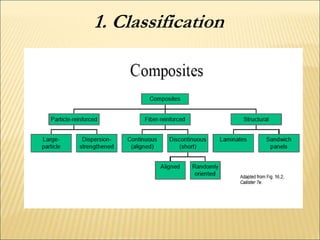
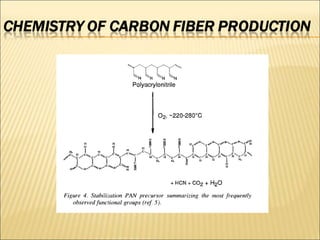
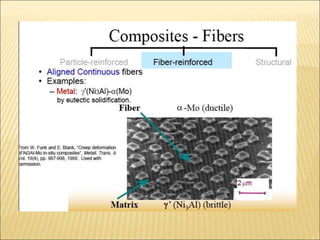
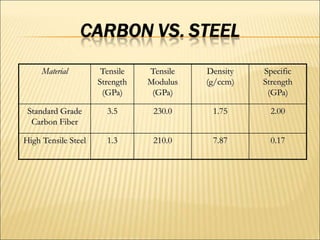
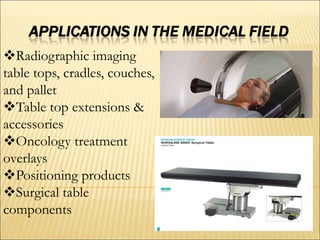
The document discusses carbon fiber, detailing its properties, history, and commercial applications across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and civil engineering. It highlights the high strength, low weight, and specific uses of carbon fiber in products like sports equipment and structural reinforcements. Additionally, it addresses cost factors, safety issues related to carbon fiber dust, and recycling methods developed to reclaim fibers.