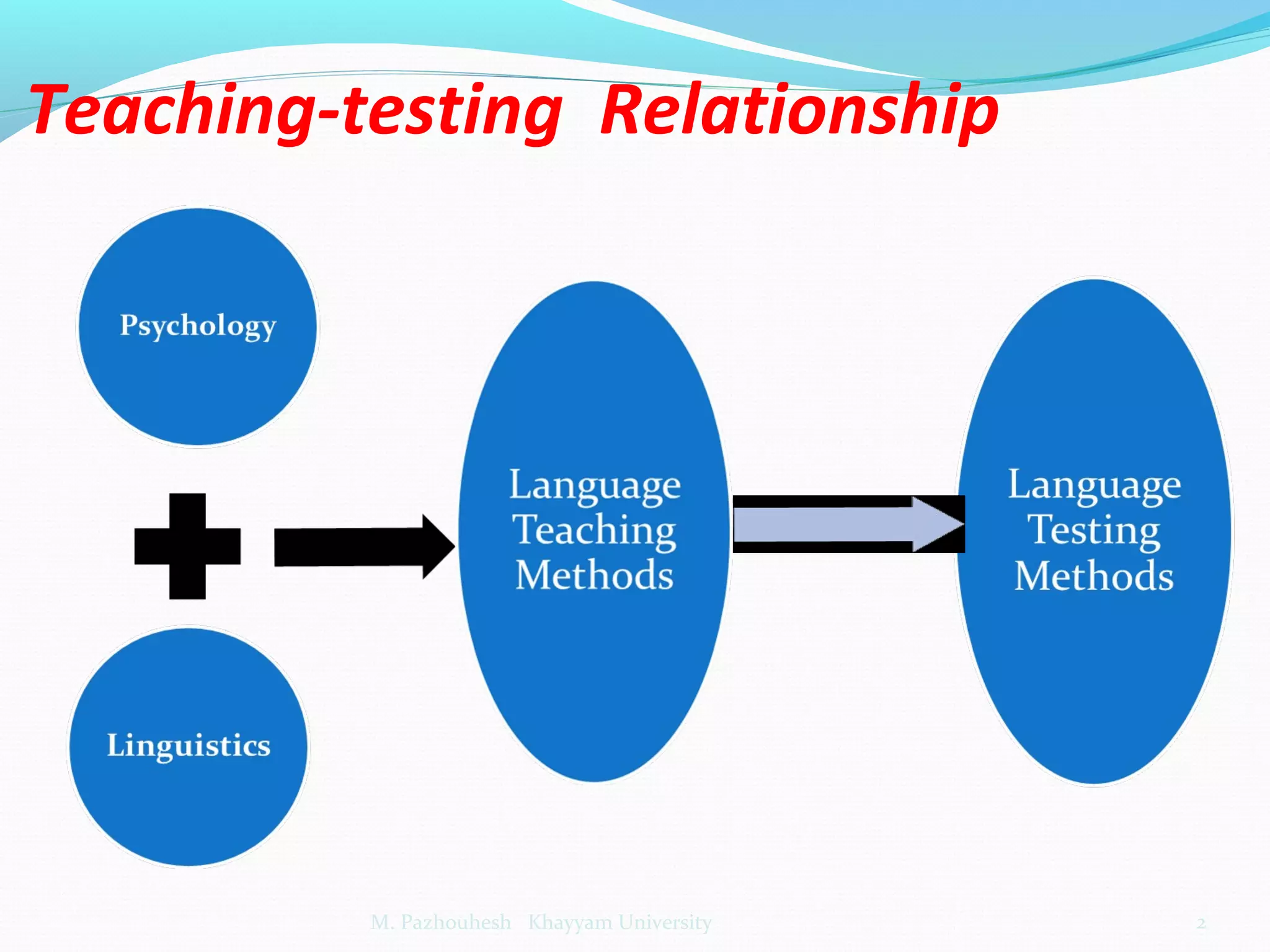
