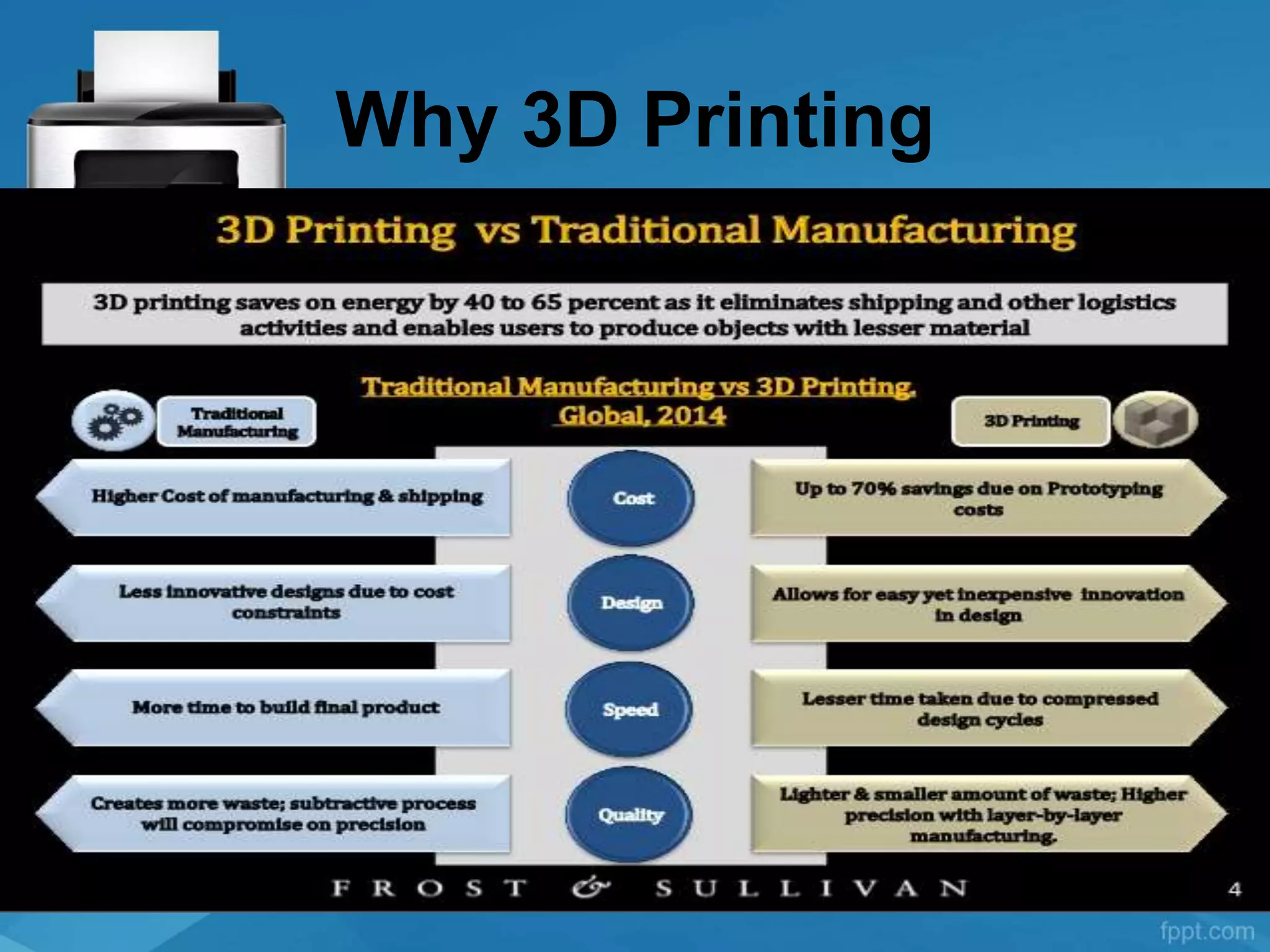
3D printing involves converting a virtual 3D model into a physical object by laying down successive layers of material. It began in the 1980s and is now used for industrial prototyping, education, medicine, fashion, food and more. Various technologies are used including stereolithography (SLA), fused deposition modeling (FDM), selective laser sintering (SLS), and others. While it provides many benefits, 3D printing has limitations such as slow speeds and potential effects on certain jobs. The future may bring larger 3D printers that can build structures and even prepare meals.