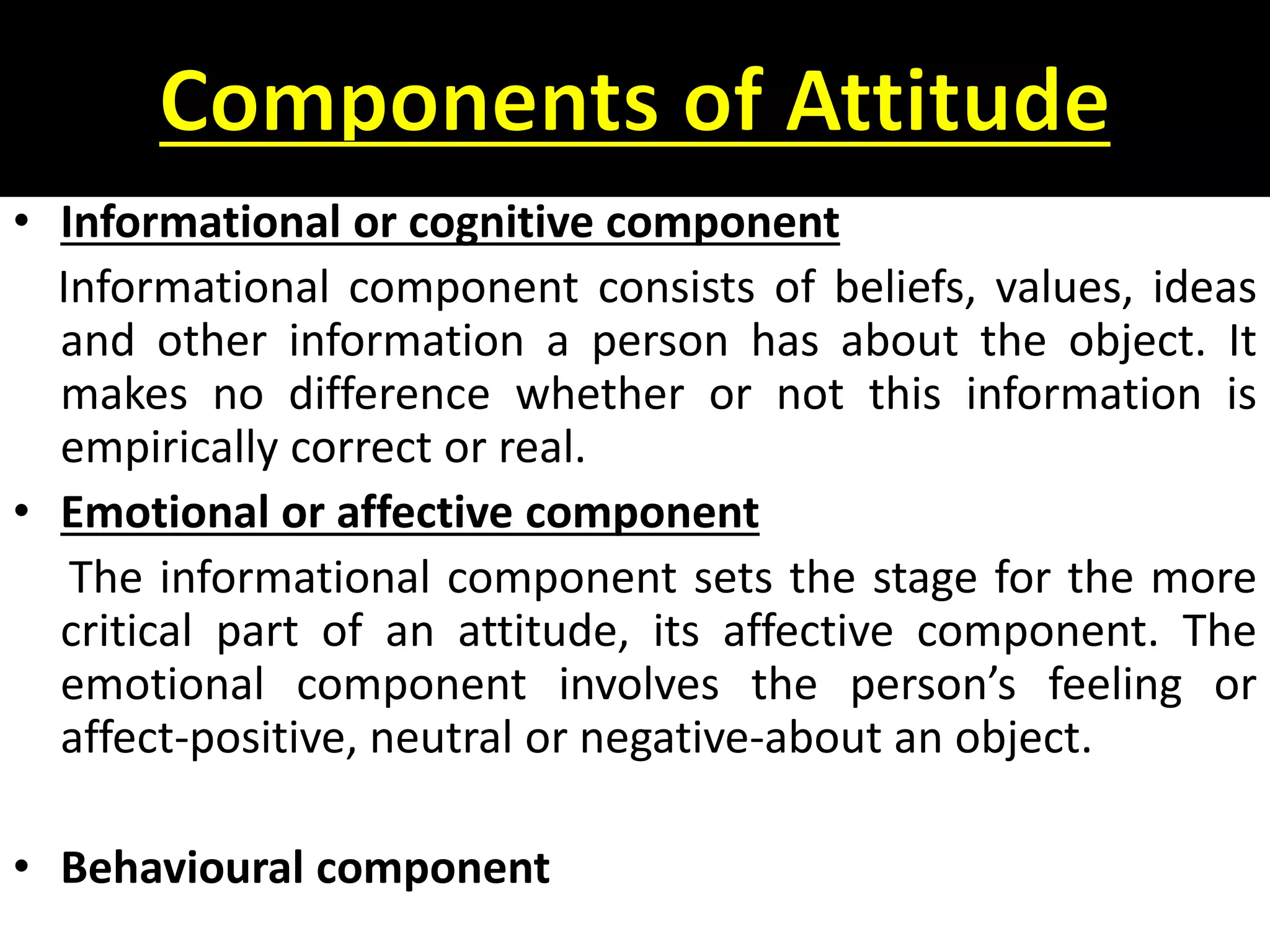
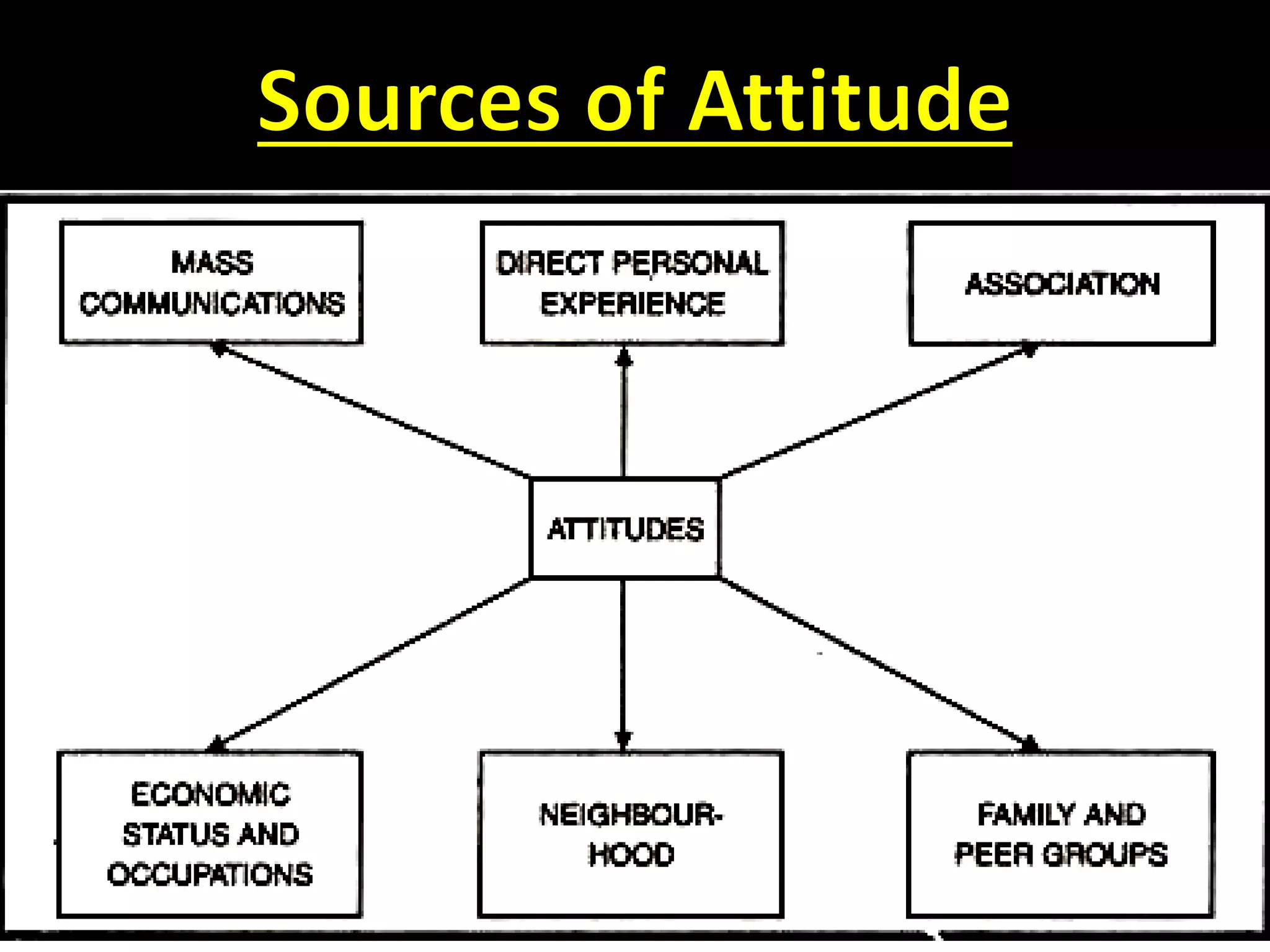
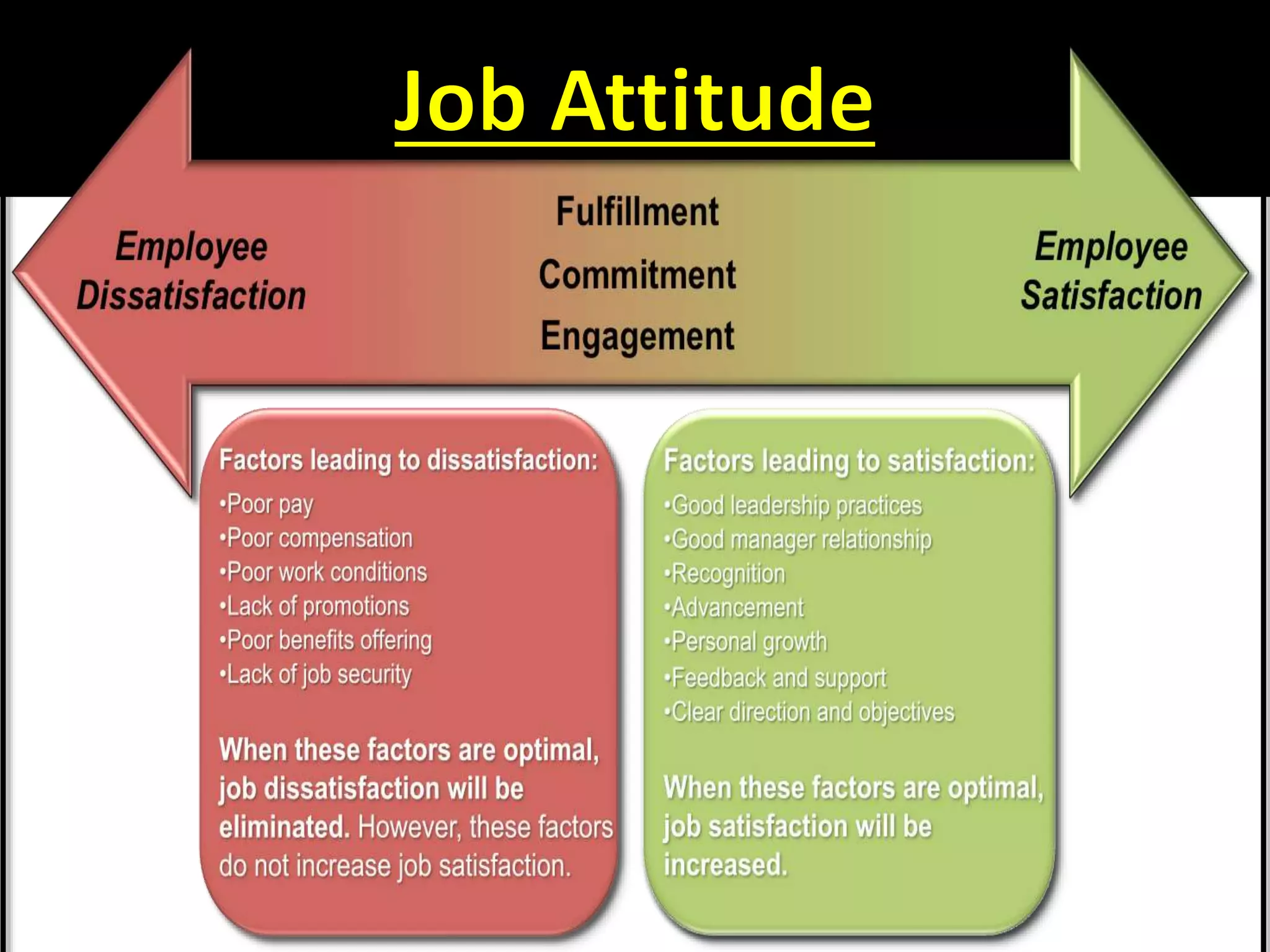
This document provides an overview of attitudes, including definitions, components, models, and theories of attitude formation. It also discusses job attitudes like job satisfaction, job involvement, and organizational commitment. Job satisfaction refers to an employee's general feelings about their job. Job involvement measures how strongly one identifies with their work. Organizational commitment refers to identifying with and wanting to remain with one's employer organization.