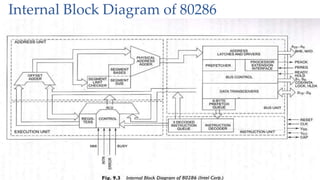
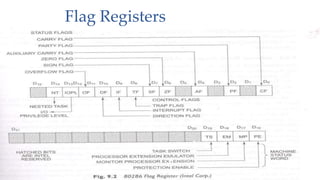
The document discusses the Intel 80286 microprocessor. It introduces the 80286 as a 16-bit microprocessor introduced in 1982 with separate address and data buses. It had approximately 134,000 transistors and clock speeds up to 12.5 MHz. The 80286 supported both real and protected virtual addressing modes, advanced memory management, and was compatible with the 8086 instruction set. It had features like 4-level memory protection and could address up to 16MB of physical memory or 1GB of virtual memory.