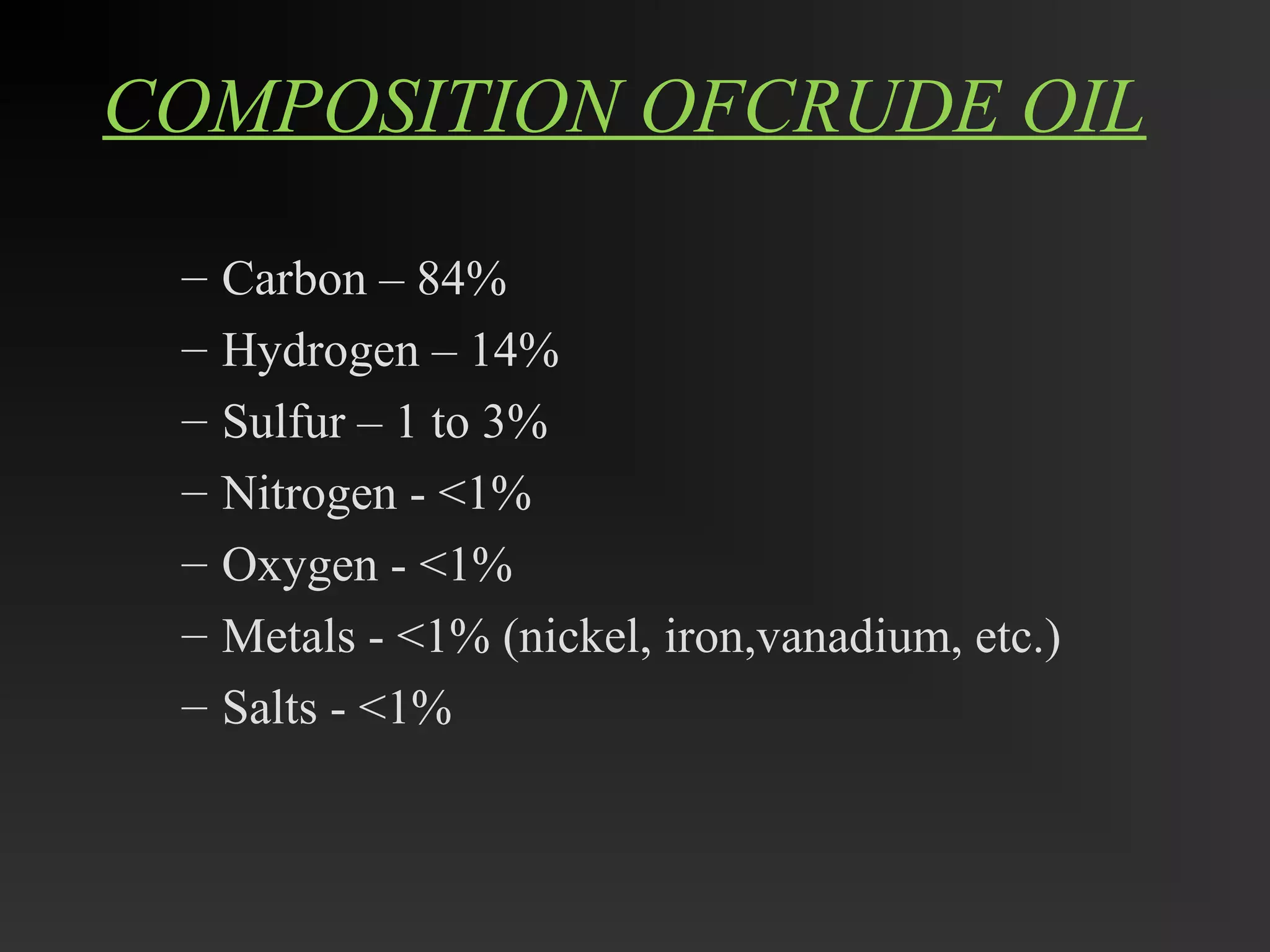
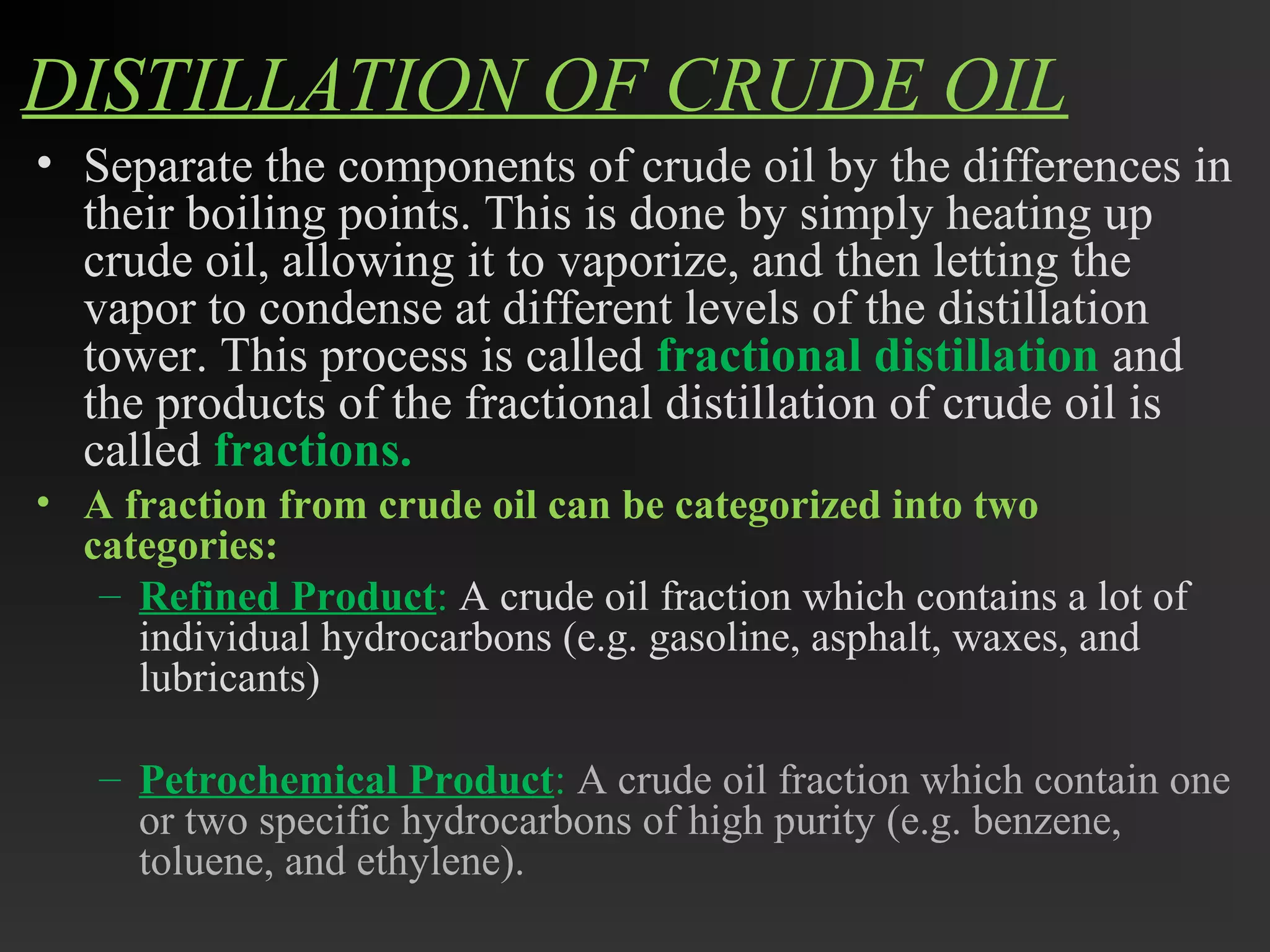
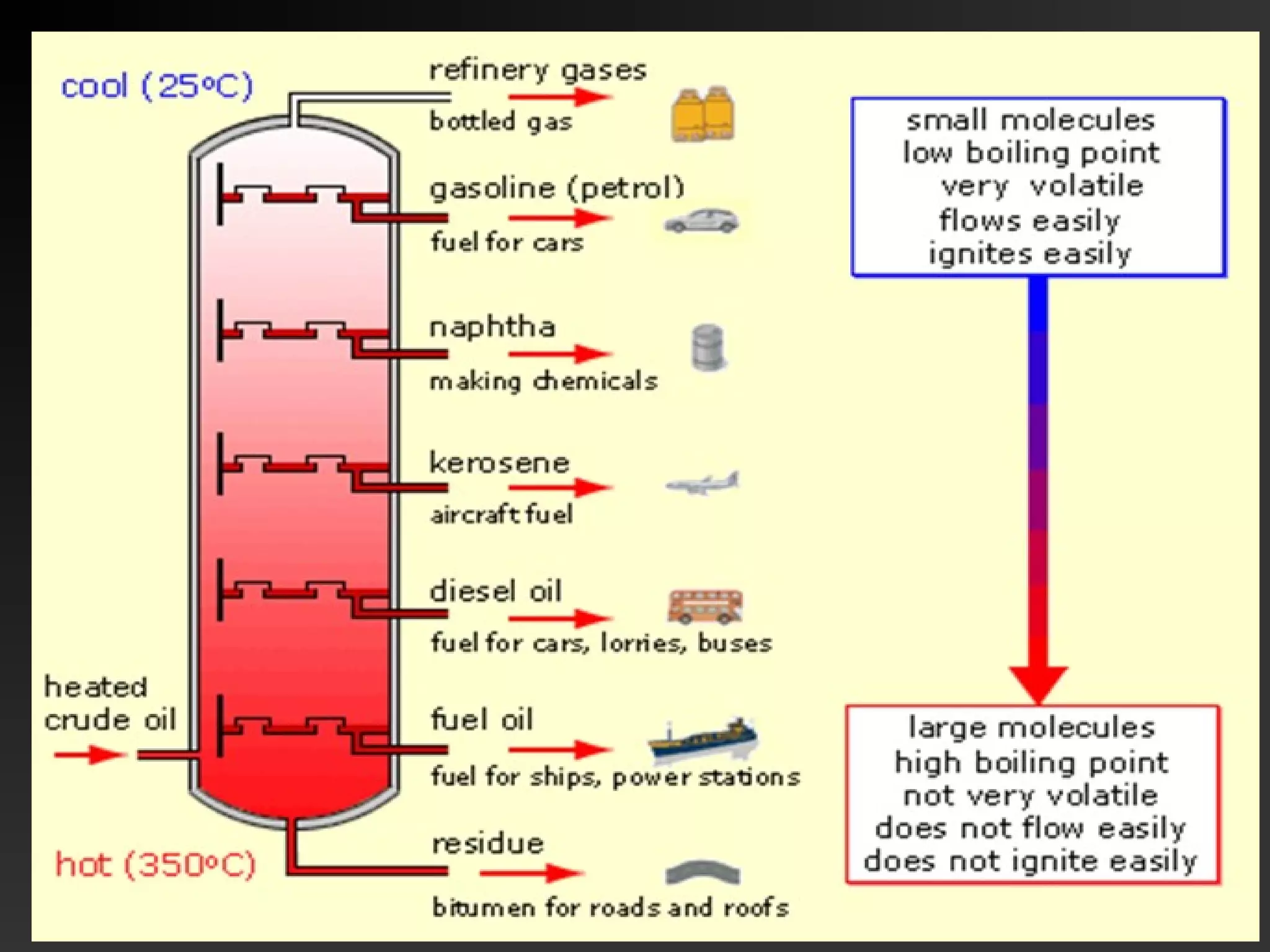
