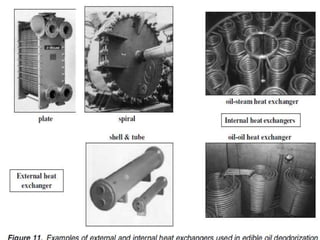
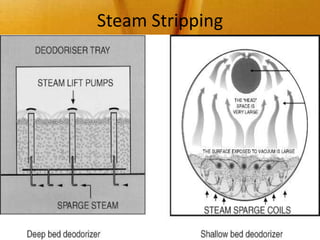
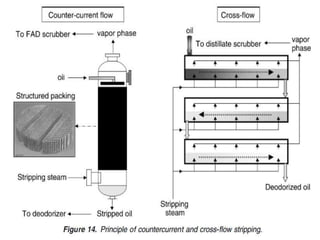
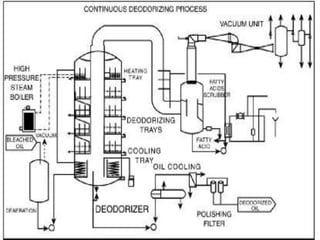
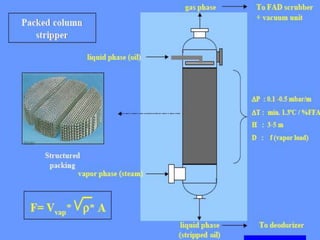
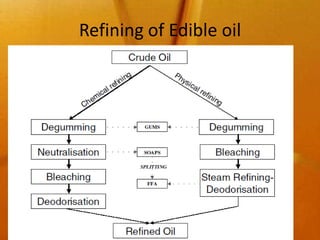
This document summarizes various deodorization techniques used in refining edible oils. It discusses the deodorization process, which involves de-aeration, heating the oil to high temperatures under reduced pressure, steam stripping of volatile compounds, and cooling. Different deodorizer systems are also summarized like batch, semi-continuous, and continuous deodorization systems. Newer technologies like dual temperature deodorization and dry ice condensation are also briefly described to improve efficiency.




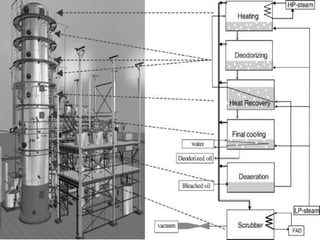


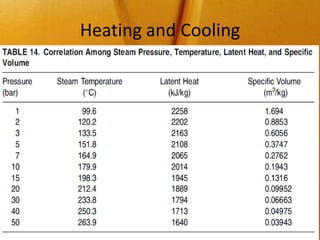
![Heating and Cooling
• Source of Heating in the final stages are
1) High-pressure steam boilers
2) Thermal Oil Heaters
3) Downtherm A (diphenyl/diphenyloxide)
• The net heating energy required for a
deodorization system can be calculated as:
H= [ O.c.(T2-T1).fL.fR ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deodorization-120325055814-phpapp01/85/Deodorization-9-320.jpg)