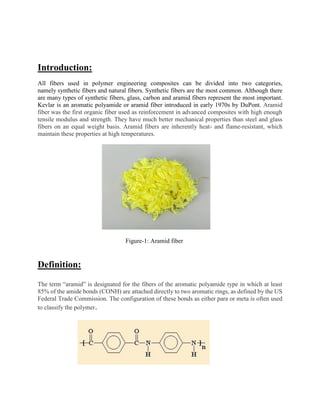
The document provides an in-depth examination of aramid fibers, specifically their types, production methods, properties, advantages, and disadvantages. Key applications include protective clothing, body armor, and composite materials, stemmed from their high strength and thermal resistance. Despite some limitations, like moisture sensitivity and UV degradation, aramid fibers are positioned as a vital material in various industrial applications.