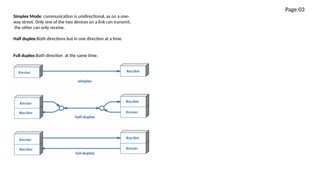
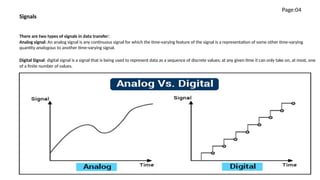
Class work covered topics including data flow, signals, networking addressing, and devices. There were five components of a data communication system identified as the sender, receiver, data, transmission medium, and protocol. The document discussed analog and digital signals, different network types including LAN, MAN, WAN, common networking devices like modems, hubs, switches, and routers, and IP address classes.