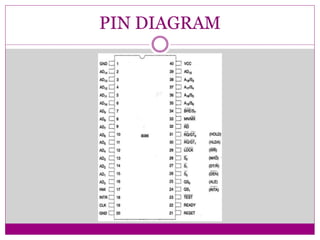
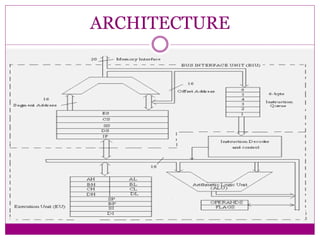
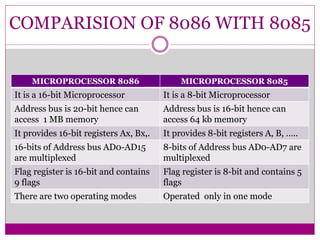
The document summarizes key features and specifications of the Intel 8086 microprocessor. It introduced 16-bit data transfer and reverse compatibility. The 8086 set the stage for the modern computer architecture still used today. It describes the pin diagram, architecture including addressing modes, and compares the 8086 to the earlier 8085 microprocessor, noting the 8086 had 16-bit registers and bus, could access more memory, and had an expanded 16-bit flag register.