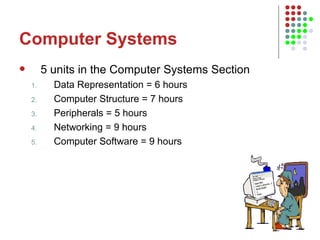
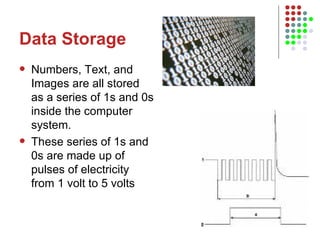
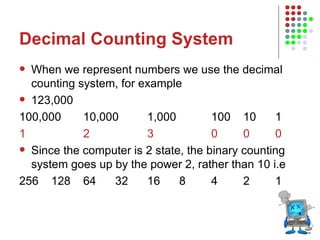
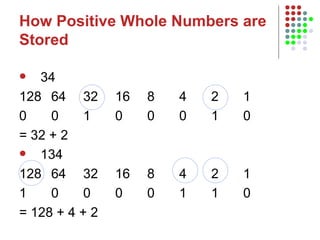
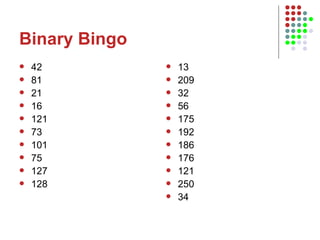
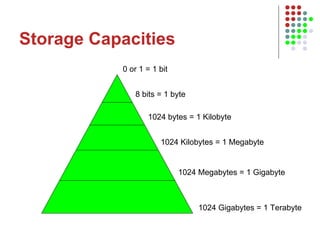
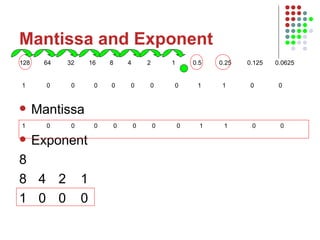
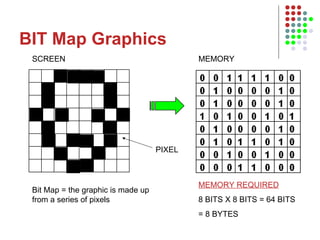
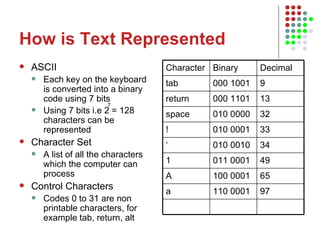
The document outlines the course content for an Intro to Computing course, which is divided into three main units on computer systems, software development, and artificial intelligence. The computer systems unit covers topics such as data representation, computer structure, networking, and representing graphics. Sample lesson plans describe how numbers, text, and images are stored in binary and how floating point numbers are represented using mantissa and exponent.