The document summarizes key developments in artificial intelligence, including:
1. It describes human intelligence and the Turing test for testing machine intelligence.
2. It explains early developments in AI focused on game playing and language processing with programs like ELIZA.
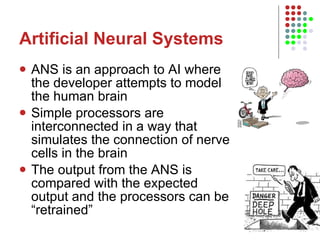
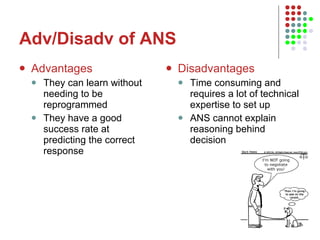
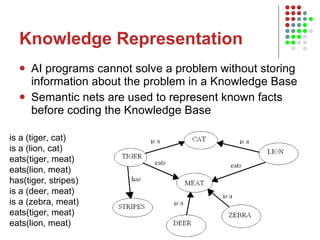
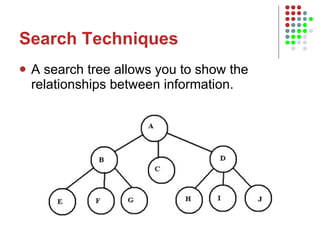
3. It discusses expert systems, neural networks, vision systems, speech recognition, and knowledge representation using semantic nets.
4. It also mentions developments in hardware that supported AI and applications of intelligent robots.