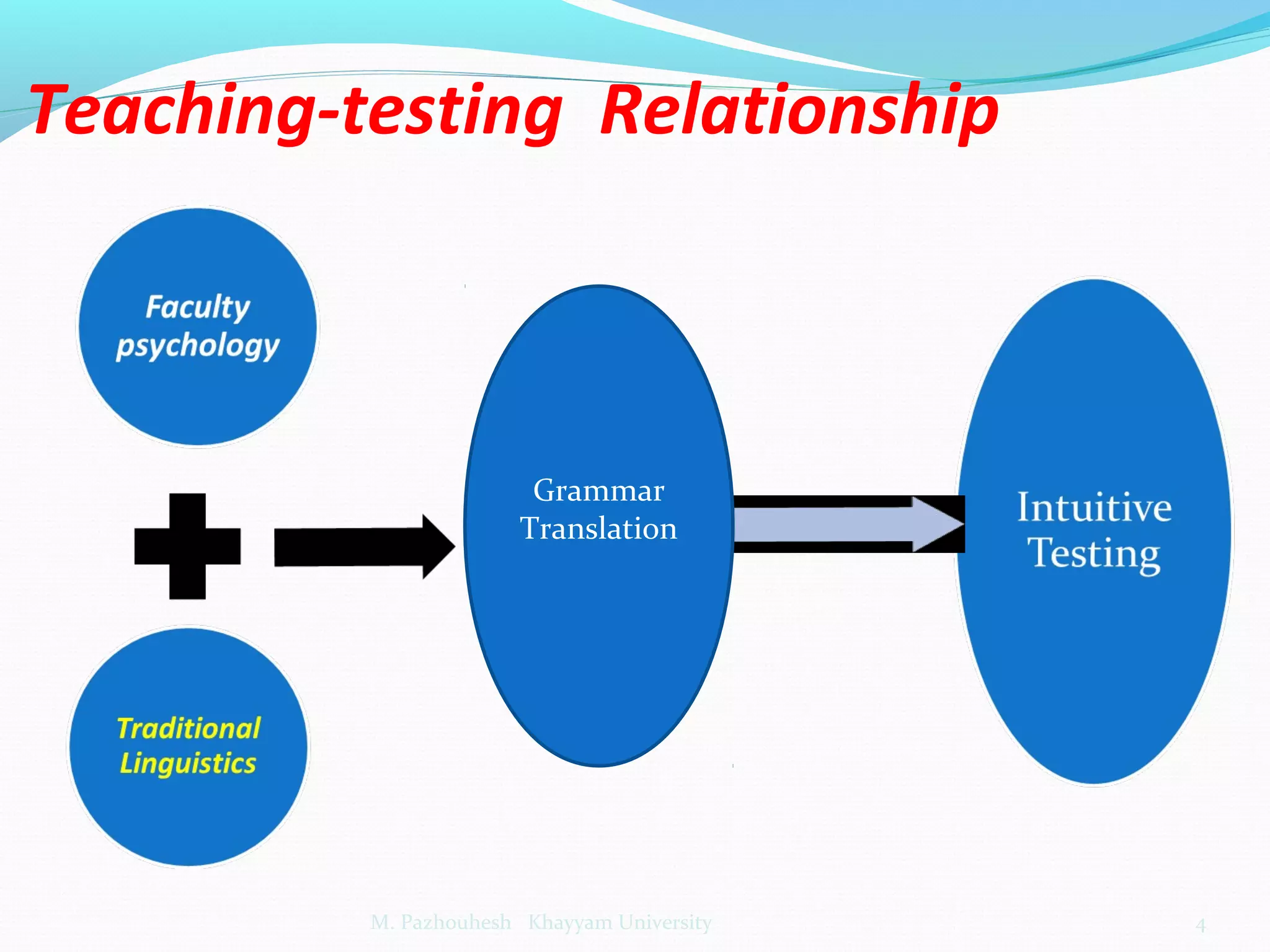
