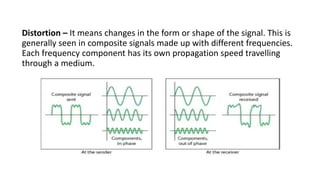
The document discusses the OSI model and TCP/IP model, which are conceptual frameworks for networking systems.
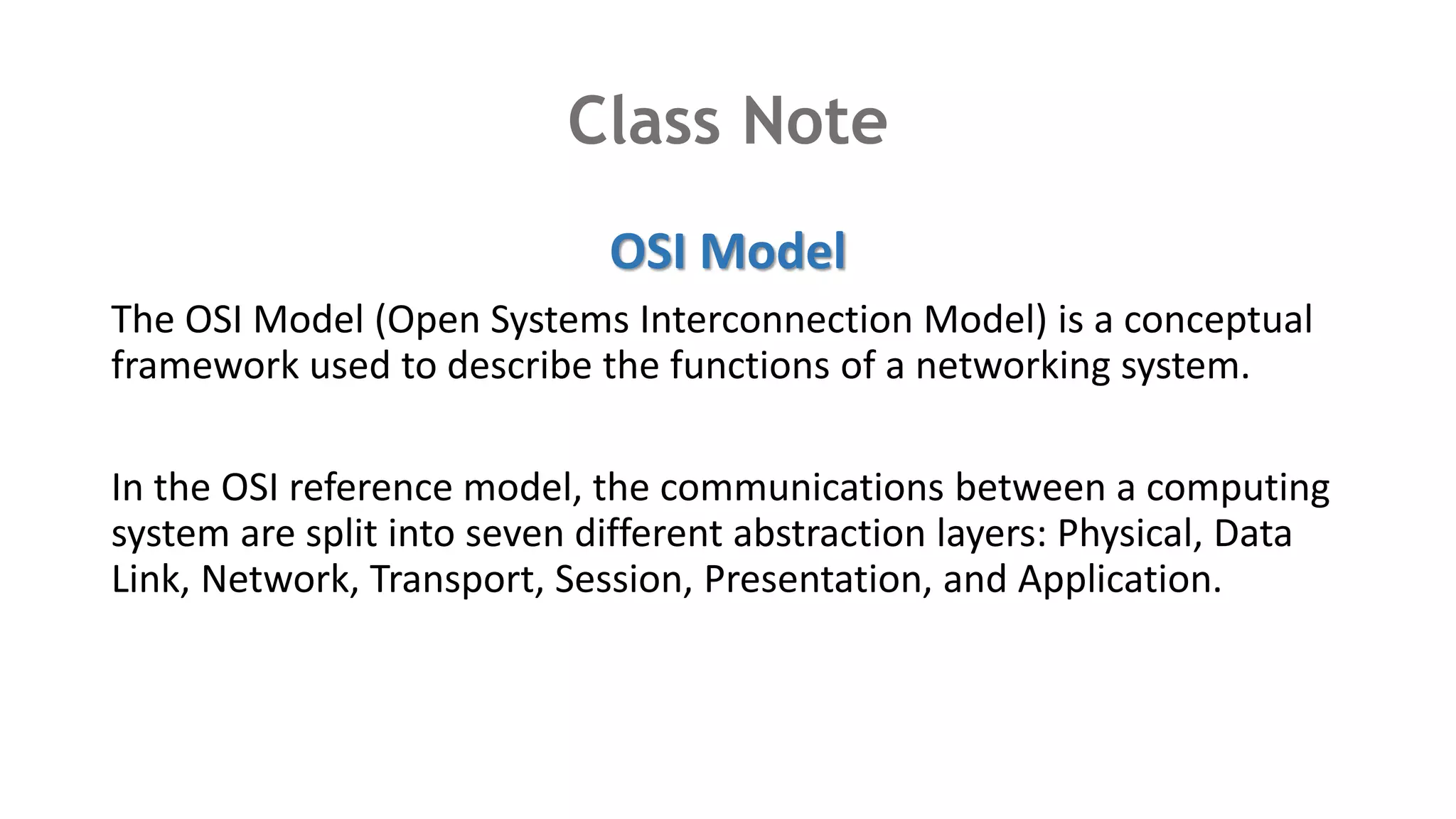
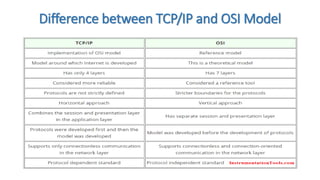
The OSI model splits communication functions into 7 abstraction layers: physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application. It describes the responsibilities of each layer.
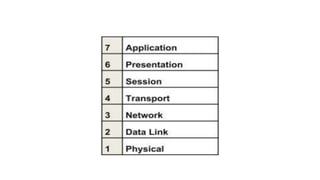
The TCP/IP model has 4 layers: application, transport, internet, and network access. It describes how data is sent between connected devices and networks.