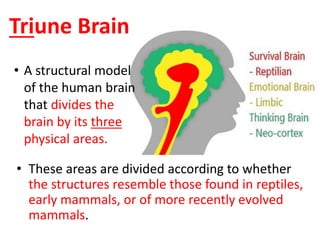
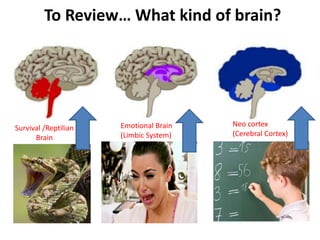
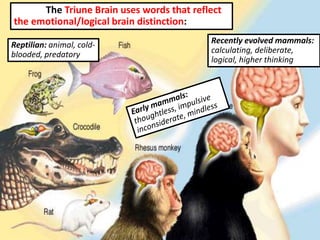
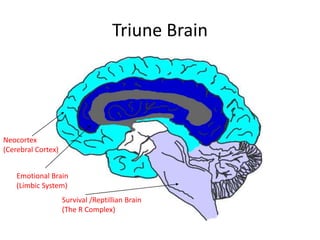
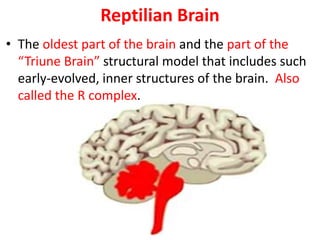
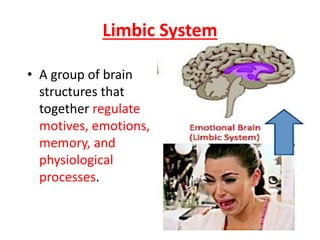
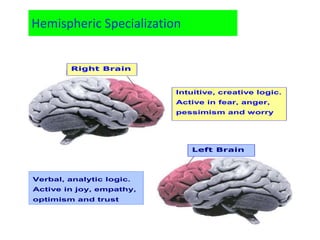
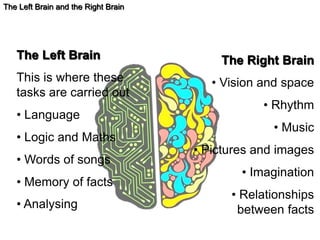
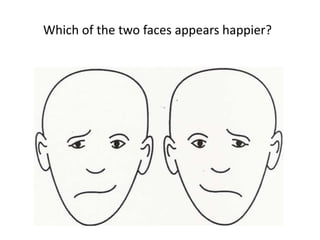
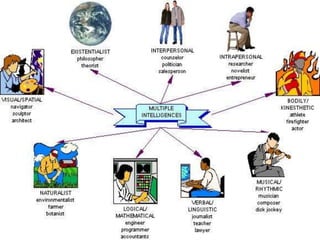
The document outlines an educational overview of the brain, including its structure, functions, and models such as the triune brain, which divides the brain into three areas: the neocortex, limbic system, and reptilian brain. It describes how these areas impact learning and emotional responses, emphasizing the management of threats and motivation in the learning process. Additionally, it introduces the concept of multiple intelligences, highlighting nine types that people possess.