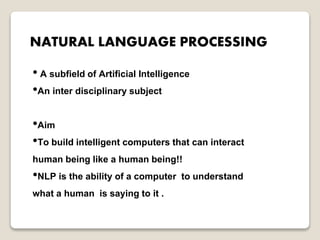
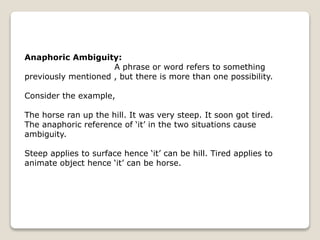
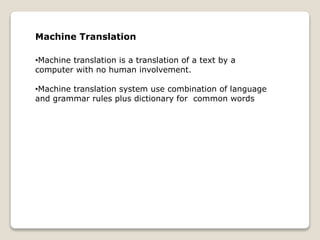
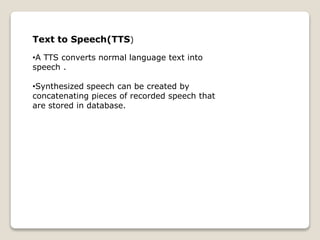
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of artificial intelligence that aims to allow computers to understand human language. NLP involves analyzing and representing text or speech at different linguistic levels for applications like question answering or machine translation. Challenges for NLP include ambiguities in language like lexical, syntactic, semantic, and anaphoric ambiguities. Common NLP tasks include part-of-speech tagging, parsing, named entity recognition, and sentiment analysis. Applications of NLP include text processing, machine translation, speech processing, and converting text to speech.