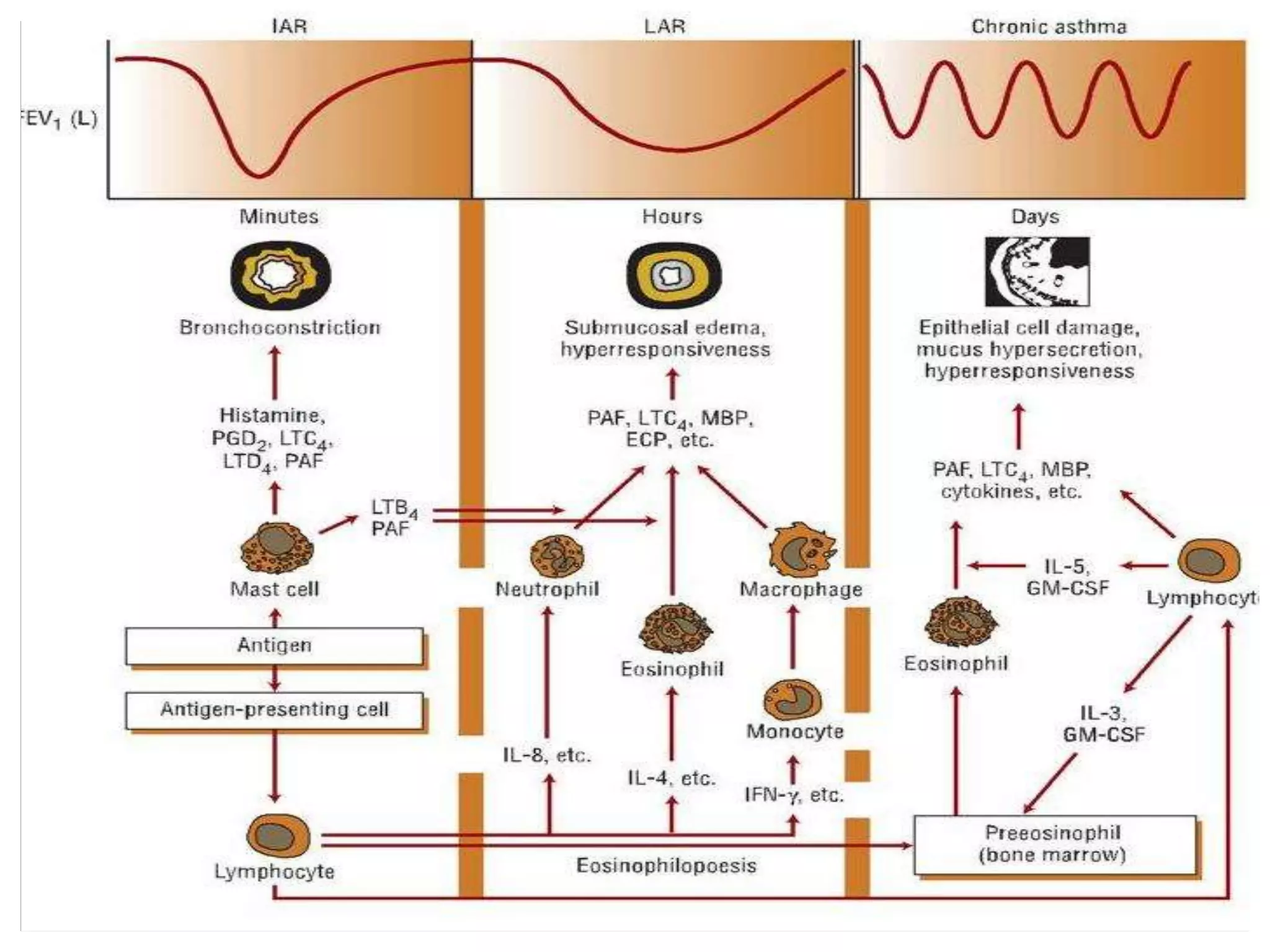
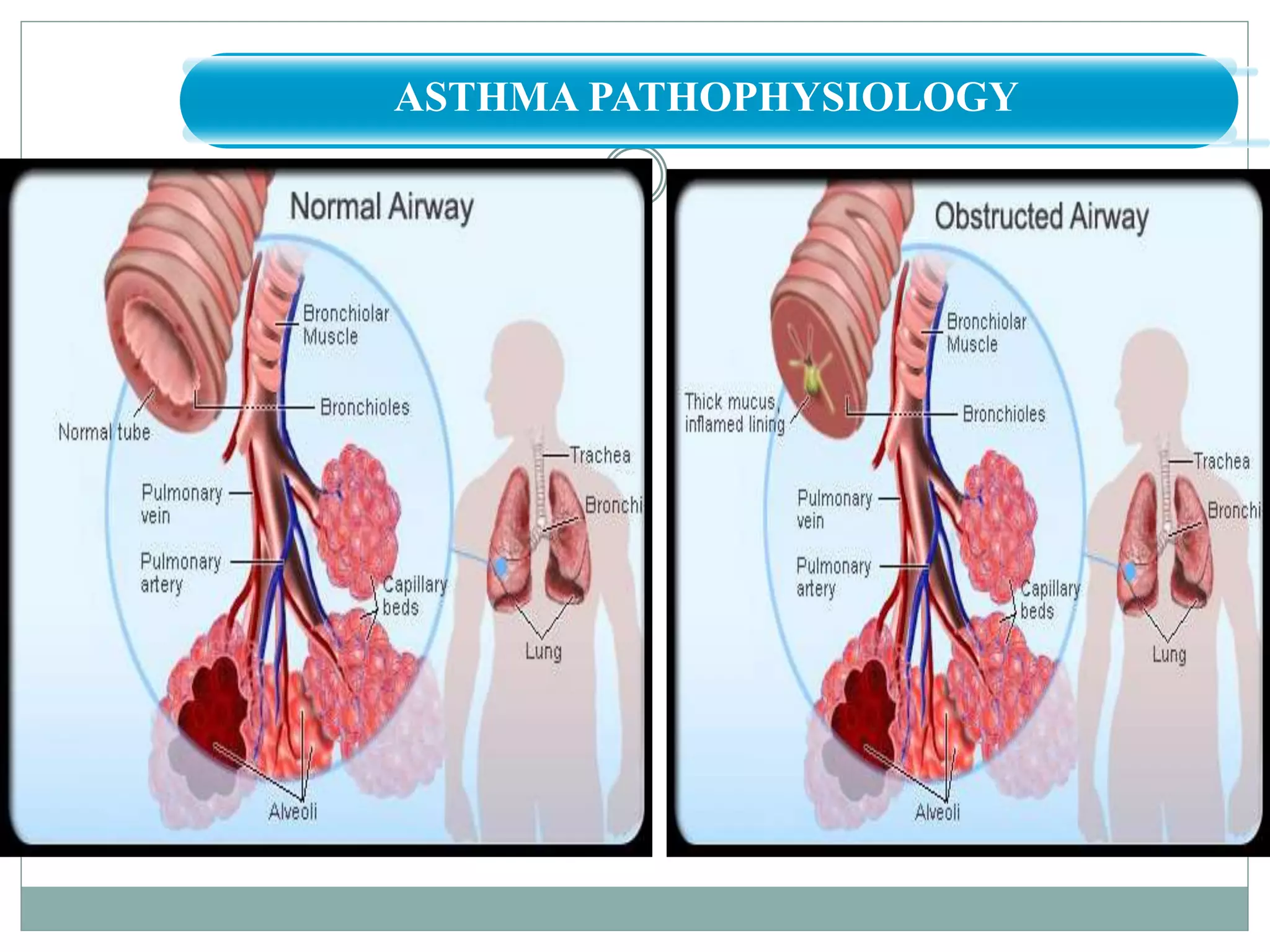
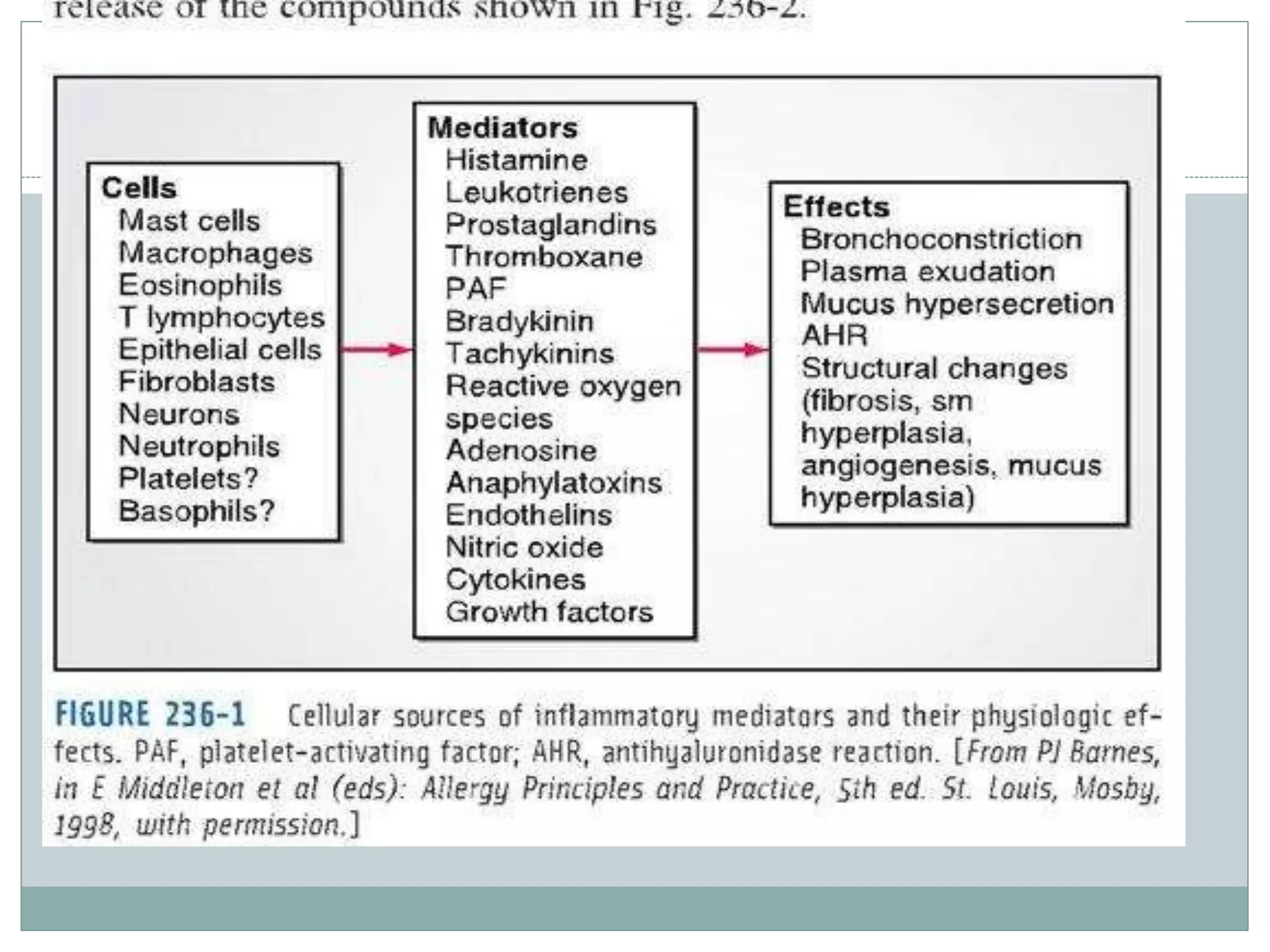
This document discusses asthma, including its pathophysiology. It describes how asthma involves chronic airway inflammation with activated cells like eosinophils, T cells, mast cells, macrophages, and epithelial cells. These cells release inflammatory mediators that cause bronchospasm, mucus production, and airway remodeling. Histamine, leukotrienes, prostaglandins, and other mediators are involved in the inflammatory process and cause symptoms like wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. Overall, the document provides an overview of the inflammatory pathophysiology underlying asthma.















![Eosinophils
Eosinophils play an effector role in asthma by release of proinflammatory mediators,
cytotoxic mediators, and cytokines.
Circulating eosinophils migrate to the airways by cell rolling, through interactions with
selectins, and eventually adhere to the endothelium through the binding of integrins to