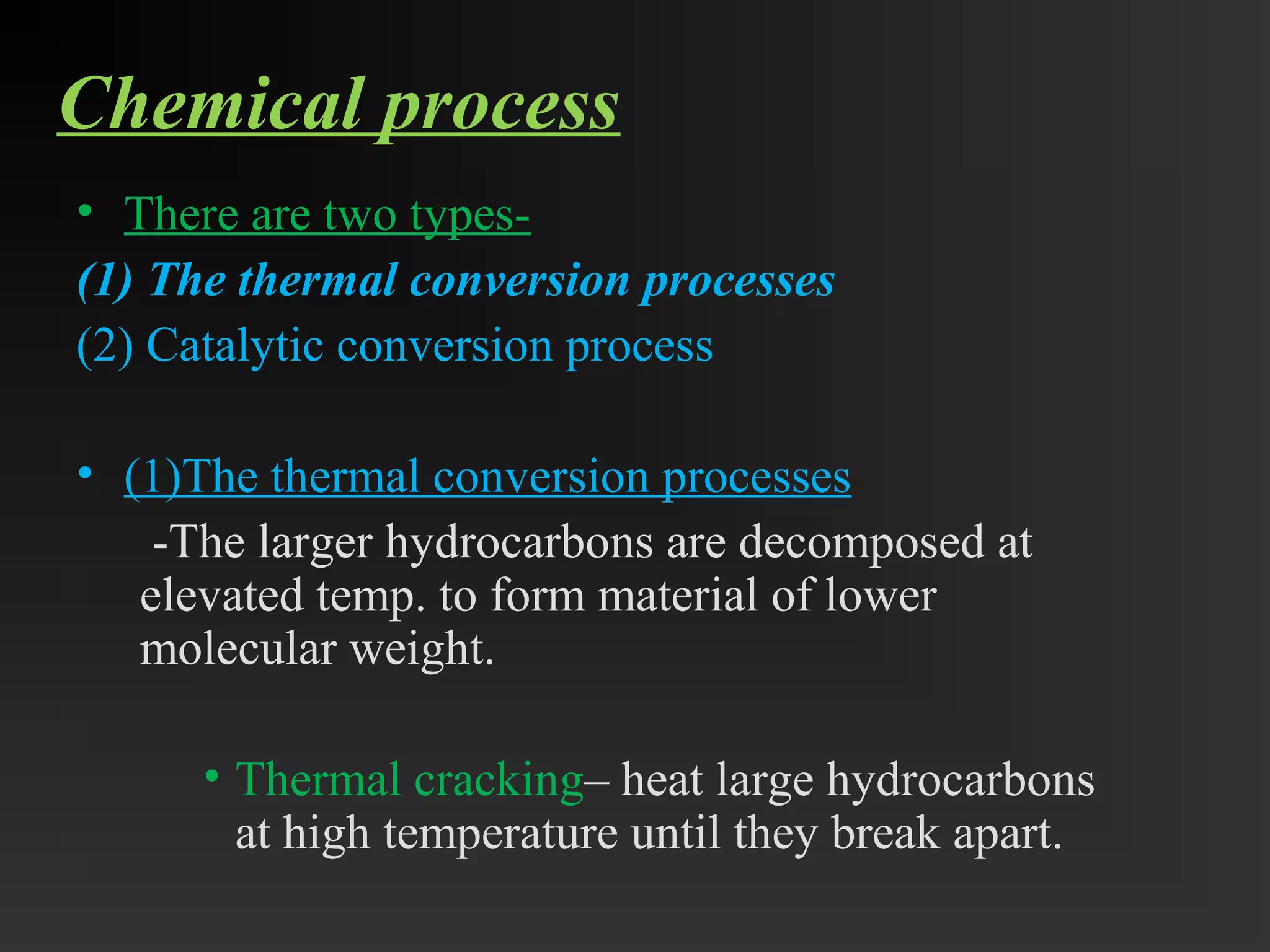
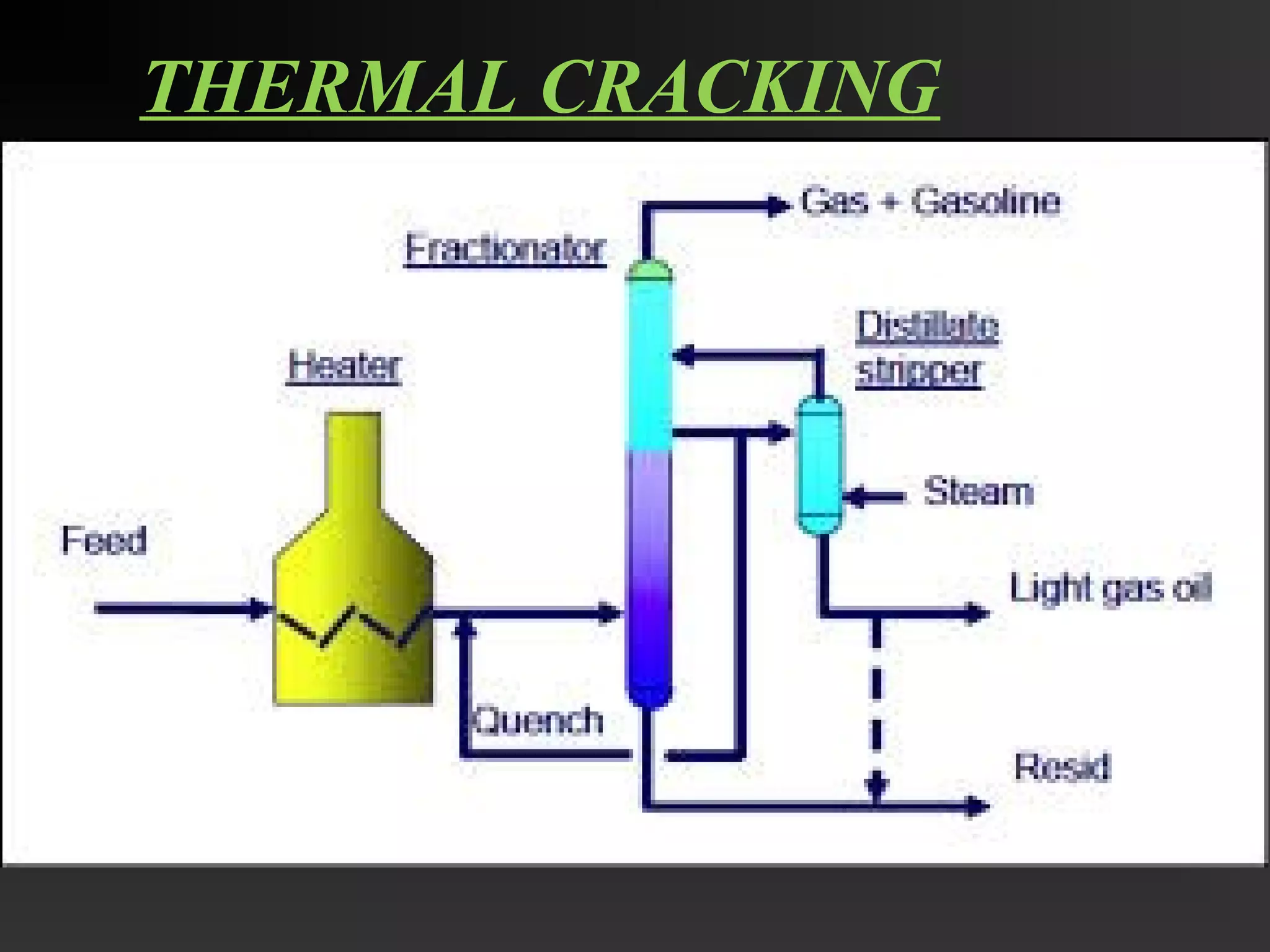
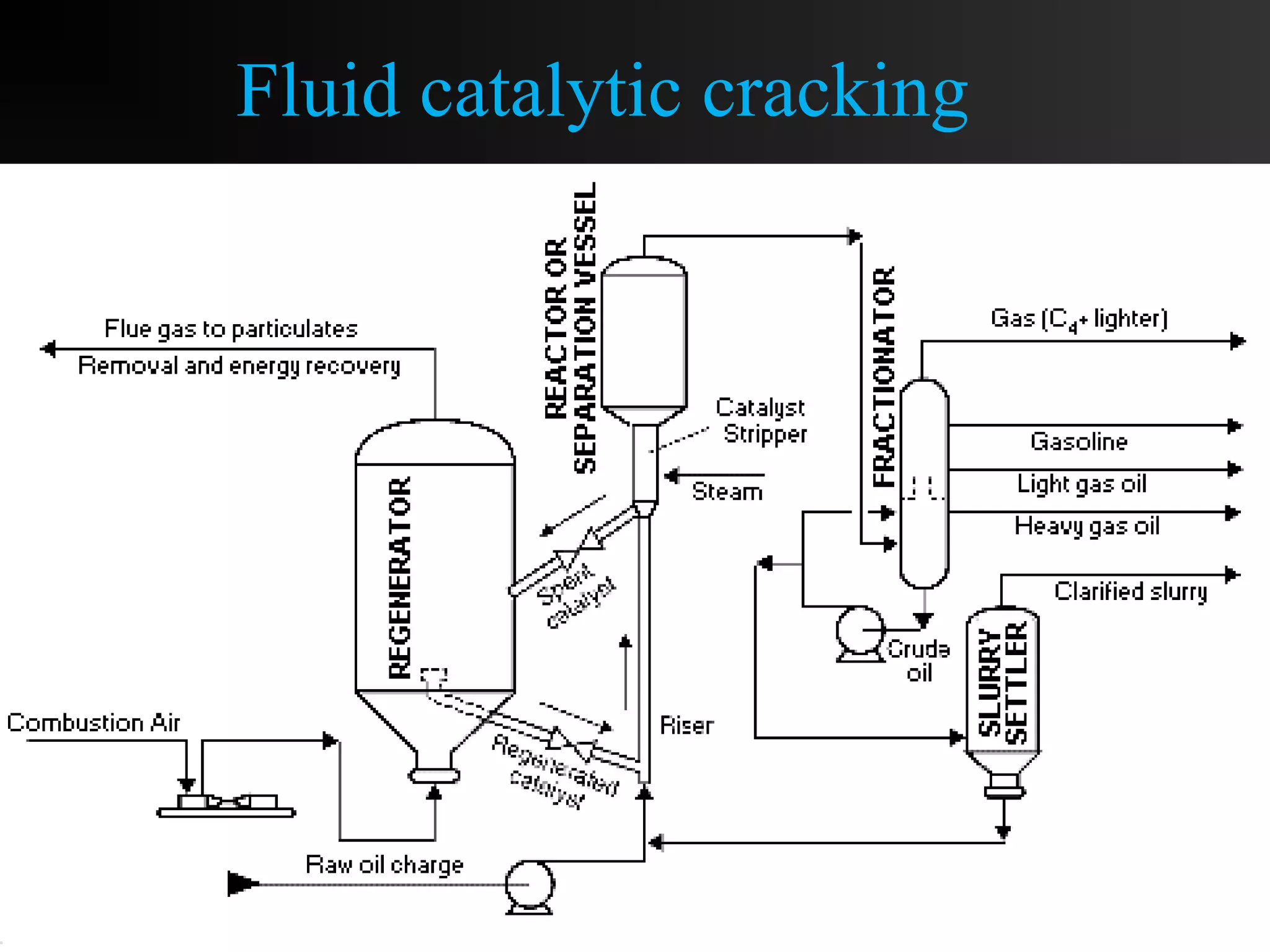
