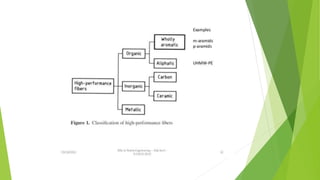
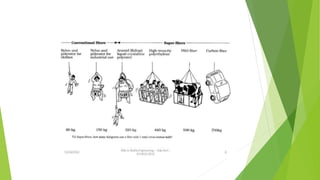
This document provides an overview of high performance fibers (HPF). It defines HPF as fibers with high strength, temperature resistance, flexibility, light weight, fine diameter and durability, mainly used for technical textiles. Key qualities for HPF include tensile strength, operating temperature, limiting oxygen index, and chemical resistance. The document then lists and describes common types of HPF, including glass fiber, carbon fiber, aramid fiber, polybenzimidazole, polyphenylenebenzobisoxazole, polyphenyl sulfide, melamine, fluoropolymers, high-density polyethylene, ceramic fibers, and chemically and thermally resistant fibers. It provides details on the properties and uses of several of