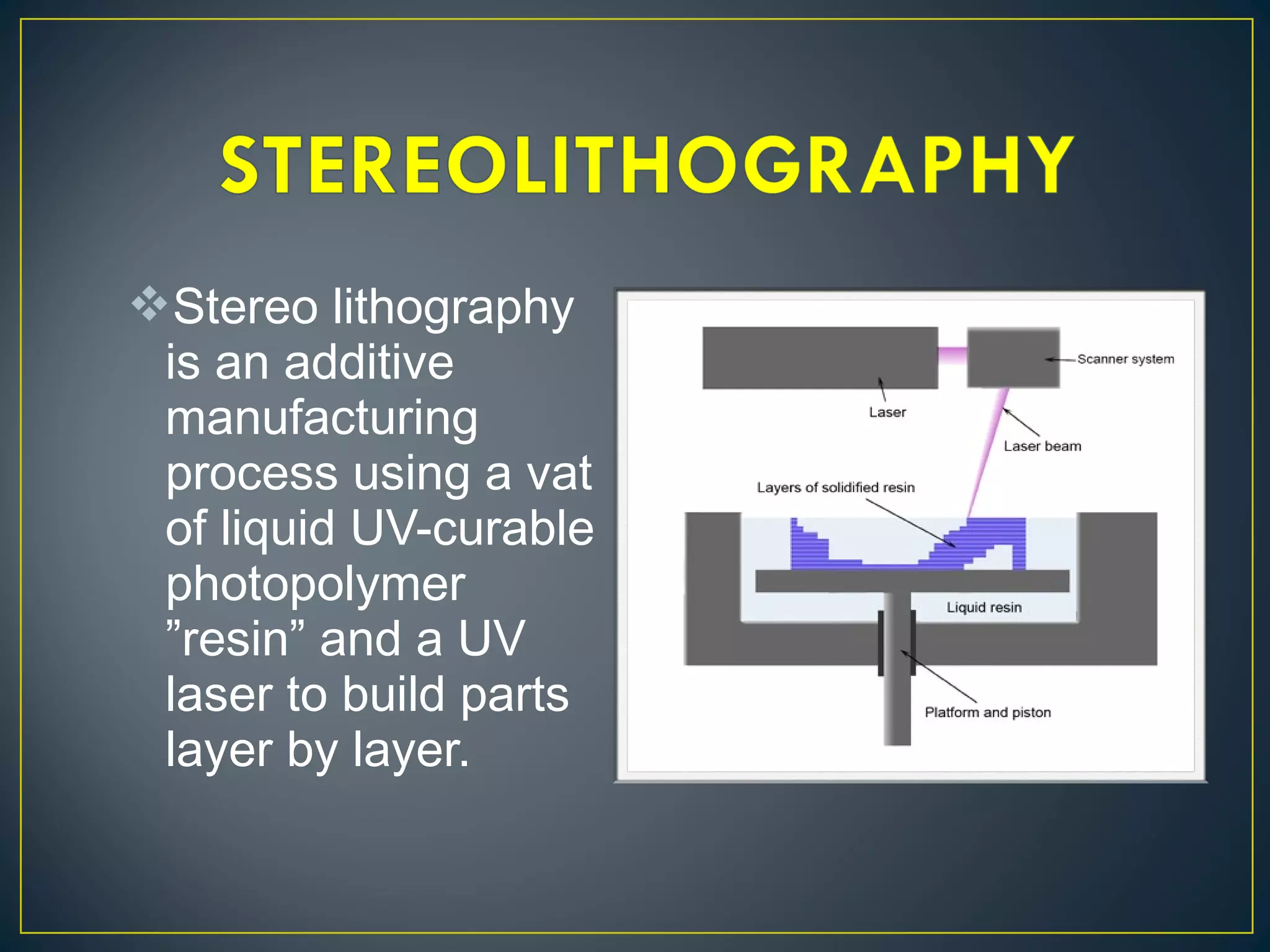
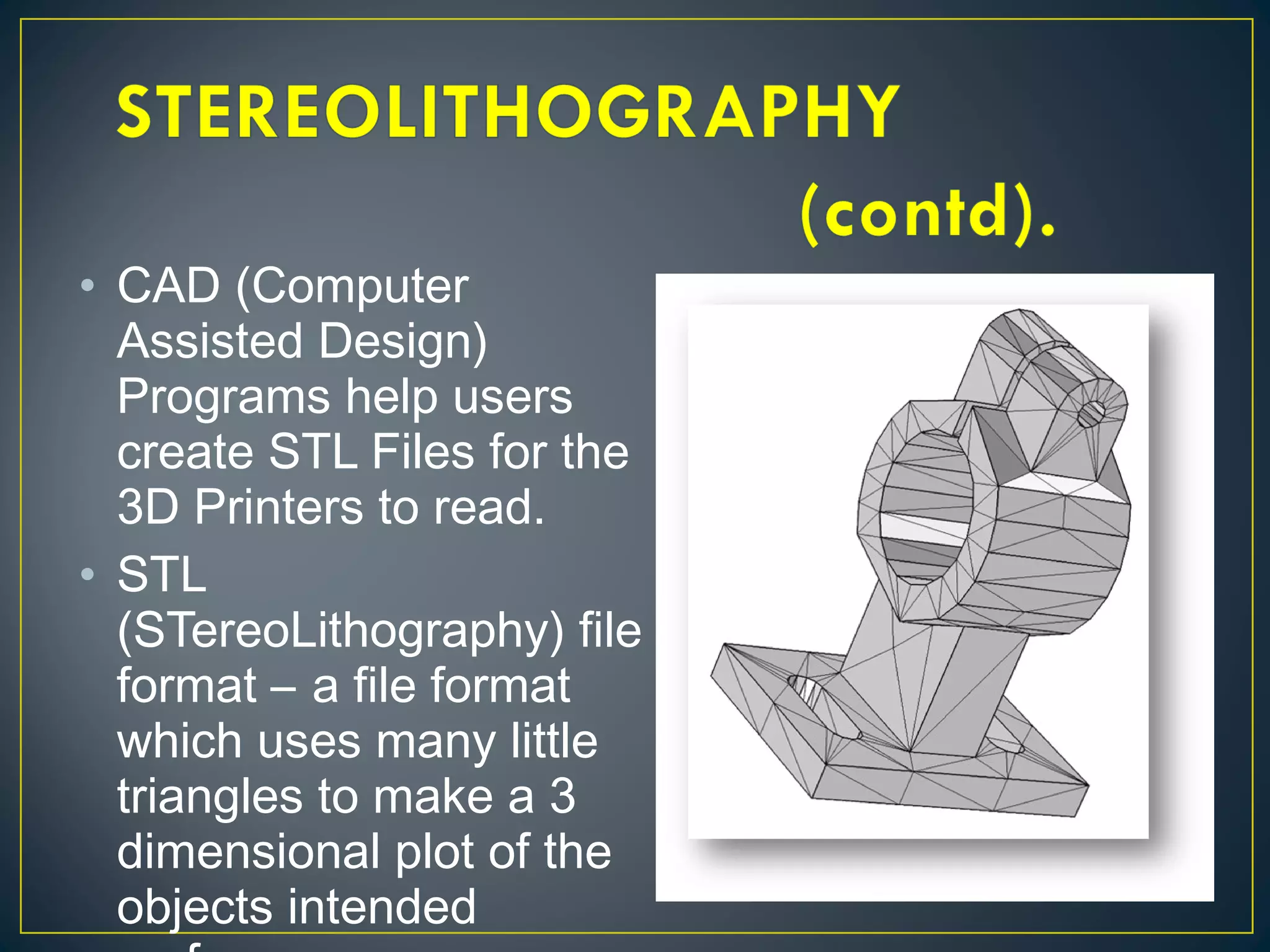
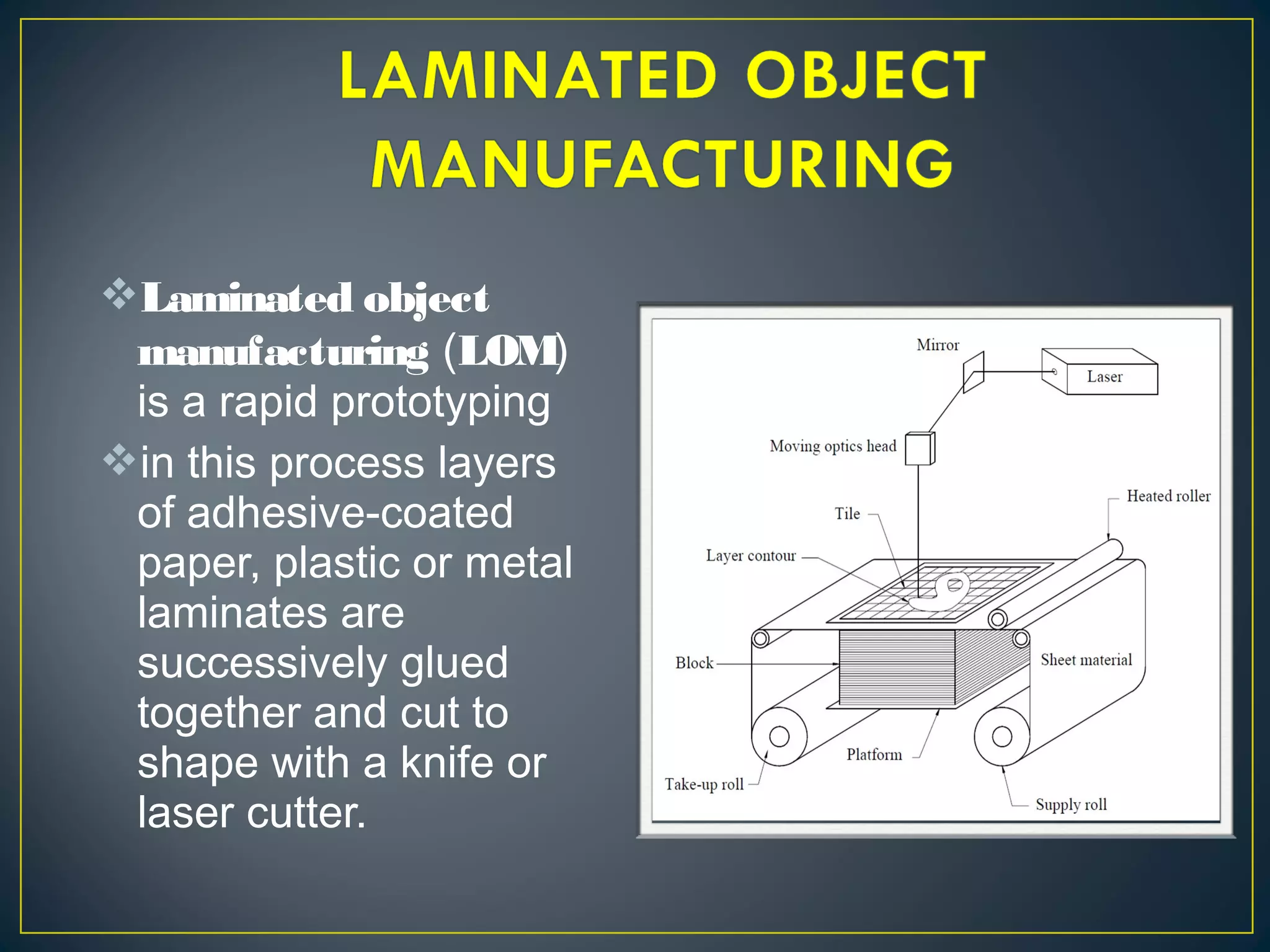
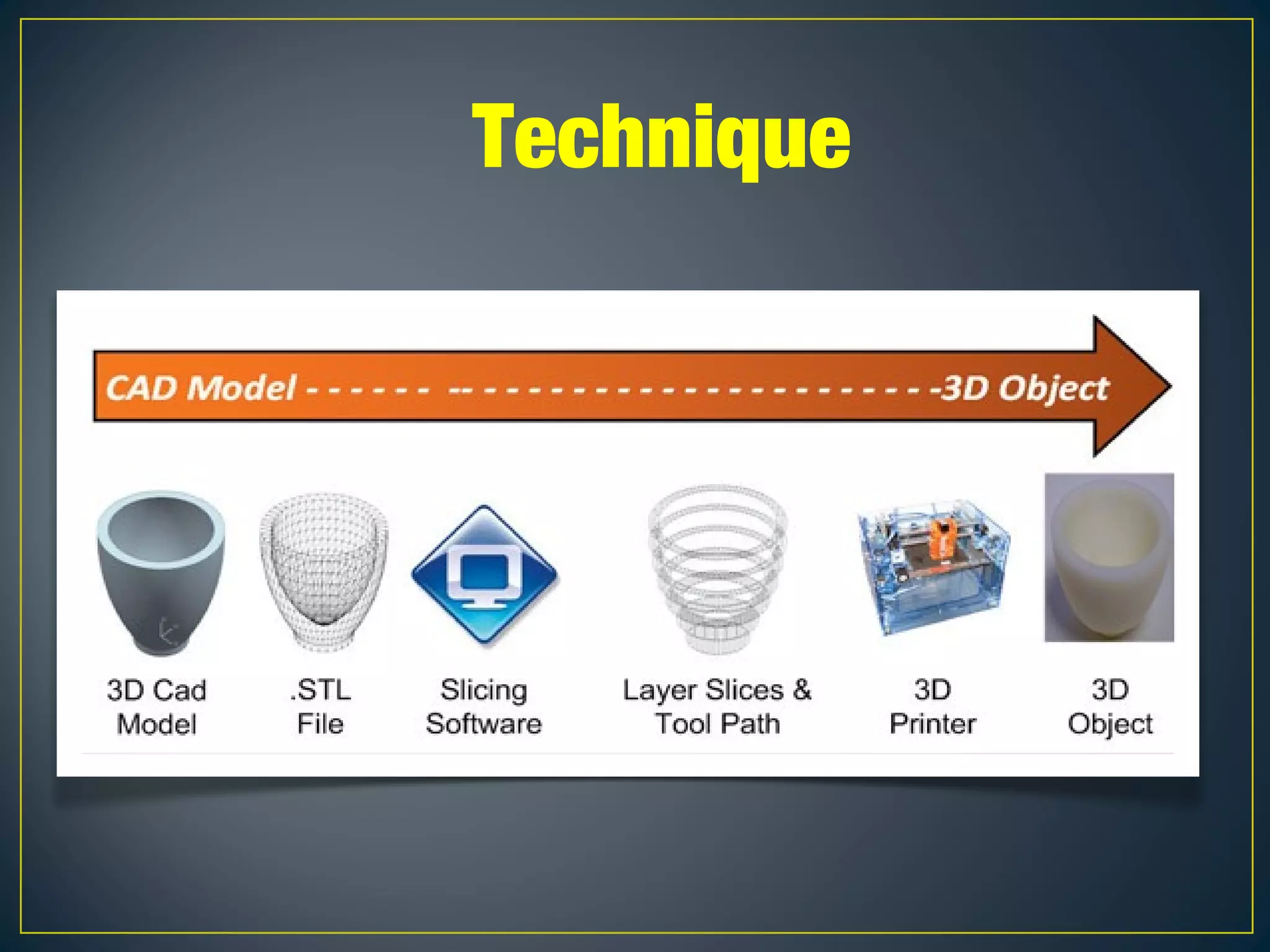
