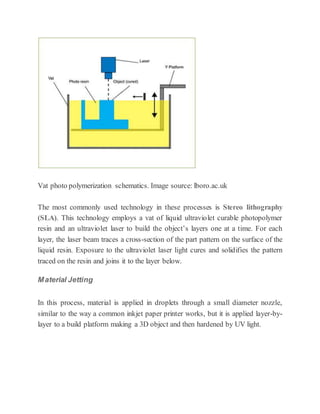
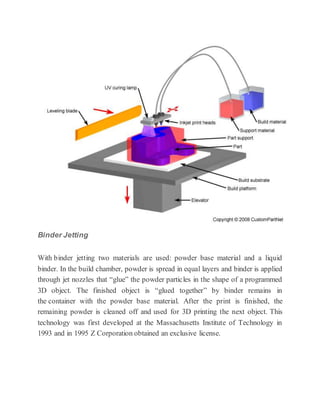
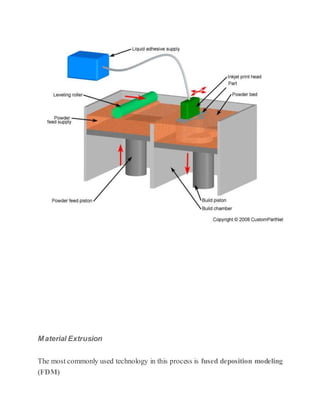
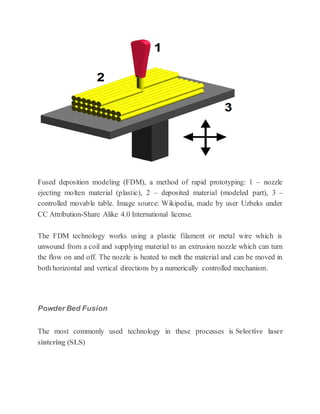
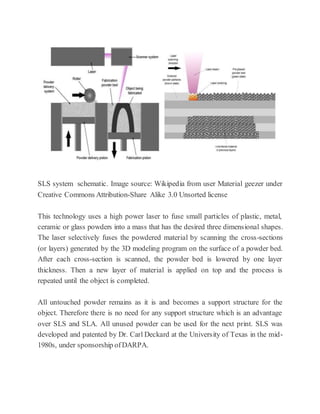
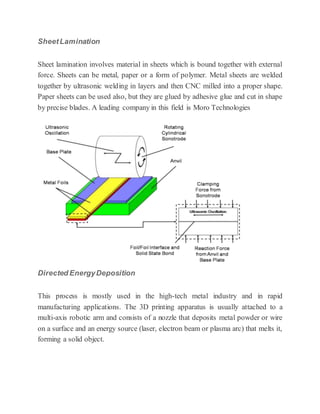
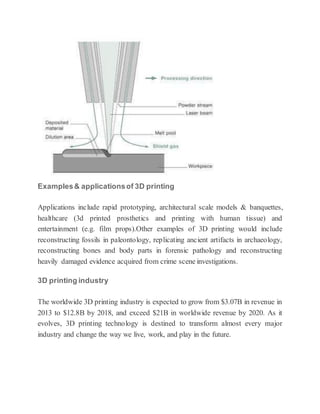
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process that creates three-dimensional solid objects from a digital file by building up successive layers of material. The digital file is first designed in a CAD program or scanned with a 3D scanner. The file is then sliced into thin horizontal layers and printed one layer at a time. There are several 3D printing technologies that differ in how the layers are deposited including photopolymerization, material extrusion, powder bed fusion, and directed energy deposition. 3D printing has applications in rapid prototyping, healthcare, entertainment, and is expected to significantly impact and transform many industries.