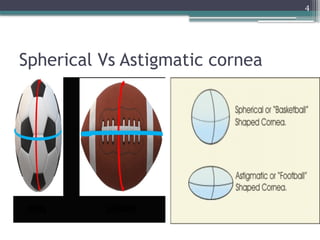
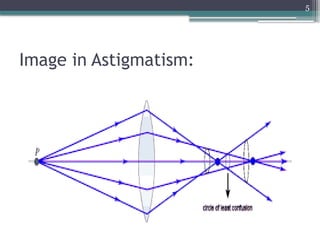
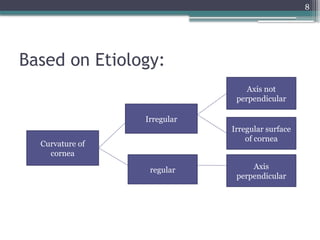
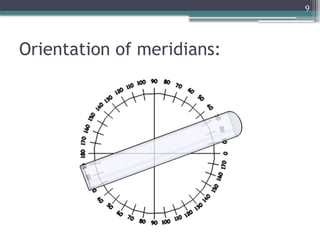
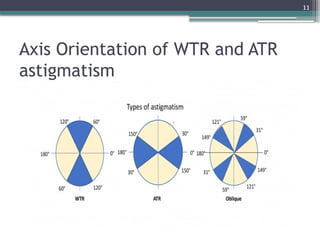
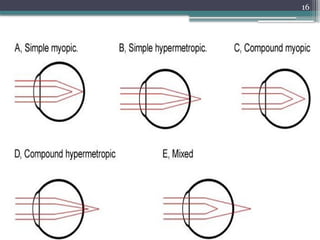
The document provides an overview of astigmatism, including its definition, etiology, classification, signs and symptoms, clinical tests, and management options. It explains the condition as irregular focusing of light due to variations in corneal curvature, with types classified based on etiology, orientation of meridians, and focal points relative to the retina. Various clinical tests for diagnosis and management strategies, including corrective lenses and surgical procedures, are also discussed.