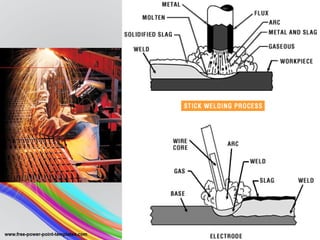
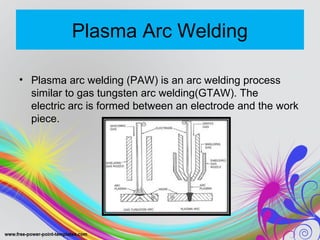
The document discusses arc welding, including:
- Arc welding is commonly used to join metal pieces by creating an electric arc that melts and fuses the metals together. It involves an electrode, electric arc, and sometimes filler material.
- There are several types of arc welding processes including shielded metal arc welding, gas metal arc welding, gas tungsten arc welding, and others.
- Arc welding has advantages like efficiency and flexibility but also limitations like safety hazards, high labor costs, and difficulty detecting defects. Proper safety equipment and techniques are important when arc welding.