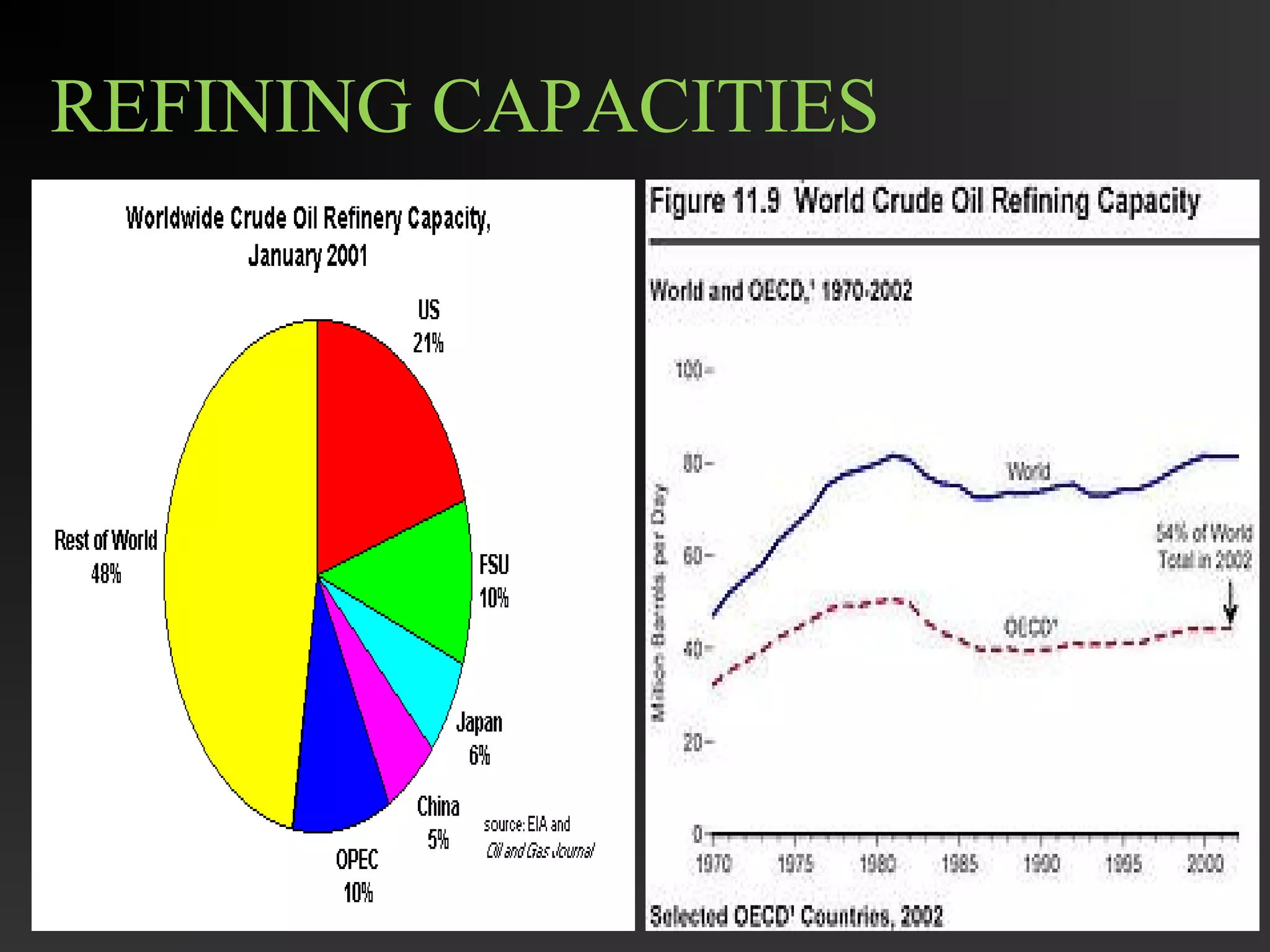
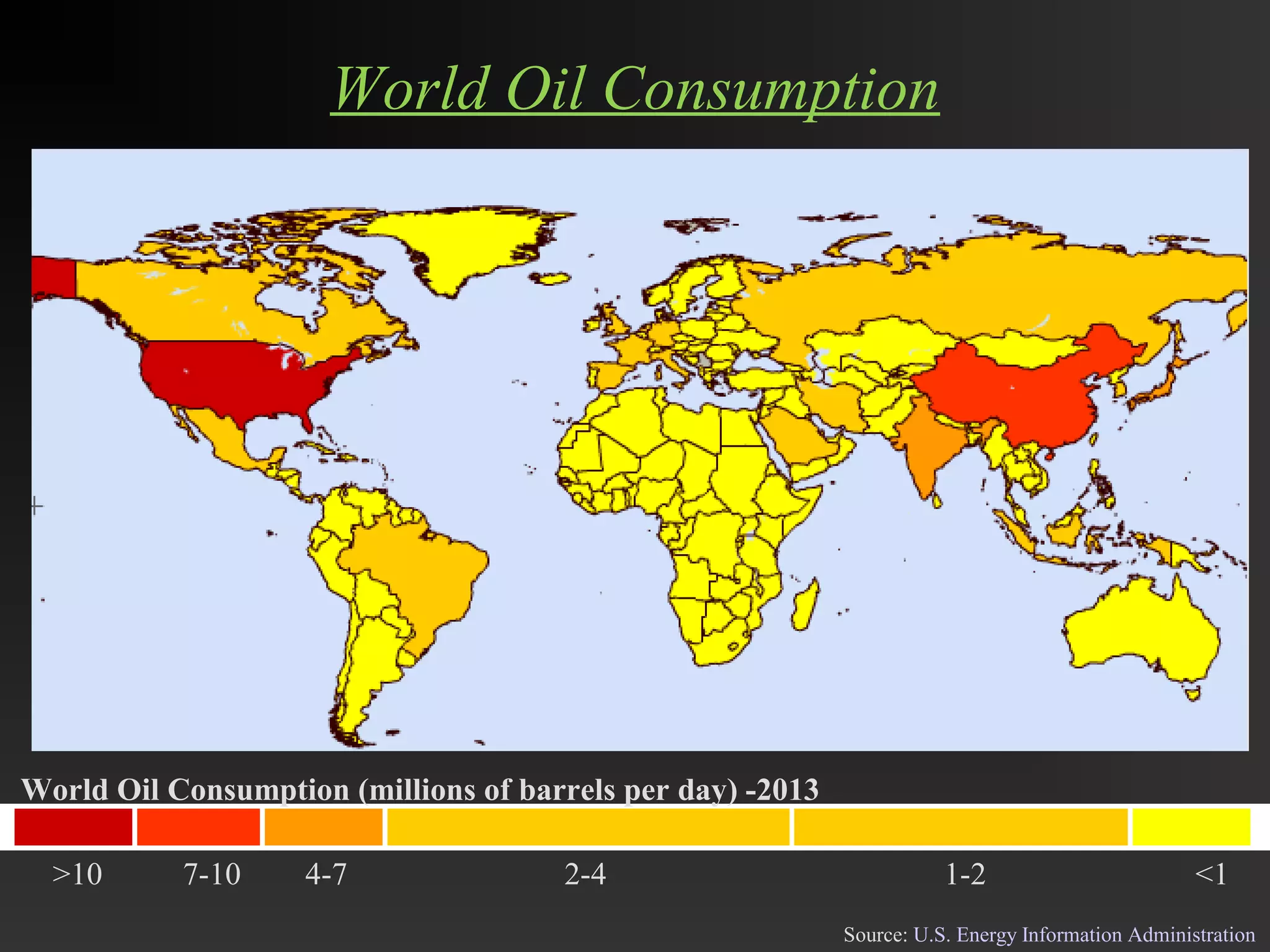
This document discusses the refining of crude oil. It begins by describing crude oil as a complex mixture of hydrocarbons found in the Earth's crust. The refining process separates crude oil into fractions using fractional distillation based on differences in boiling points. Major fractions include petroleum gas, naphtha, gasoline, kerosene, diesel, lubricating oil, and fuel oil. Further processing using thermal cracking and catalytic cracking converts heavier fractions into more valuable products like liquefied petroleum gas and gasoline. Refineries are upgraded in response to market demands and clean air regulations.