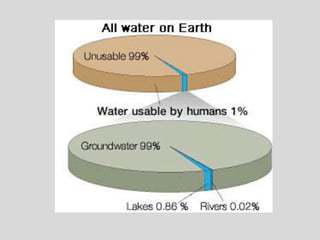
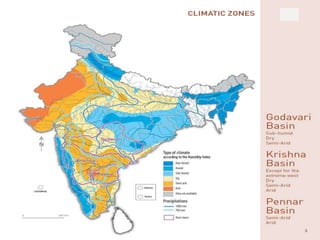
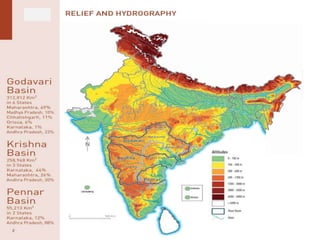
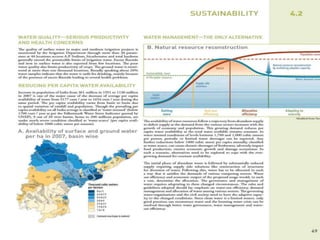
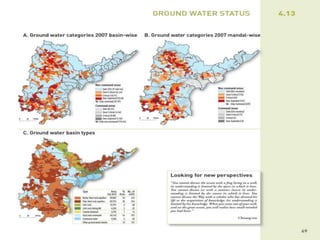
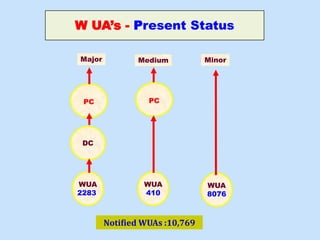
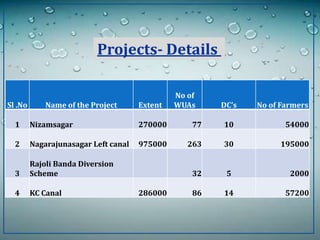
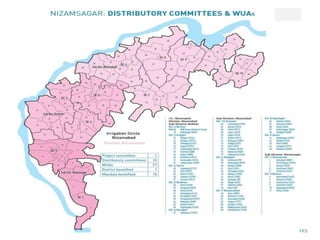
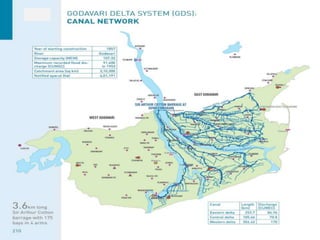
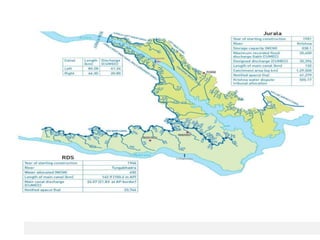
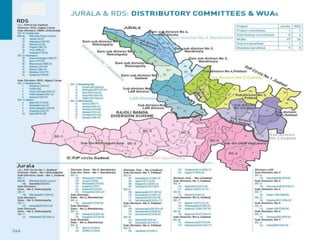
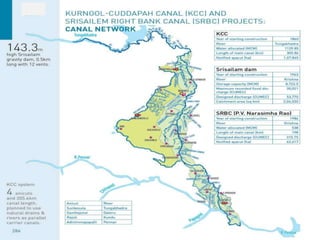
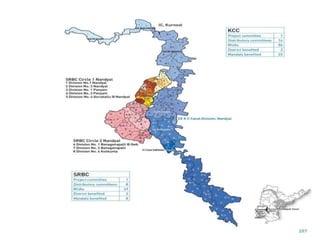
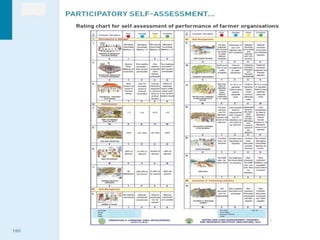
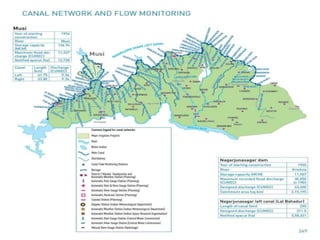
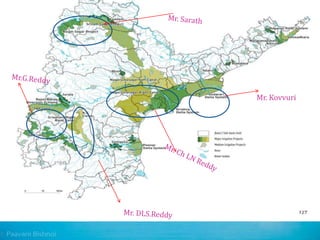
The document discusses water challenges and management in Andhra Pradesh, India. It notes that India is already water stressed and will become more so by 2020. Andhra Pradesh receives average annual rainfall of 500-1100mm but faces issues like depleting groundwater, overexploitation of resources, and a growing population. Various government initiatives aim to improve irrigation infrastructure, promote crop diversification, water conservation, and establish water user associations. Recommendations include expanding micro-irrigation, low-input sustainable agriculture, improved crop insurance and water harvesting, and facilitating contract farming and market access for farmers.