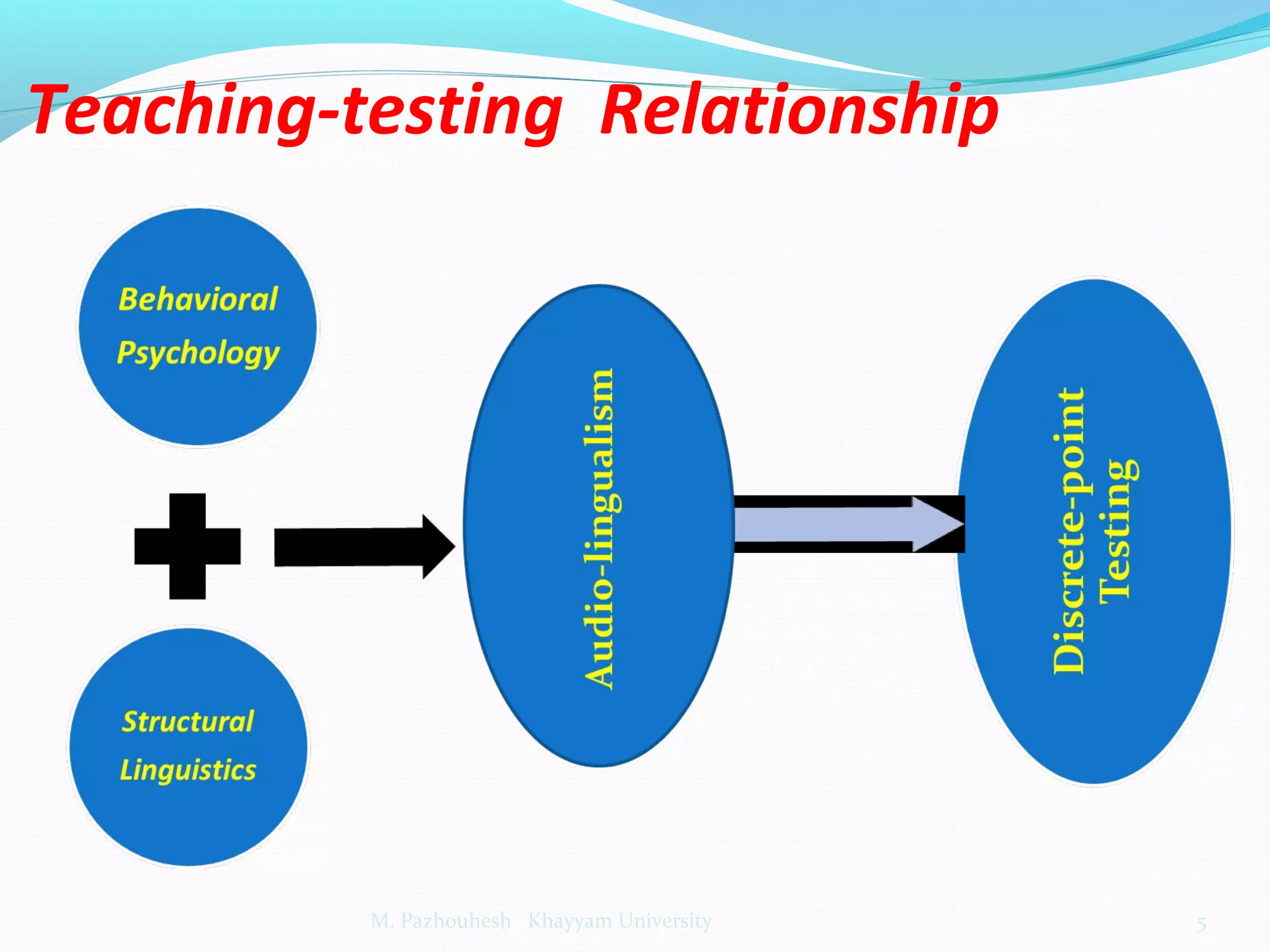
