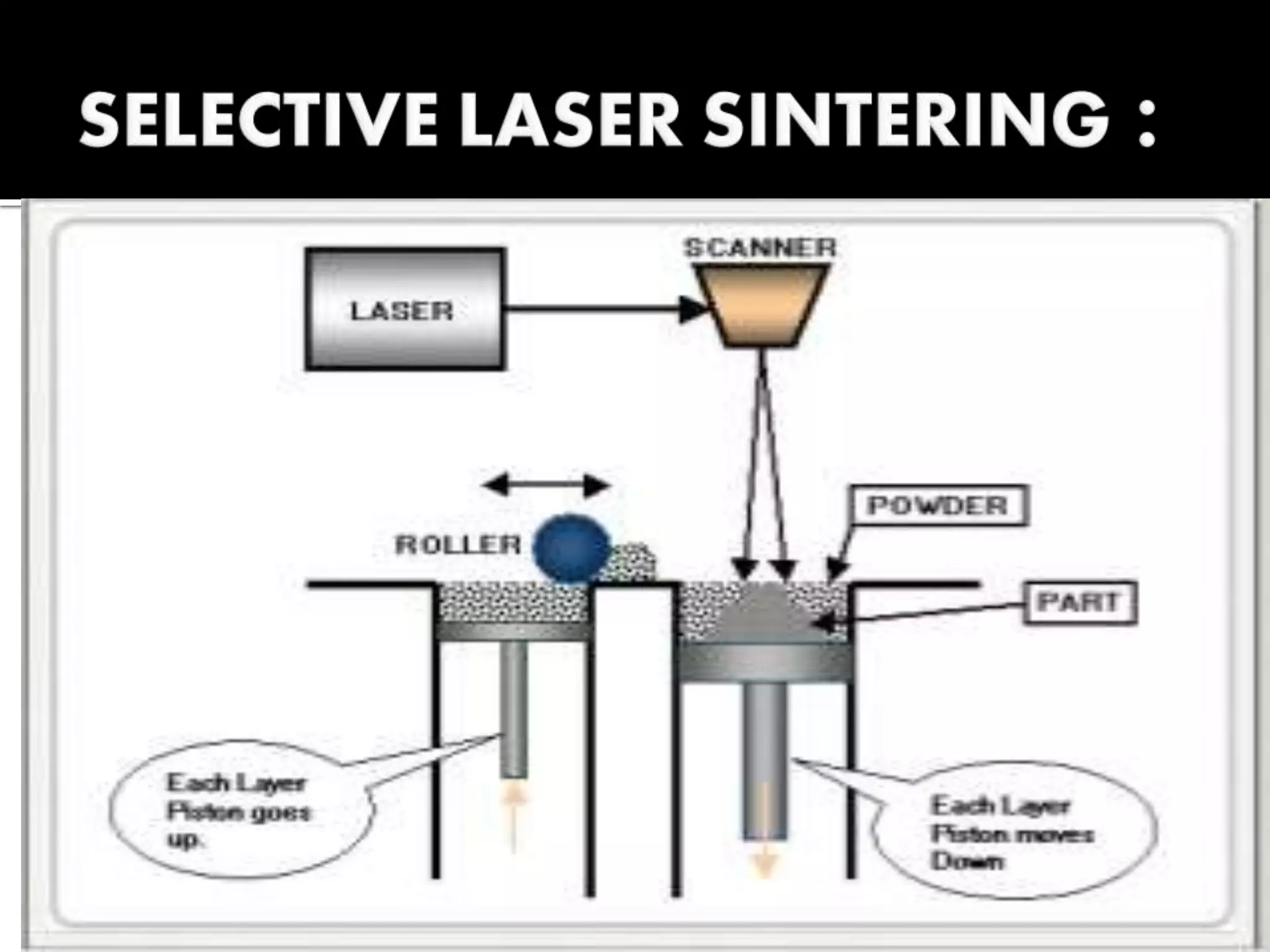
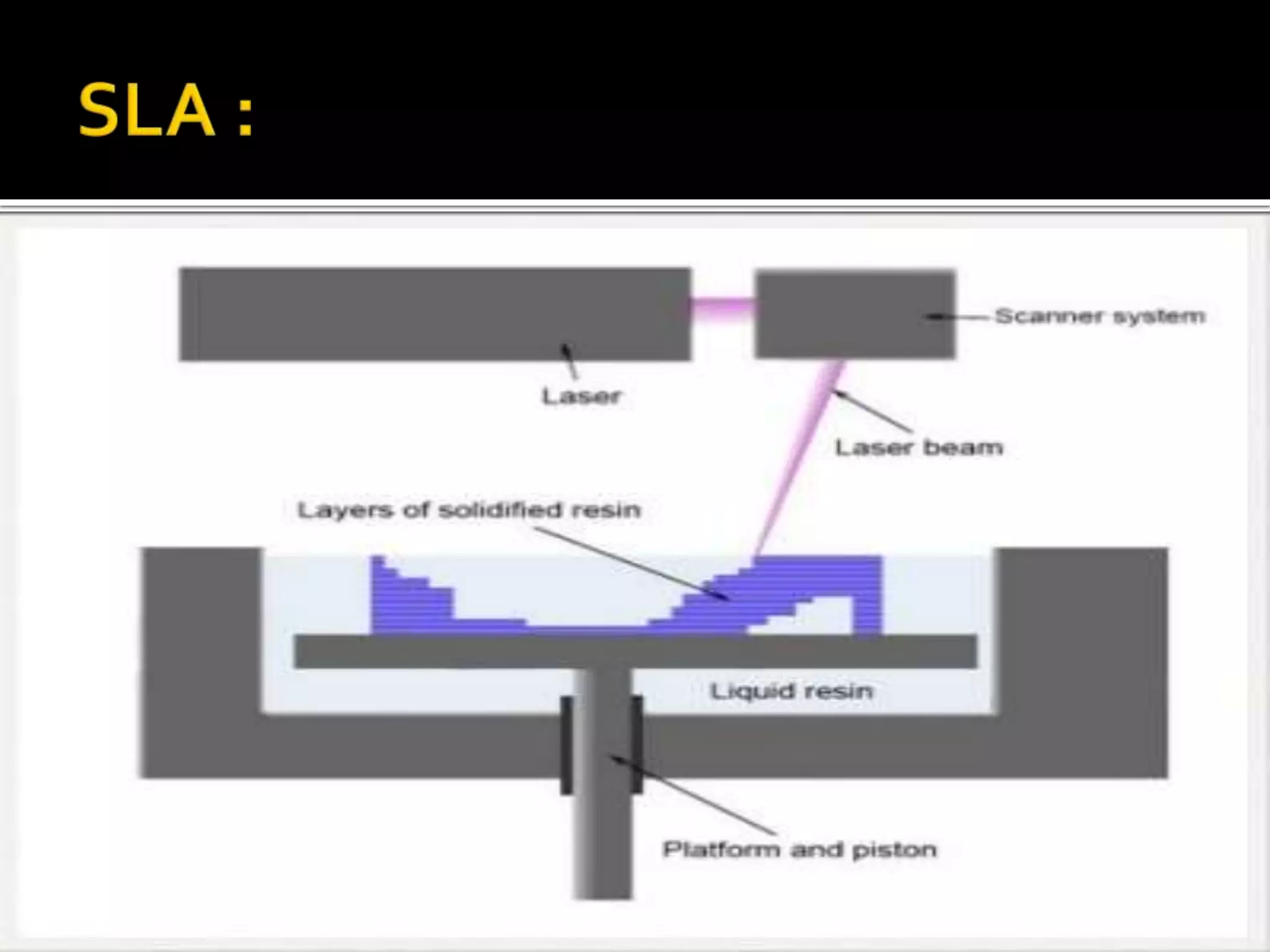
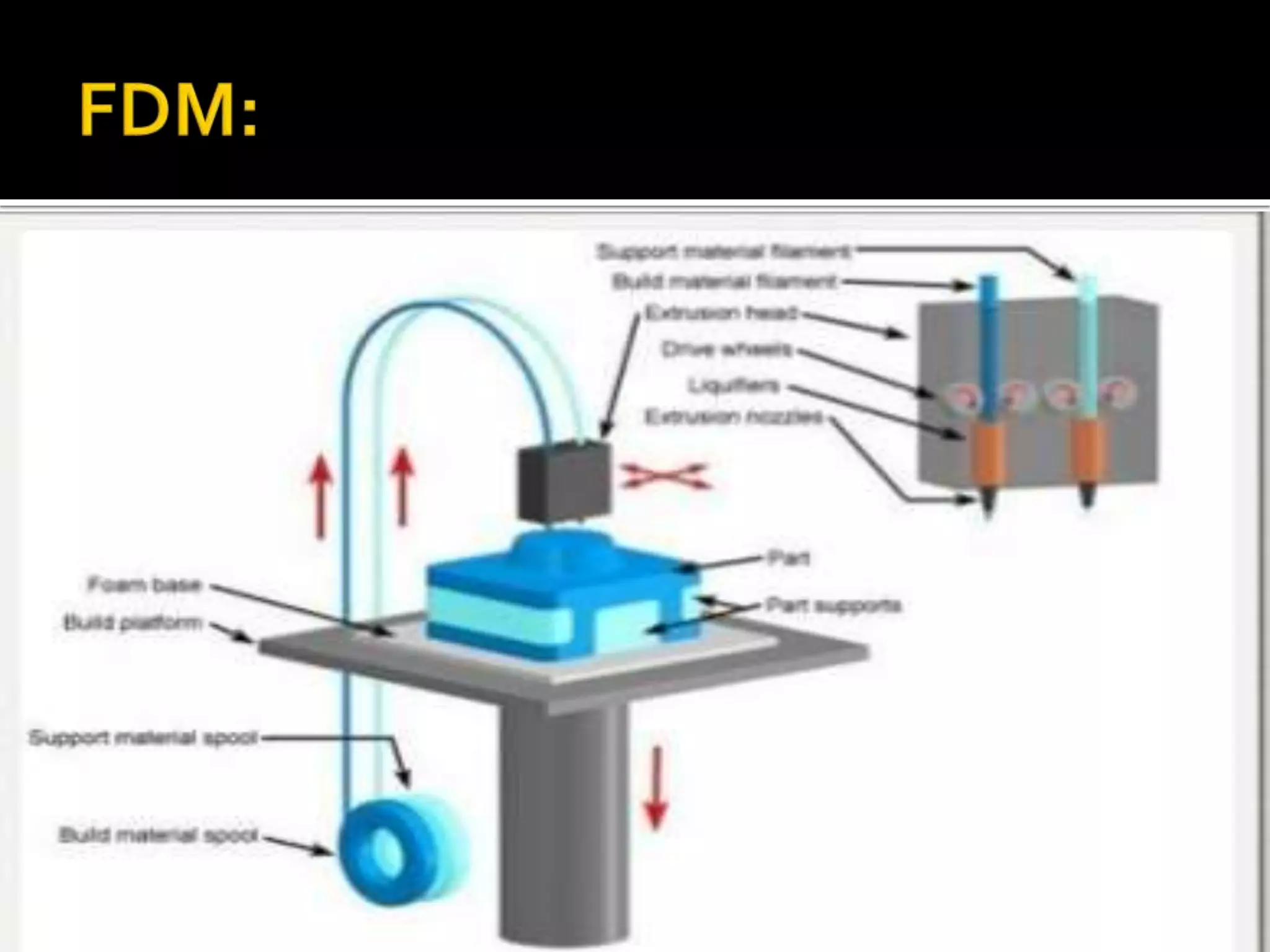
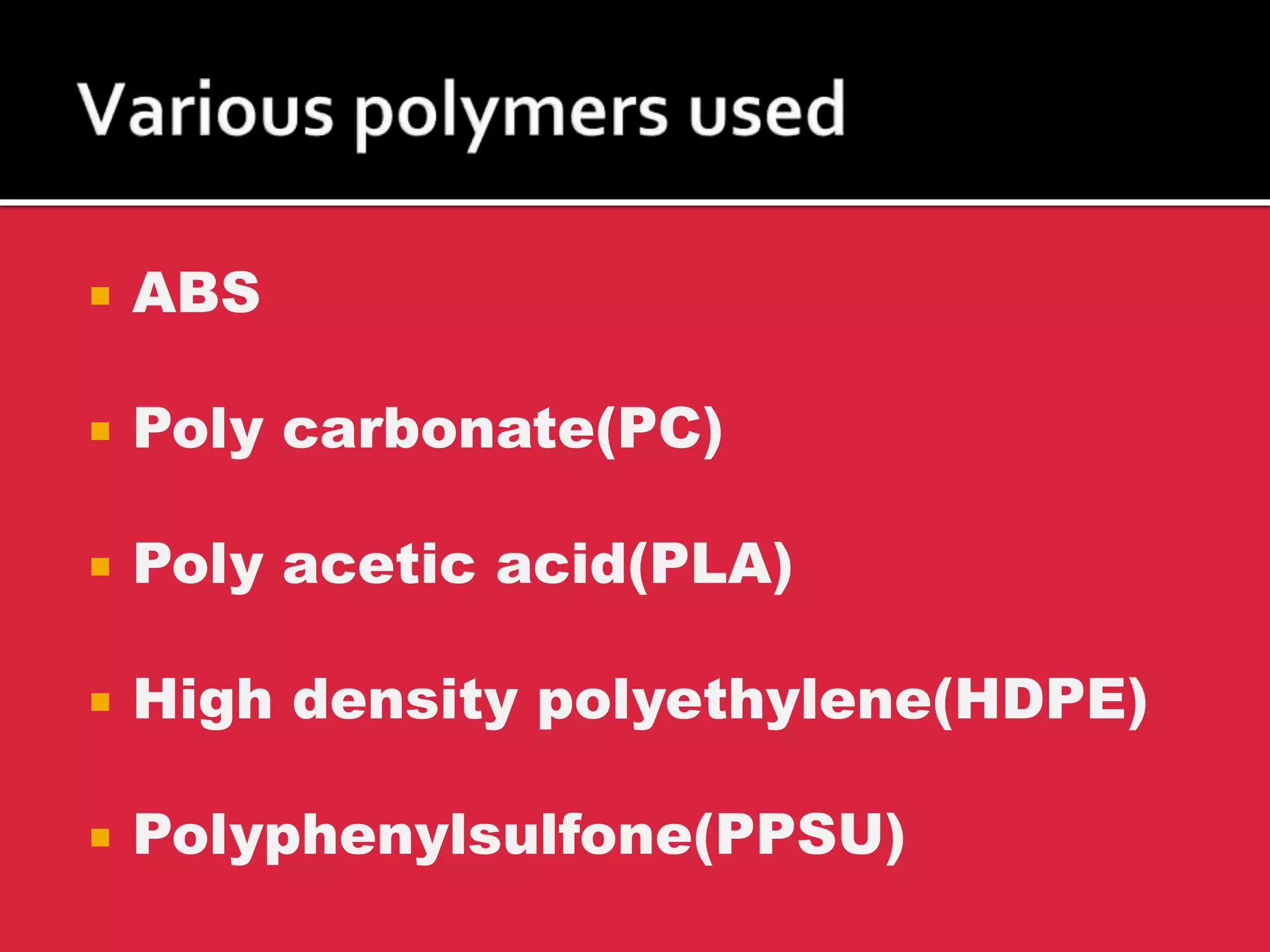
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process where a 3D model is sliced into layers and material is deposited layer by layer to build a physical object. There are three main methods - selective laser sintering uses a laser to sinter powdered material, stereolithography uses a UV laser to cure liquid resin layer by layer, and fused deposition modeling extrudes melted plastic through a nozzle to build layers. Common materials used include ABS, PLA, and nylon. 3D printing produces little waste and can be used to make replacement parts, though the machines can be expensive and materials may not be strong enough.