- Psychological testing is used for personnel selection and must meet professional and legal standards by directly relating to job requirements.
- Employment interviews can be biased while tests, when used with interviews, can improve selection success.
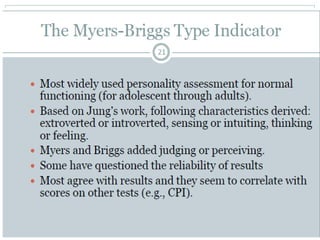
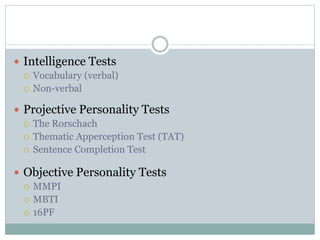
- Various psychological tests are used for employee selection, including personality, honesty, intelligence, aptitude, and physical tests.
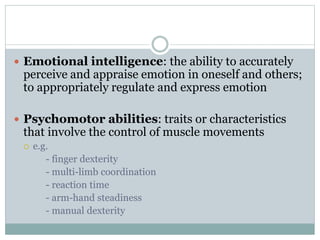
- Abilities, skills, and aptitudes can predict job performance when measured by cognitive, emotional intelligence, psychomotor, and physical tests.