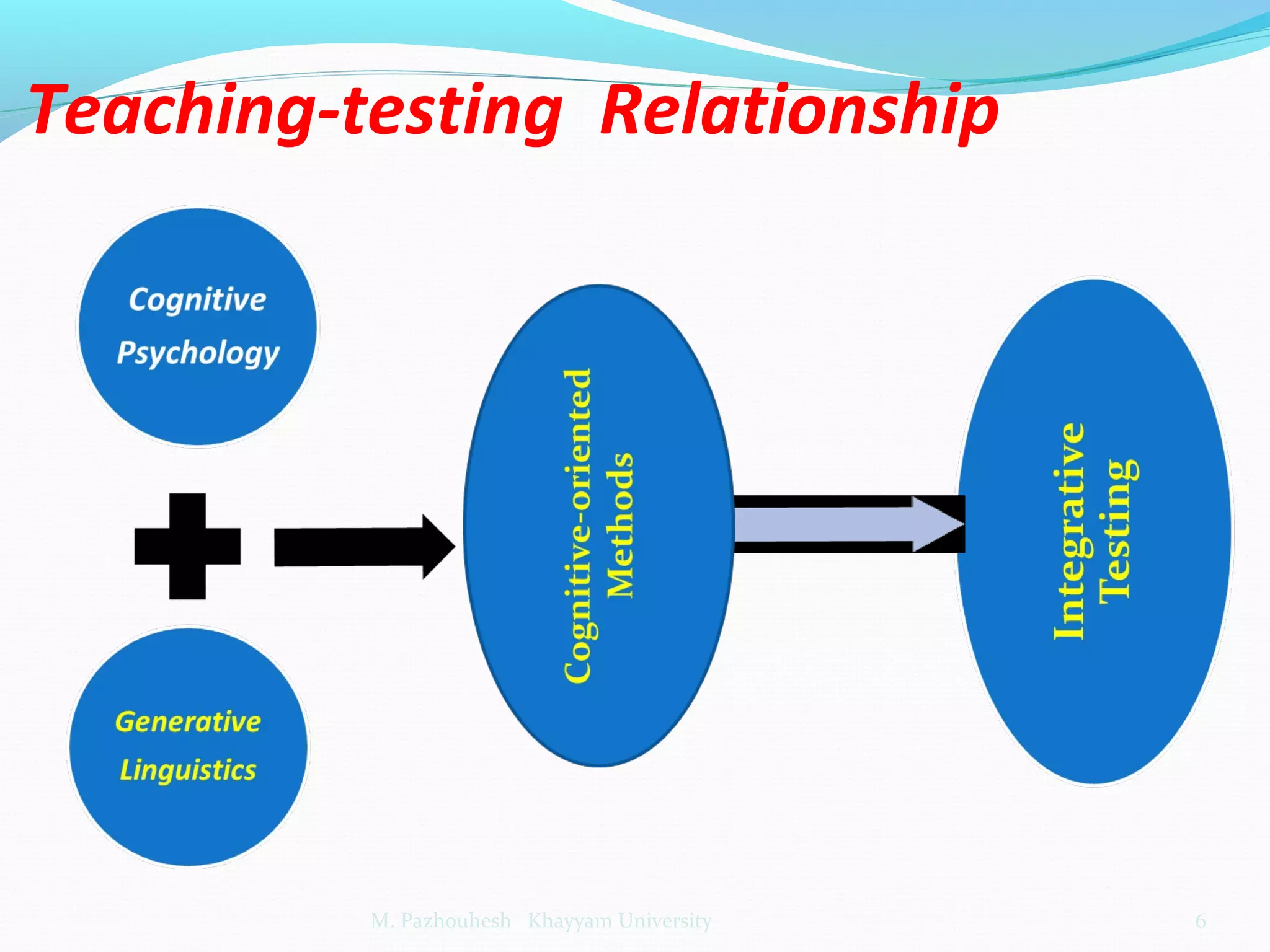
