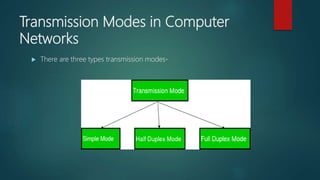
The document discusses various topics related to computer networks including transmission modes, Internet, intranet, network interface cards, MAC addresses, IP addresses, types of area networks, analog and digital signals, hubs, switches, and routers. It explains that there are three transmission modes: simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex. It also defines Internet, intranet, network interface cards, MAC addresses, IP addresses, local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs). The document concludes by describing analog and digital signals as well as network devices like hubs, switches, and routers.