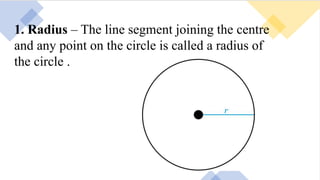
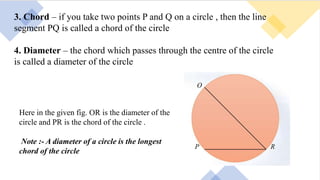
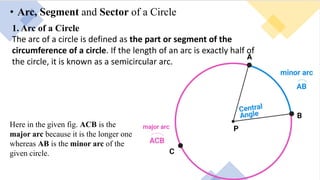
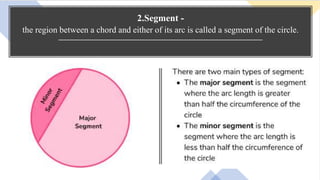
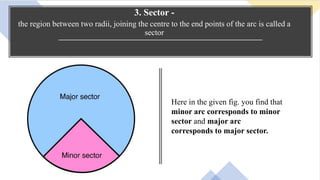
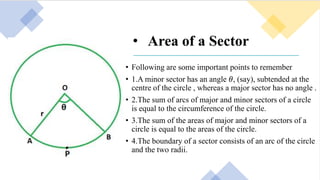
1. The document discusses various terms related to circles such as radius, diameter, chord, arc, segment, and sector. It defines each term and provides examples.
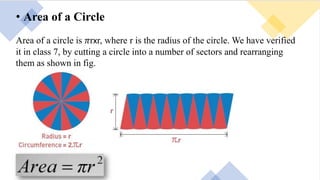
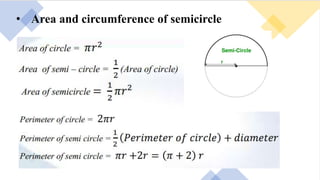
2. Formulas for calculating the circumference and area of a circle are presented. Circumference is defined as 2πr and area is defined as πr^2.
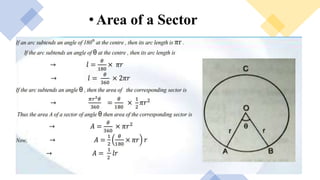
3. Methods for calculating the area of a sector and segment of a circle are described. The area of a sector is calculated based on the central angle and area of the whole circle. The area of a segment is not explicitly defined.