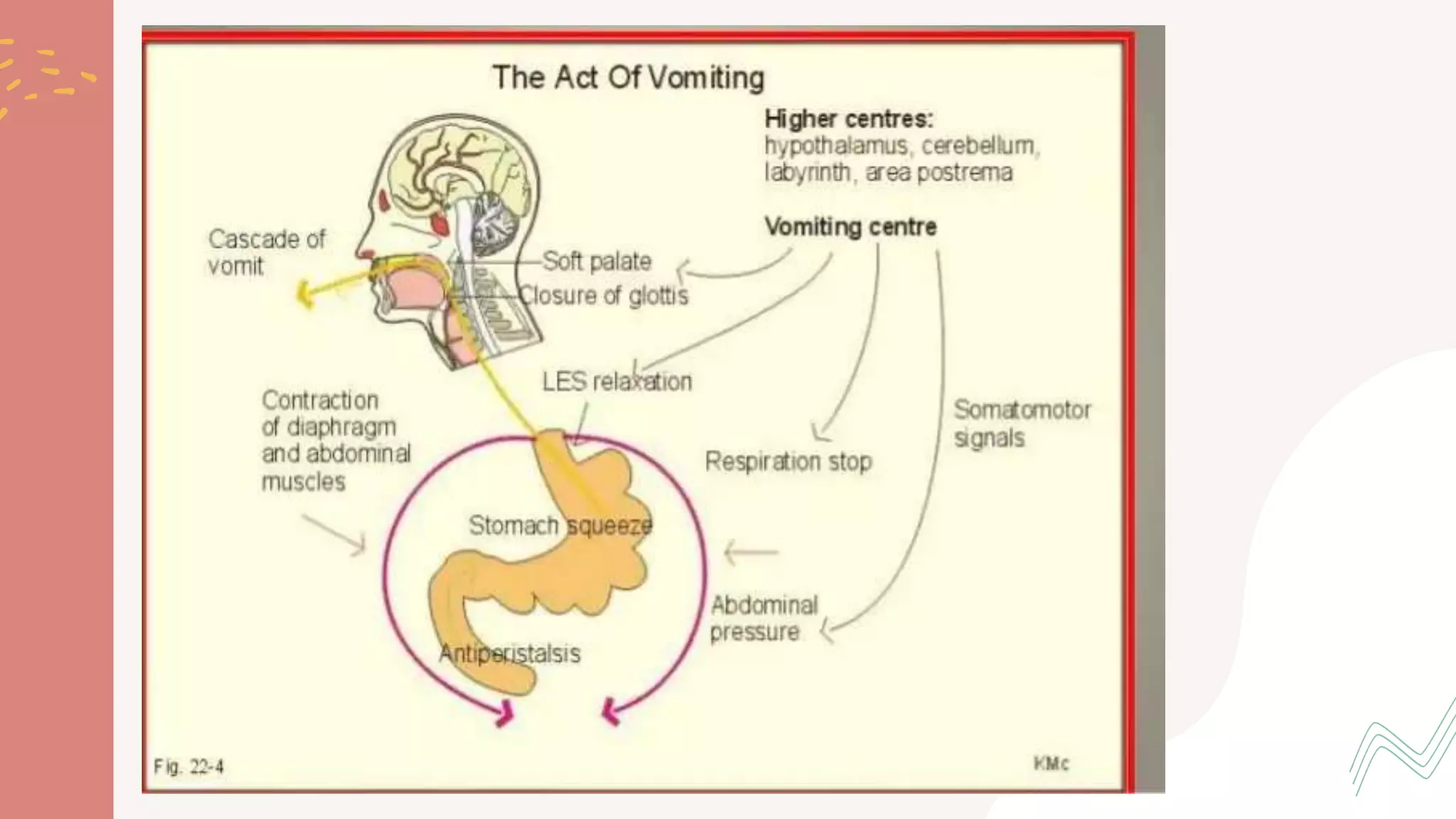
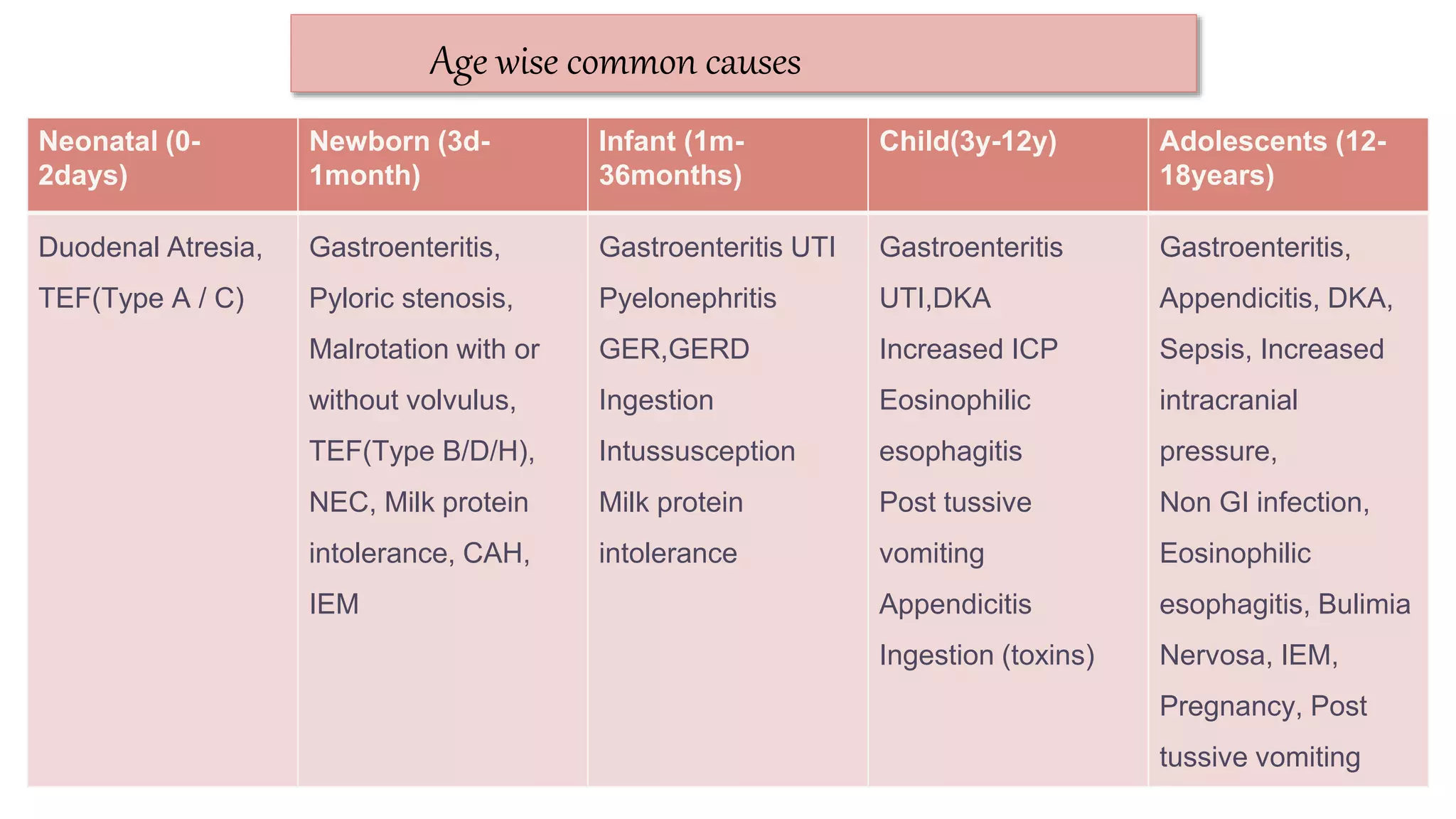
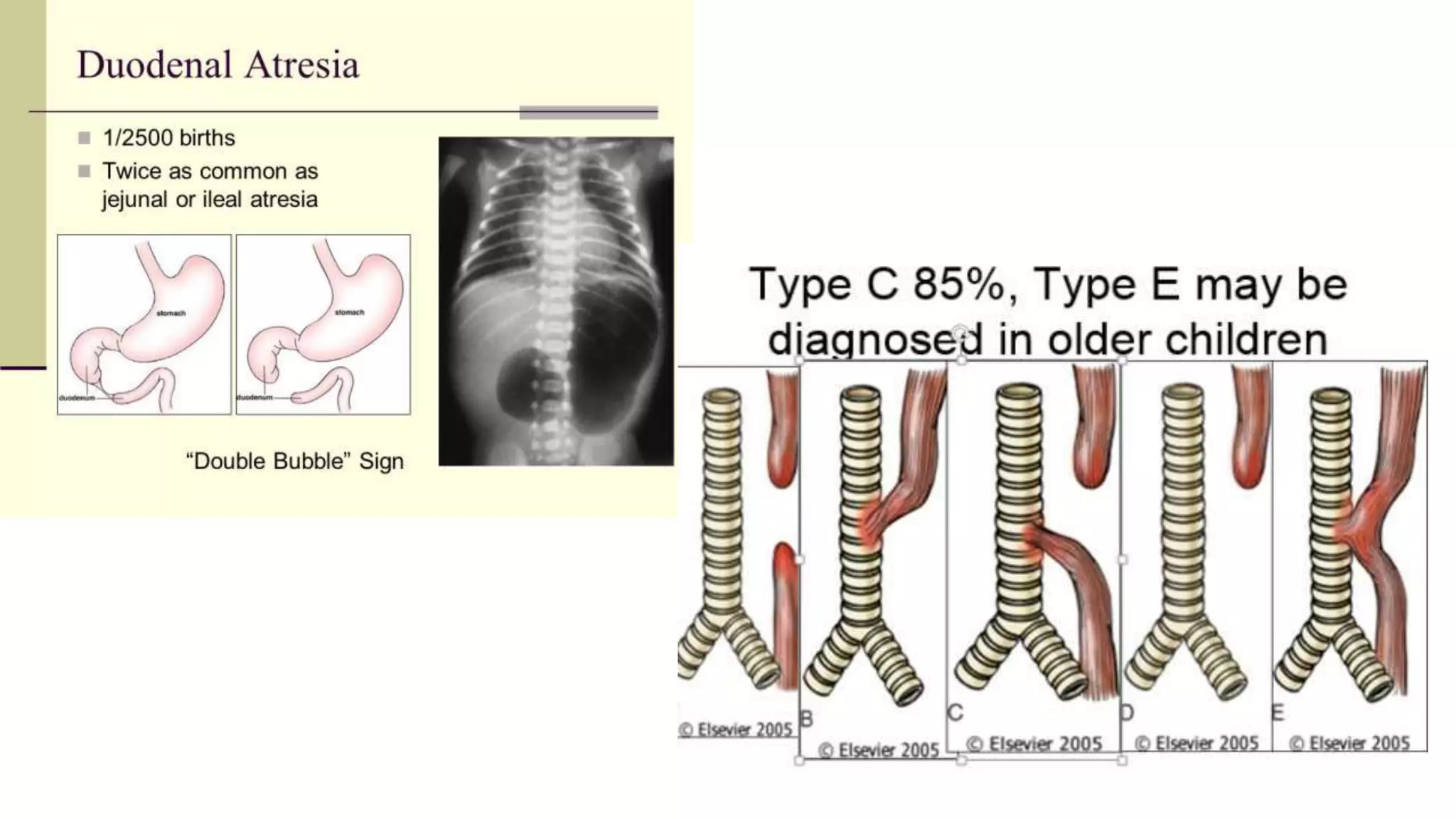
