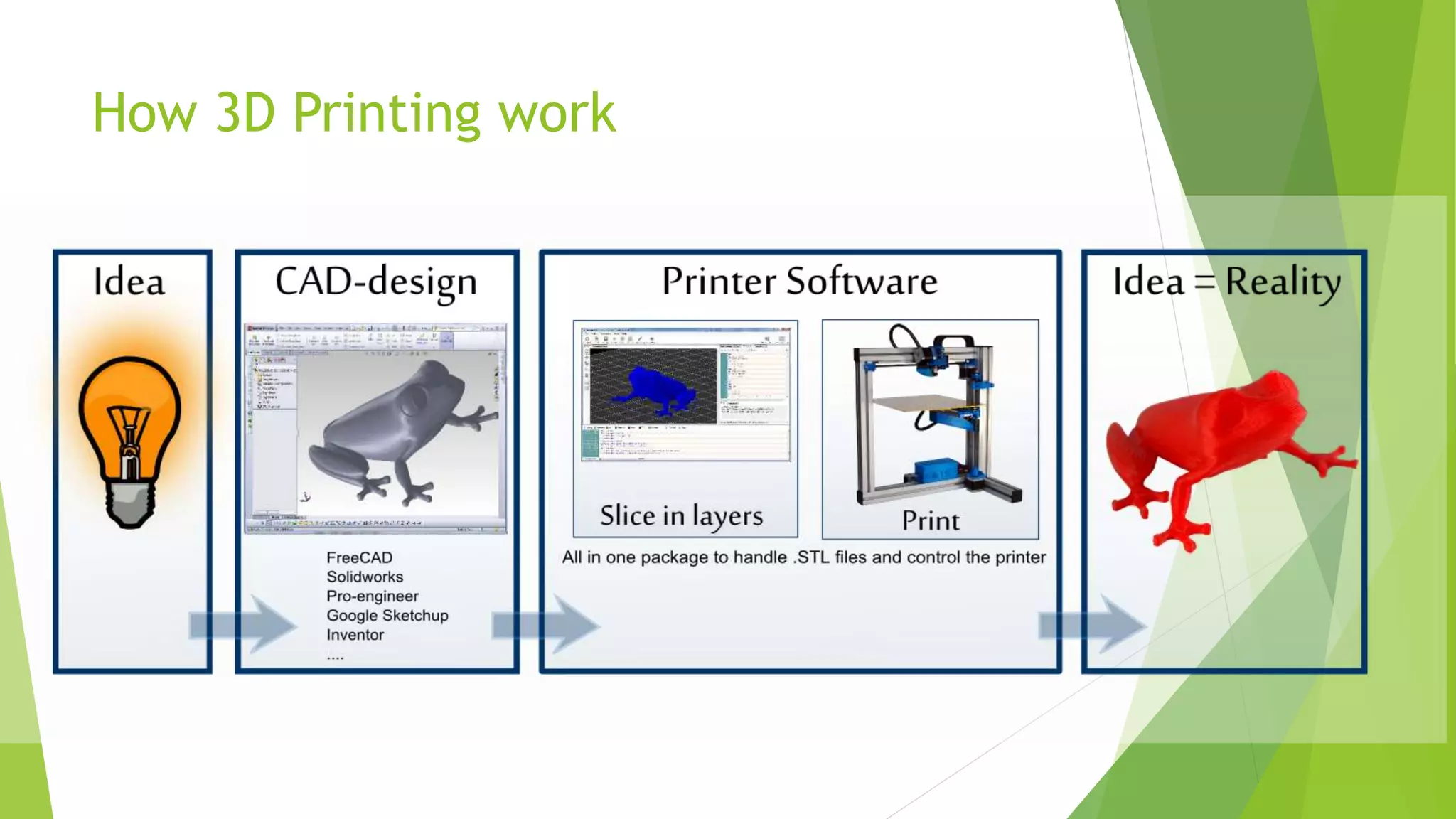
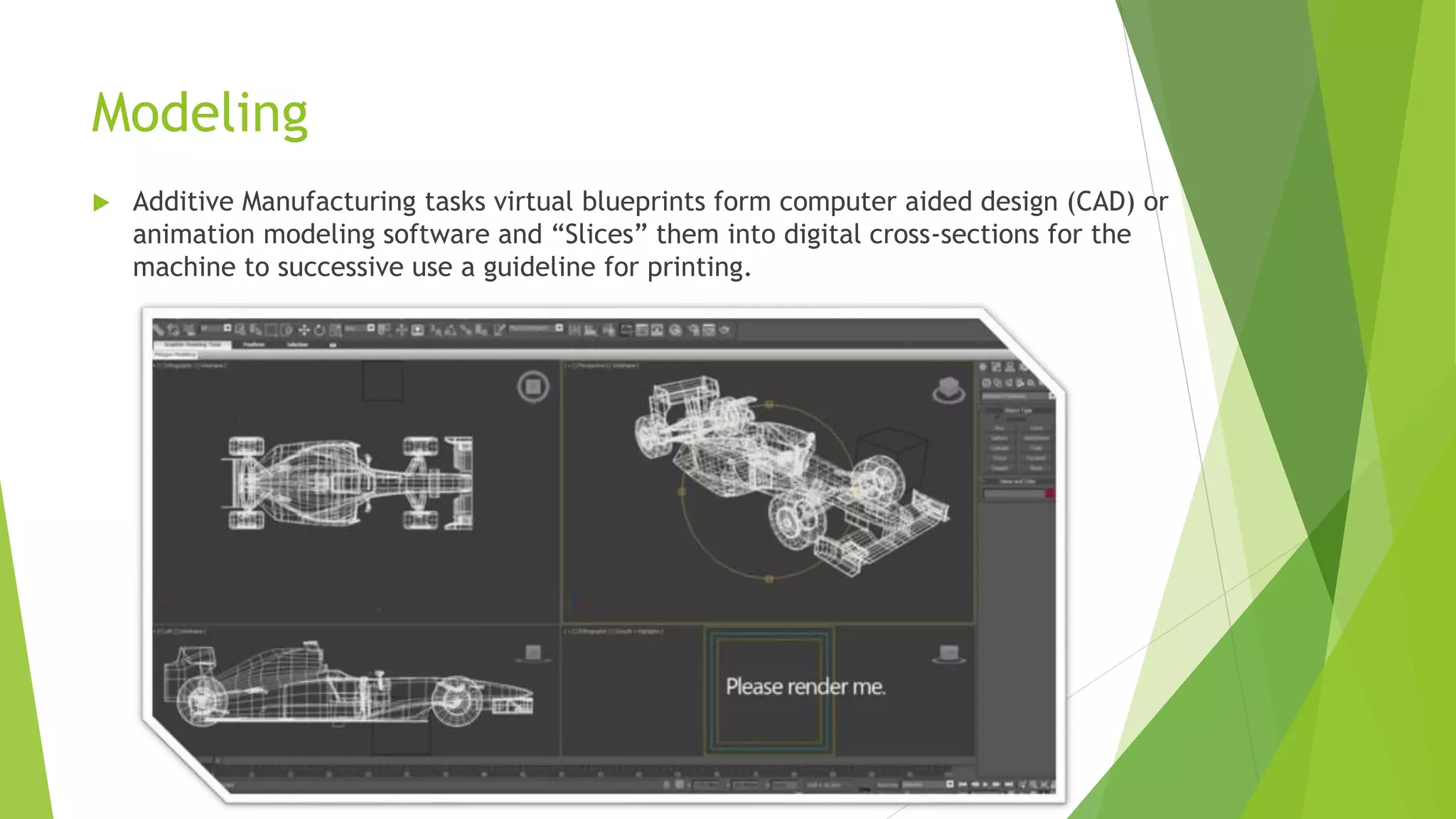
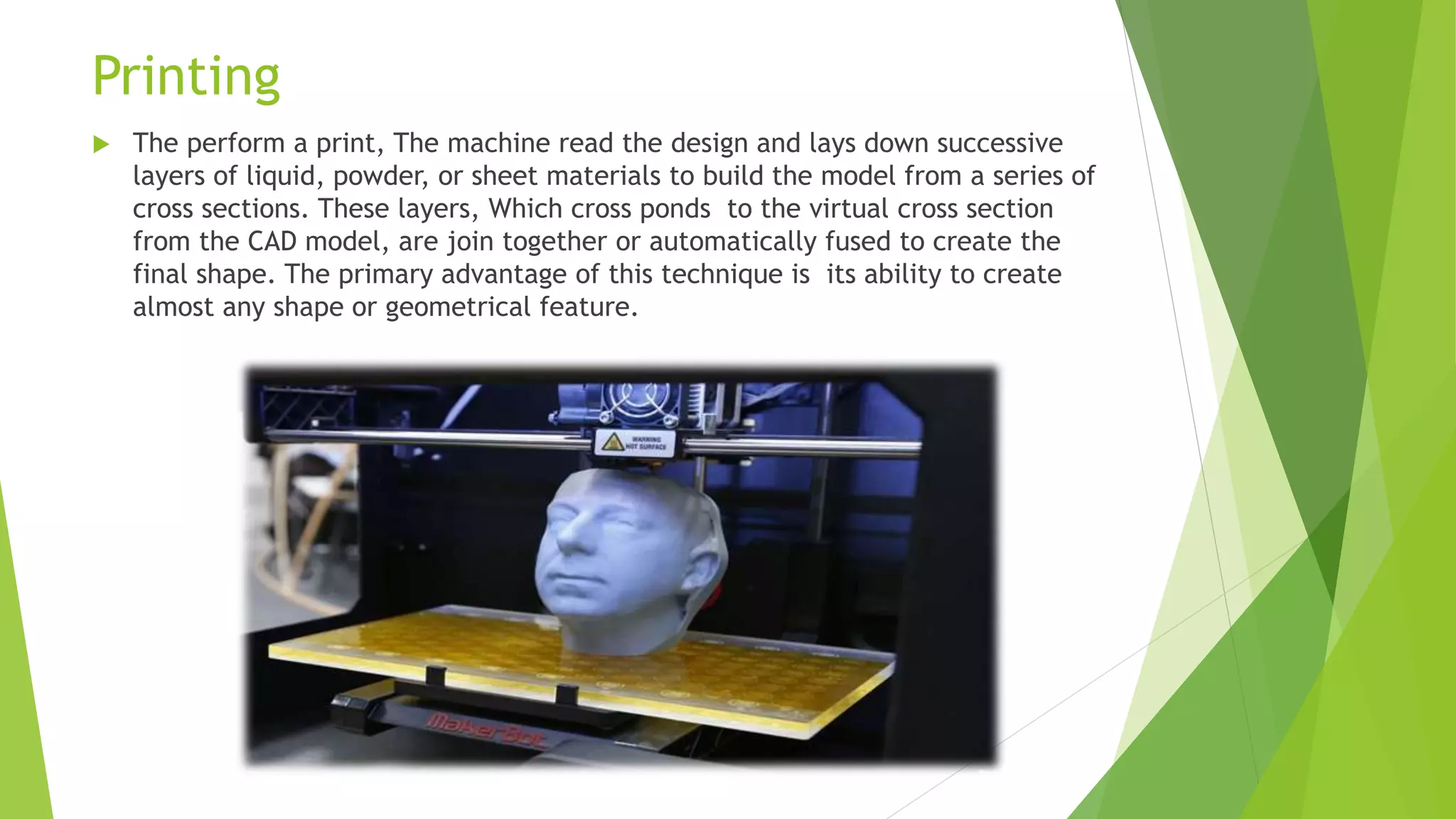
This document provides an outline and overview of 3D printing. It discusses the history of 3D printing, which was first developed in 1984. It then defines 3D printing as a process that creates 3D objects by laying down successive layers of material based on a digital file. The document outlines the general principles of 3D printing, including modeling an object digitally, printing it by adding layers, and sometimes finishing the printed object. It also discusses some common 3D printing methods and potential advantages and disadvantages.