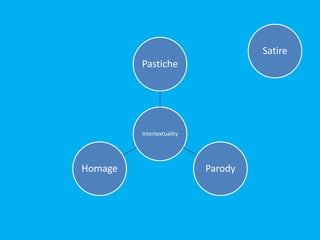
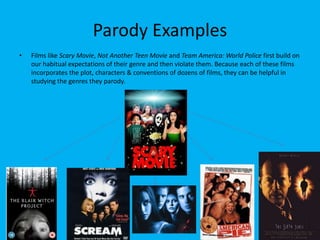
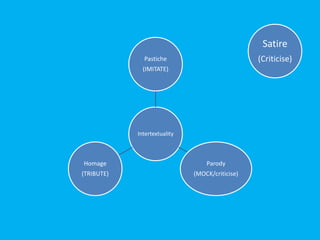
Postmodernism lesson 1 introduces some of the basic ideas and concepts of postmodernism. It discusses the origins and key themes of postmodernism, including skepticism of grand narratives, blurring of boundaries between high and low art forms, and lack of originality through techniques like pastiche and intertextuality. The document explores concepts like hybridization, bricolage, and juxtaposition that are characteristic of postmodern works. It provides examples from film and art to illustrate self-reflexivity, parody, and how postmodernism questions what is considered real. The lesson aims to help students understand some of the defining features of postmodernism.