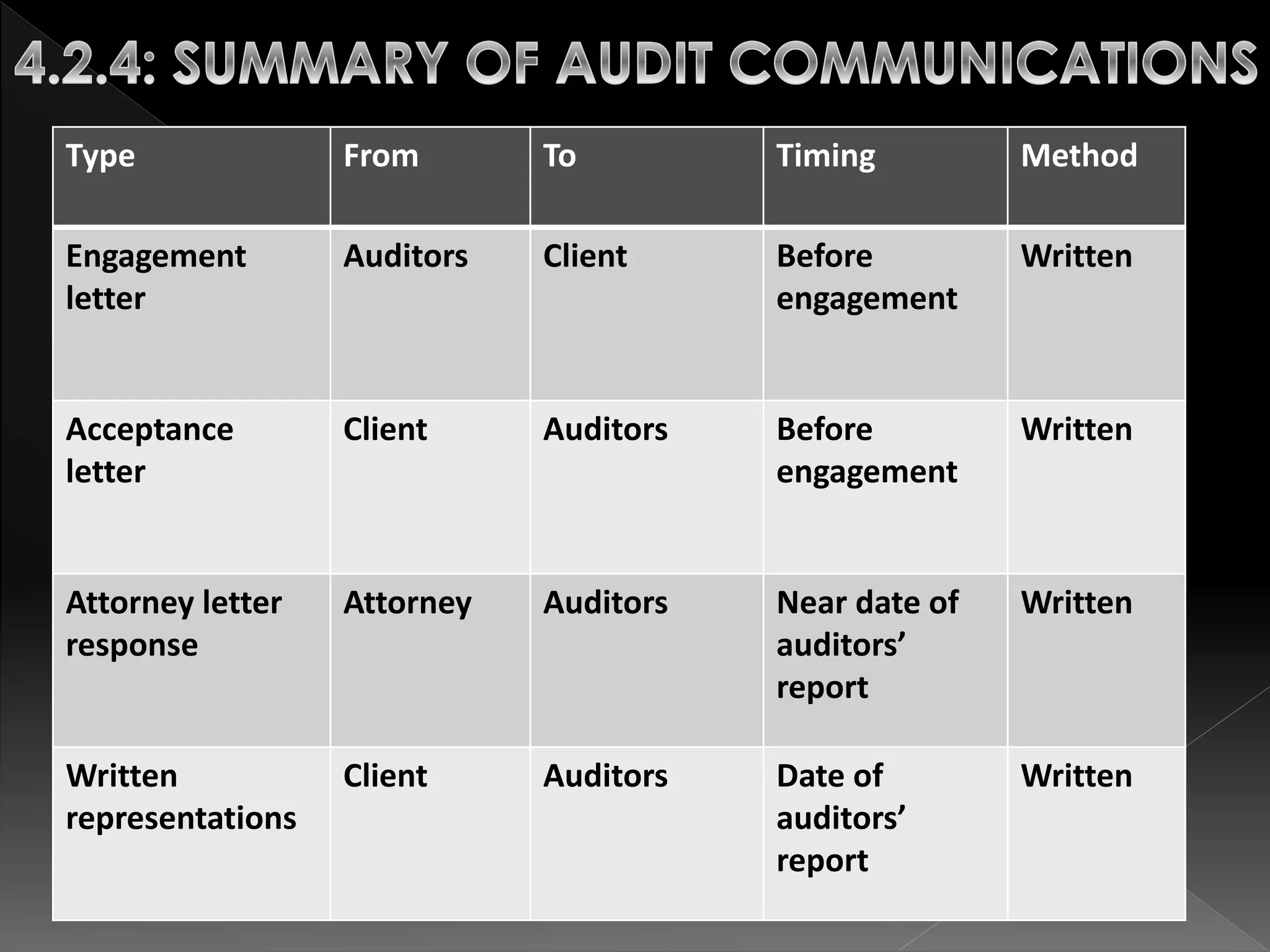
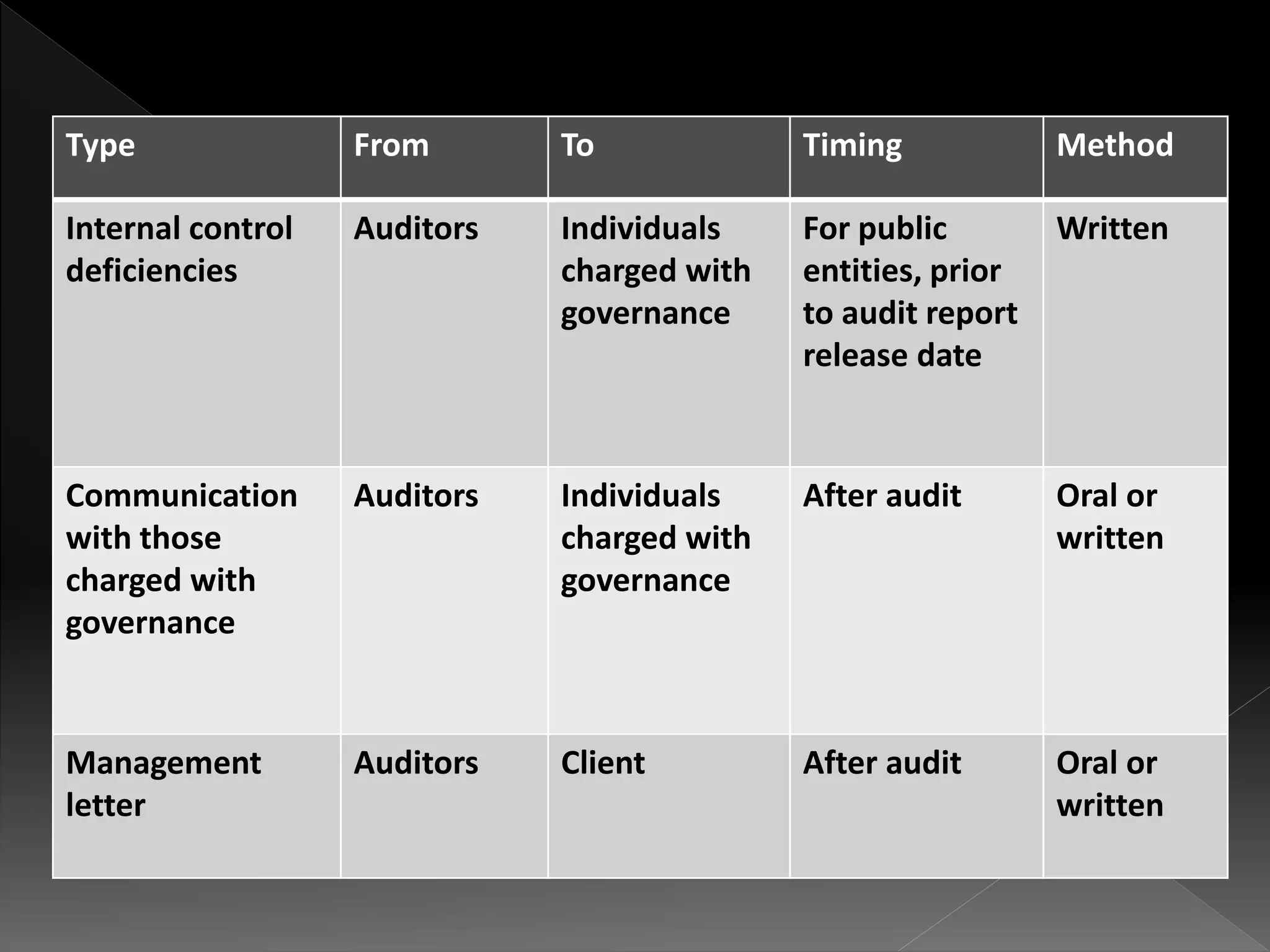
This document defines and compares subsequent events and after balance sheet events. It discusses the differences between them, provides examples of types of each, and outlines the auditor's procedures to identify subsequent events. It also reviews audit working papers, evaluates audit results, and ensures proper disclosures and compliance. The document describes communications between the auditor and client, including engagement letters, attorney response letters, and management letters.