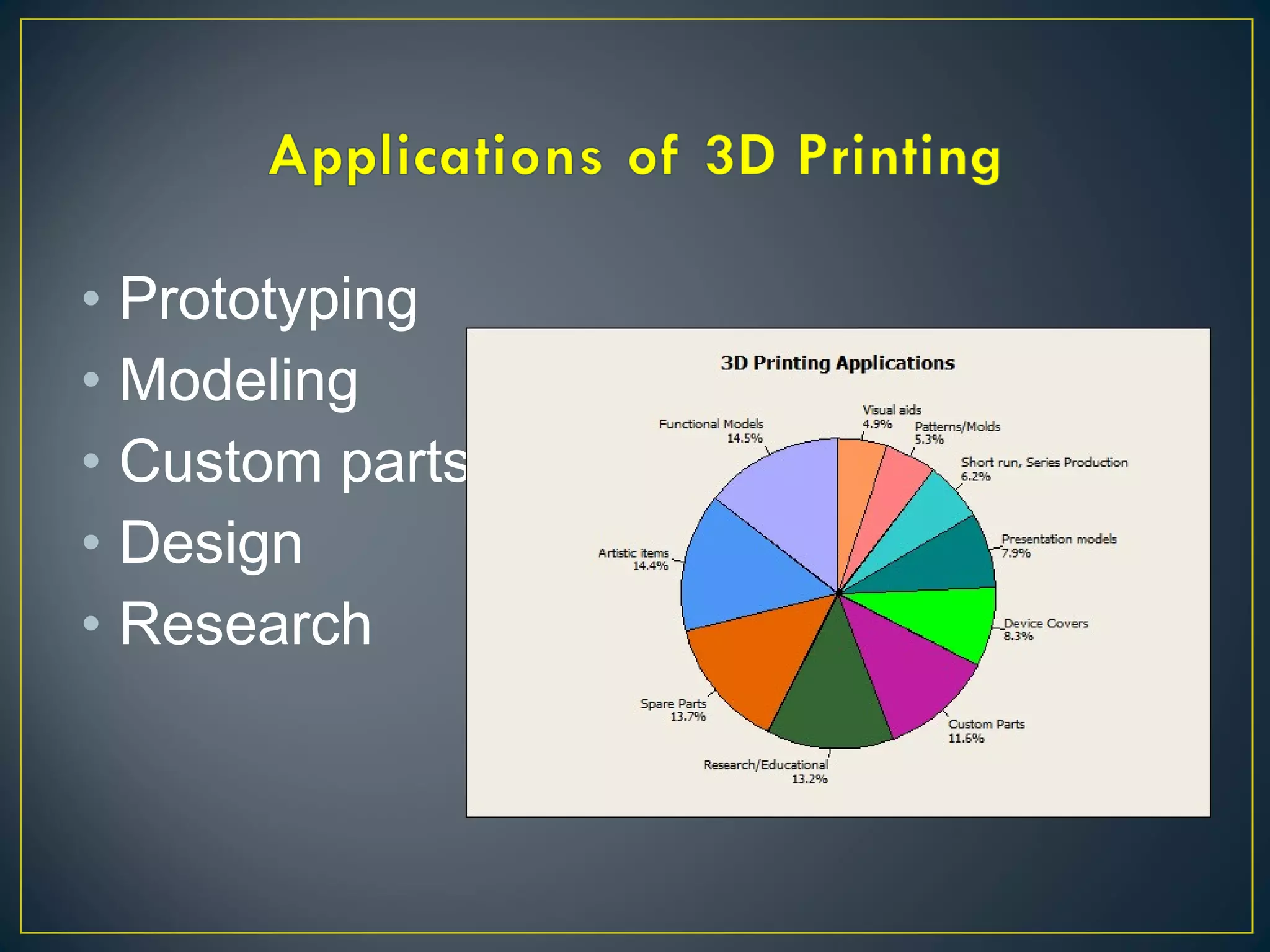
This document discusses 3D printing and additive manufacturing. It describes subtractive manufacturing and casting/forming as traditional manufacturing methods that remove or shape materials, whereas additive manufacturing builds objects up layer by layer from materials like plastic, metal or ceramic powders. Specific additive methods covered include selective laser sintering, stereo lithography, fused deposition modeling, and laminated object manufacturing. The document outlines the benefits of 3D printing such as reduced waste, complex designs, and customization, but also notes potential intellectual property and misuse concerns.