adhesion proteins (vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 [VCAM-1] and intercellular
adhesion molecule 1 [ICAM-1]).
As eosinophils enter the matrix of the membrane, their survival is
prolonged by interleukin (IL)-5 and granulocyte-macrophage col-ony-stimulating factor
(GM-CSF).
On activation, eosinophils release inflammatory mediators such as leukotrienes and
granule proteins to injure airway tissue.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4715371a-6355-4d44-b7fd-0ae9f825333b-161230045525/75/Asthma-20-2048.jpg)
















![EXERCISE-INDUCED BRONCHOSPASM
During vigorous exercise, pulmonary functions (FEV1 and peak expiratory flow [PEF])
in patients with asthma increase during the first few minutes but then begin to decrease
after 6 to 8 minutes.
EIB is defined as a drop in FEV1 of greater than 15% of baseline (preexercise value)
Most studies suggest that many patients with persistent asthma experience EIB.
The exact pathogenesis of EIB is unknown, but heat loss and/or water loss from the
central airwayappears to play an important role.
EIB is provoked more easily in cold, dry air, and warm, humid air can blunt or block it.
A number of studies have demonstrated increased plasma histamine, cysteinyl
leukotrienes, prostaglandins, and tryptase concentrations during EIB, suggesting a role
for mast cell degranulation. A refractory period following EIB lasts up to 3 hours after
exercise. During this period, repeat exercise of the same intensity produces either no
decrease in pulmonary function or a drop of less than 50% of the initial response.
This refractory period is thought o be caused by an acute depletion of mast cell
mediators and time required for their repletion. Patients with known refractoriness to
exercise will still respond to histamine, so acute hyporesponsiveness of airway smooth
muscle does not appear to be a factor.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4715371a-6355-4d44-b7fd-0ae9f825333b-161230045525/75/Asthma-38-2048.jpg)