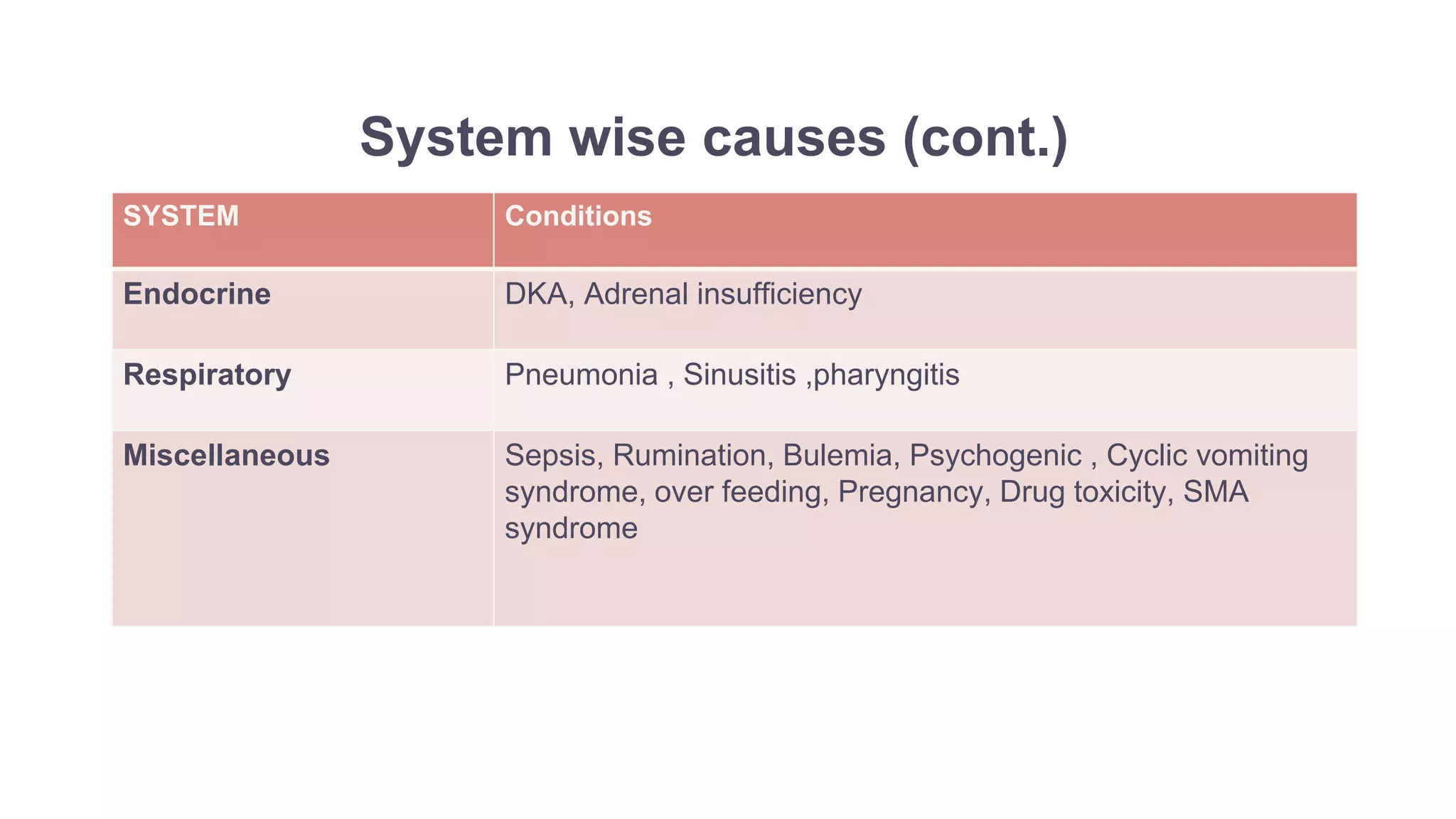
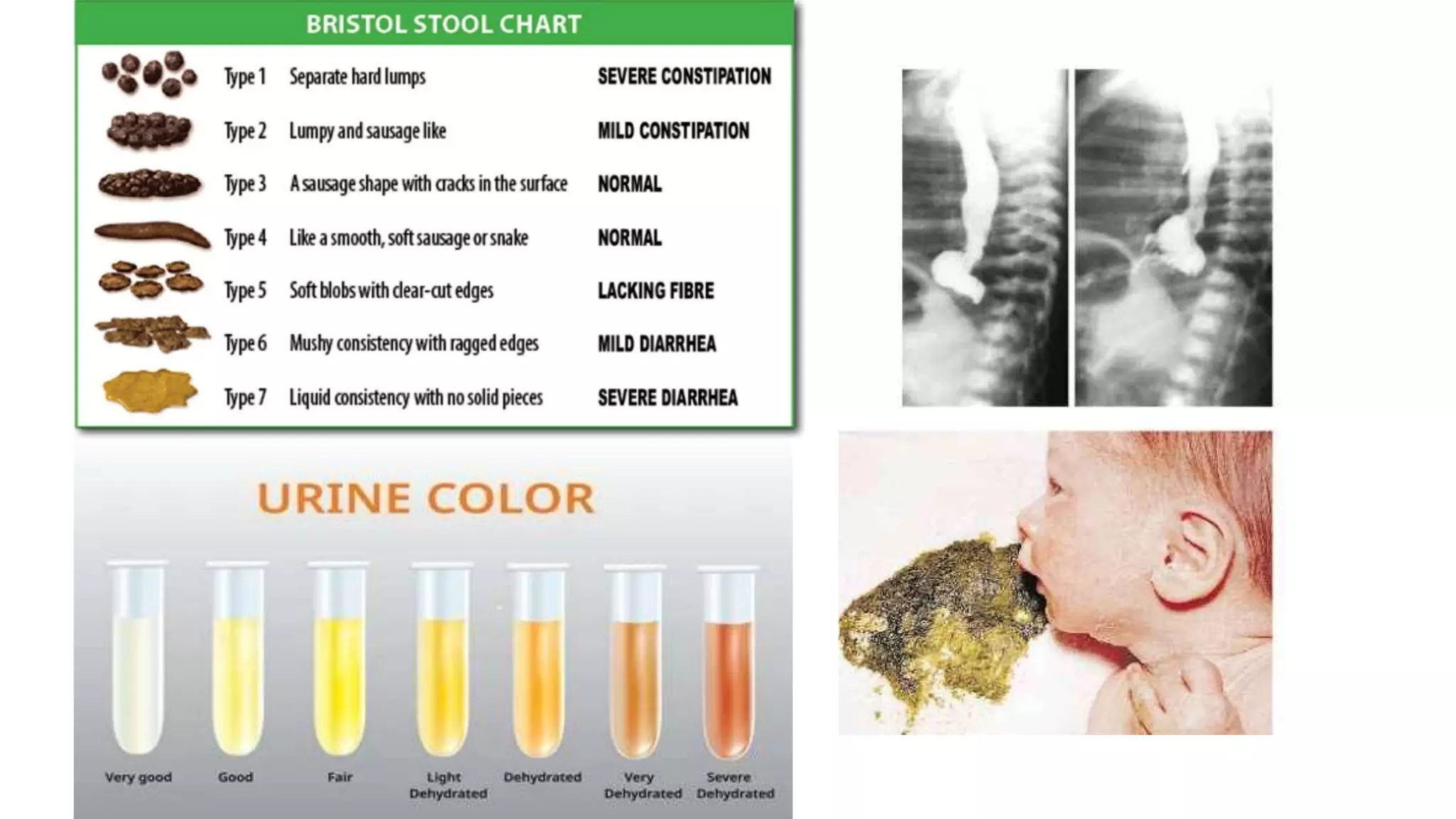
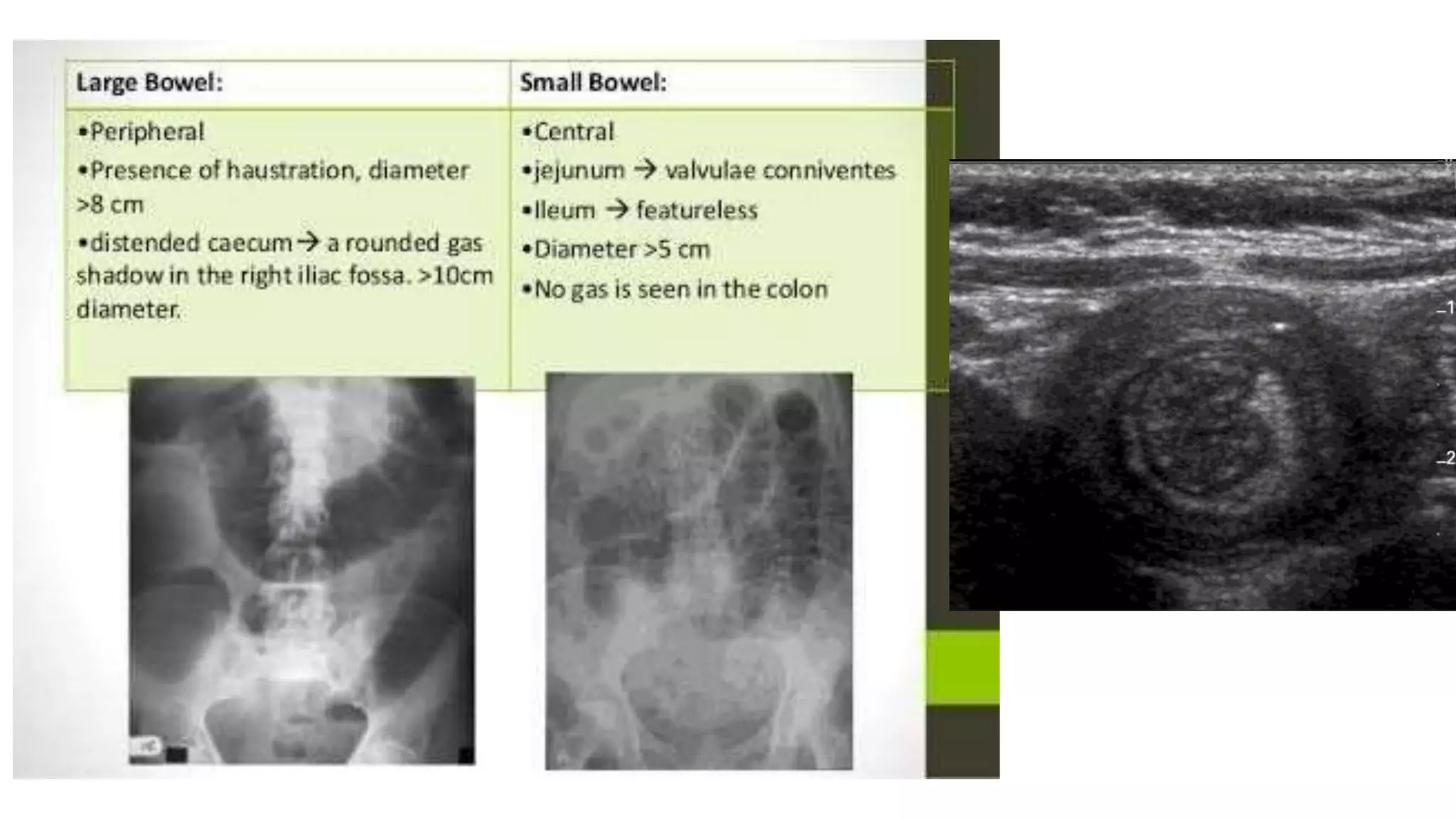
