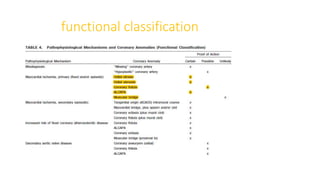
1) Coronary artery anomalies (CAAs) are defined as morphological features found in less than 1% of the population. They can be classified based on origin, course, termination, or hemodynamic significance.
2) Some important CAAs include anomalous origin of the left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery (ALCAPA), anomalous origin of the coronary artery from the opposite sinus (ACAOS), and coronary artery fistulas.
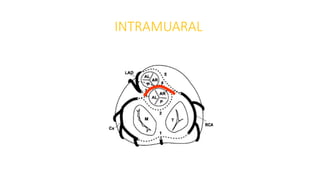
3) ALCAPA causes retrograde flow of blood from the right coronary artery to the pulmonary artery. ACAOS, especially when the ectopic artery takes an interarterial course, can cause ischemia. Coronary artery fistulas can lead to complications like aneurysm formation