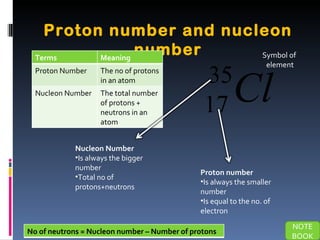
The document discusses the structure of atoms and their subatomic particles. It defines atoms as consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, while electrons orbit the nucleus. Atoms are made up of subatomic particles including protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons have no charge, and electrons have a negative charge. Isotopes are defined as atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. The periodic table arranges elements in order of increasing proton number and groups elements with similar chemical properties together.