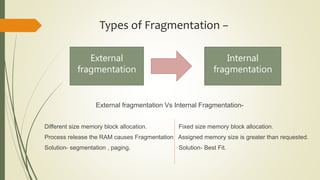
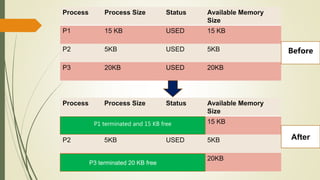
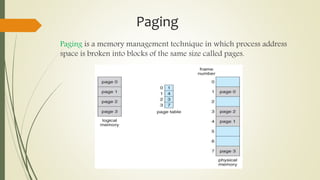
The document discusses fragmentation in operating systems. It defines fragmentation as when free memory becomes broken into small pieces that are not large enough to allocate to processes. There are two types of fragmentation: external fragmentation, which occurs when memory is released and the free space is broken into small pieces; and internal fragmentation, which occurs when allocated memory is larger than the requested size. Solutions to fragmentation include segmentation, paging, and memory allocation strategies like first fit, best fit, and worst fit.