The document provides an overview of artificial intelligence and key developments in the field, including:
1. It discusses early definitions of intelligence and issues with defining AI, as well as tests like the Turing Test.
2. Early developments in AI focused on game playing to demonstrate problem solving abilities within limited domains.
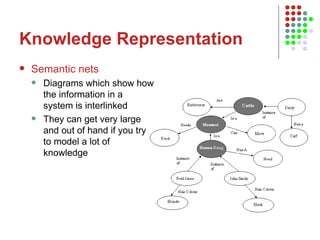
3. Research then shifted to language processing with programs like ELIZA, which could hold basic conversations, and knowledge representation using semantic nets and logic programming.