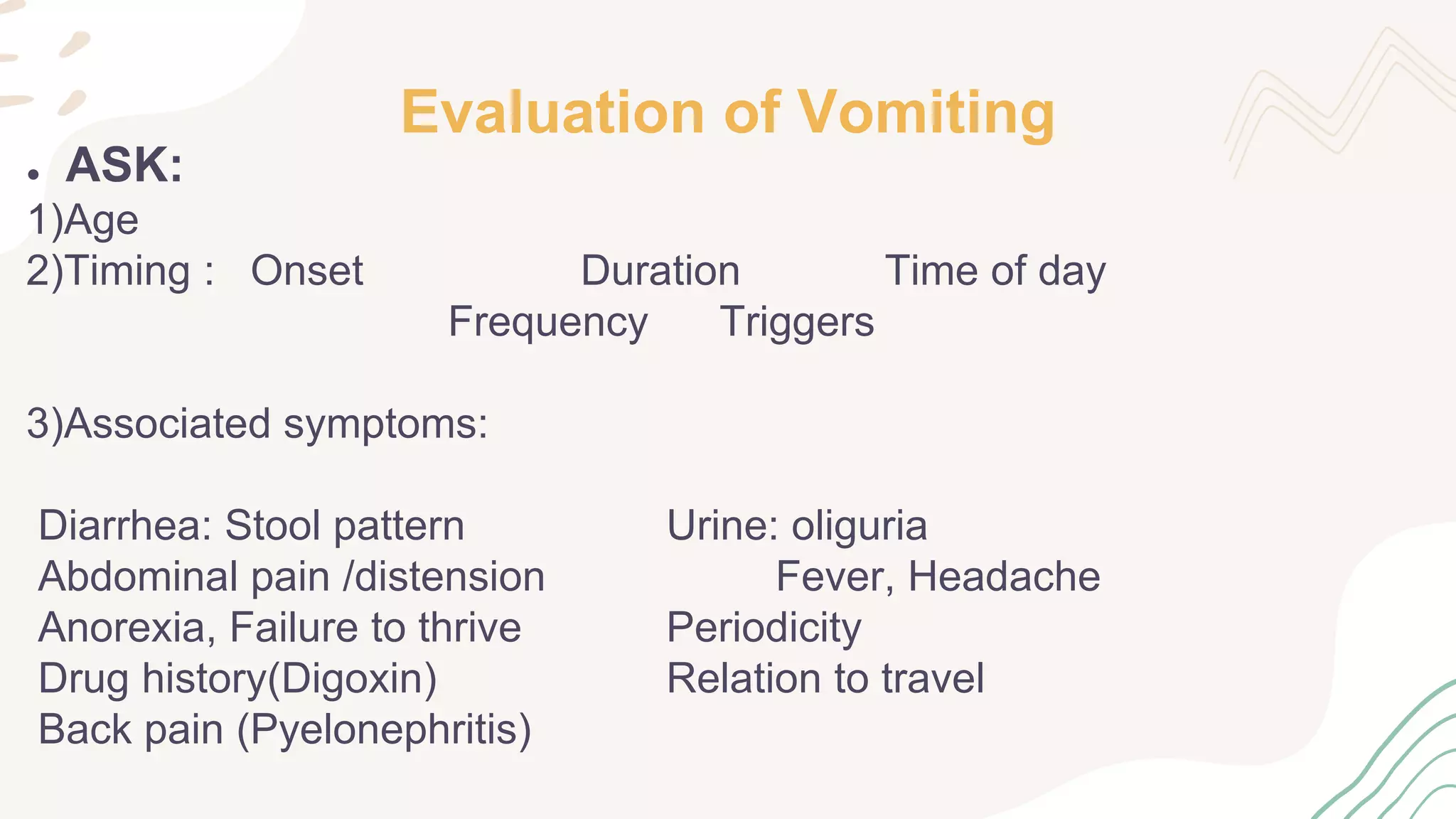
The document provides information on the approach to evaluating and managing vomiting in children. It begins with definitions of different types of vomiting. The physiology of vomiting is described, involving vagal pathways and neurotransmitters. Clinical clues are outlined to help determine potential causes. A systematic approach is proposed, distinguishing between recent onset acute vomiting and long-standing vomiting. Red flags are identified. Differential diagnoses are categorized by system. Key aspects of history, examination, and initial laboratory and radiological evaluations are summarized.