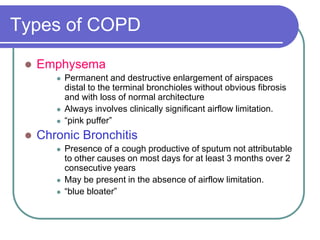
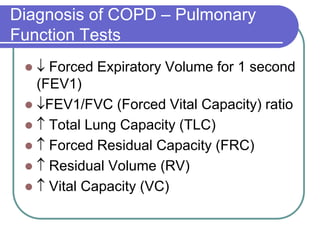
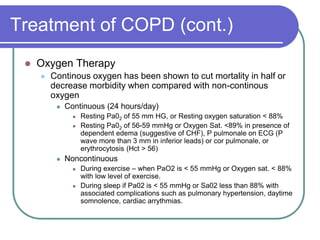
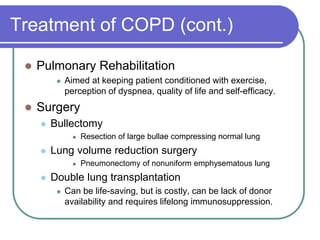
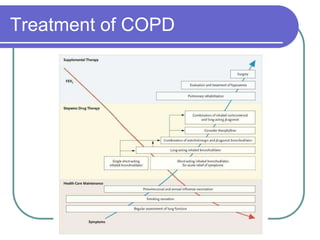
This document defines COPD as a disease characterized by airflow obstruction due to chronic bronchitis or emphysema. It affects 4-6% of white males and 1-3% of white females in the US. The two main types are emphysema, which causes permanent enlargement of airspaces, and chronic bronchitis, characterized by a cough with sputum. Smoking is the primary risk factor and causes an inflammatory response that destroys lung tissue over time. Symptoms include dyspnea, cough, and limited lung function is diagnosed through pulmonary testing. Treatment focuses on smoking cessation and bronchodilators while oxygen therapy can improve outcomes for severe cases.