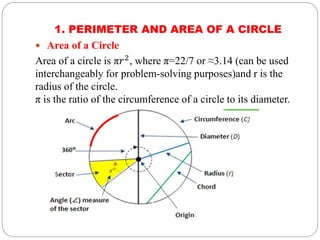
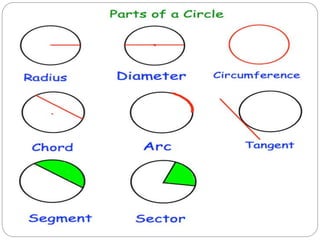
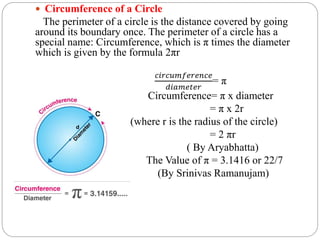
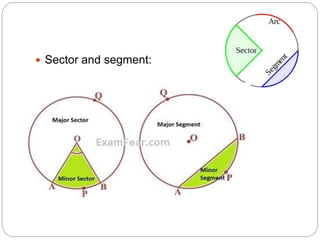
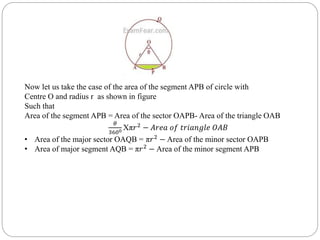
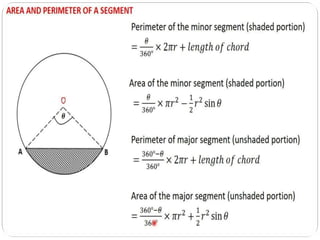
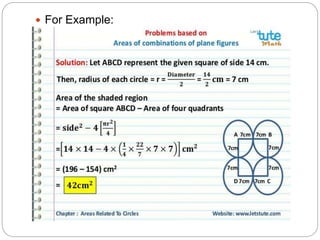
This document summarizes key concepts related to circles for a 10th grade class. It covers the perimeter and area of circles, finding the area of sectors and segments of circles, and calculating the areas of combinations of plane figures. The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference, which is 2πr. The area of a circle is πr^2. To find the area of a sector, use the formula (θ/360)×πr^2, where θ is the central angle of the sector in degrees and r is the radius. The area of combinations of shapes can be found by subtracting the area of one figure from another or adding/subtracting different areas.