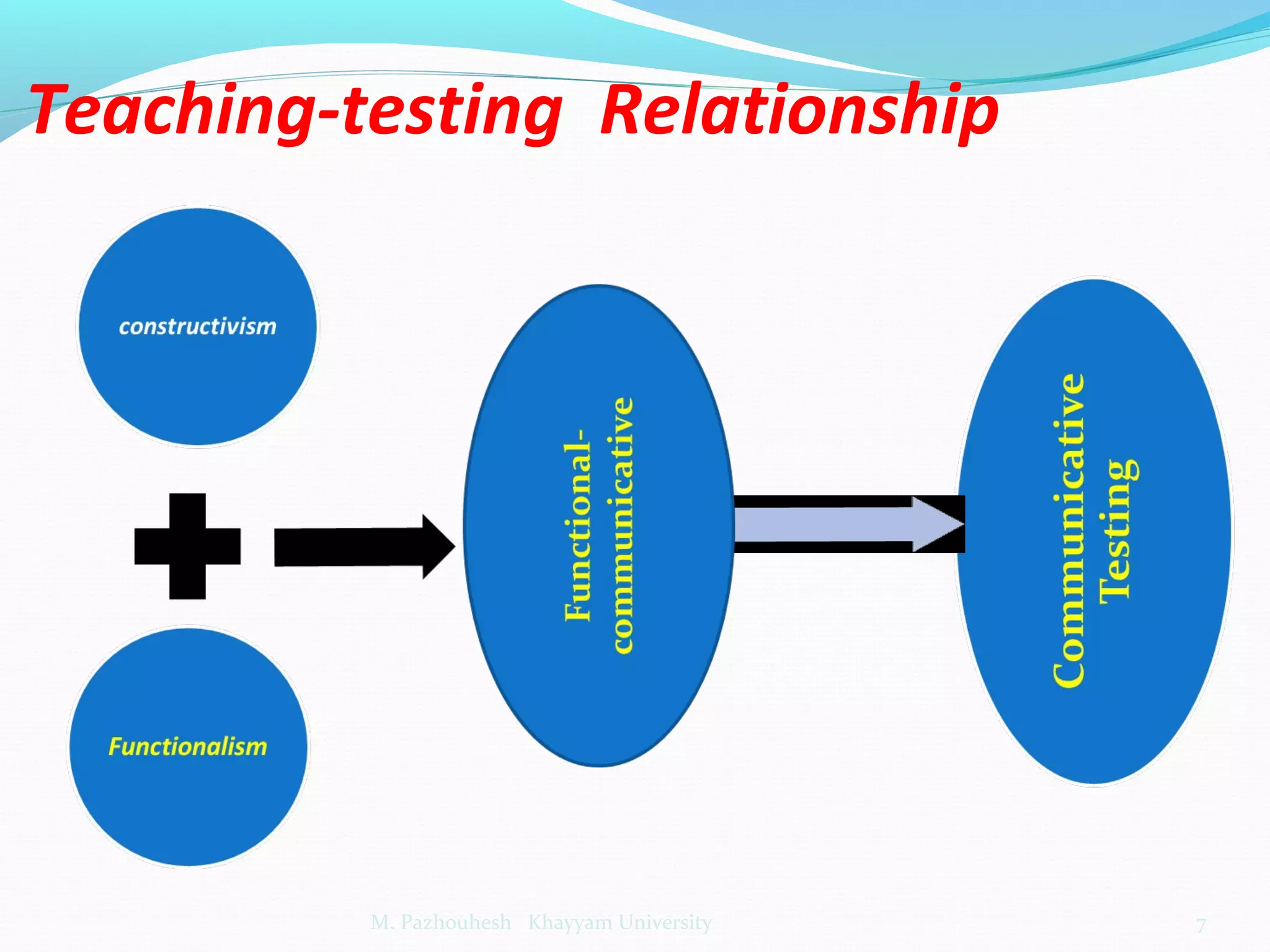
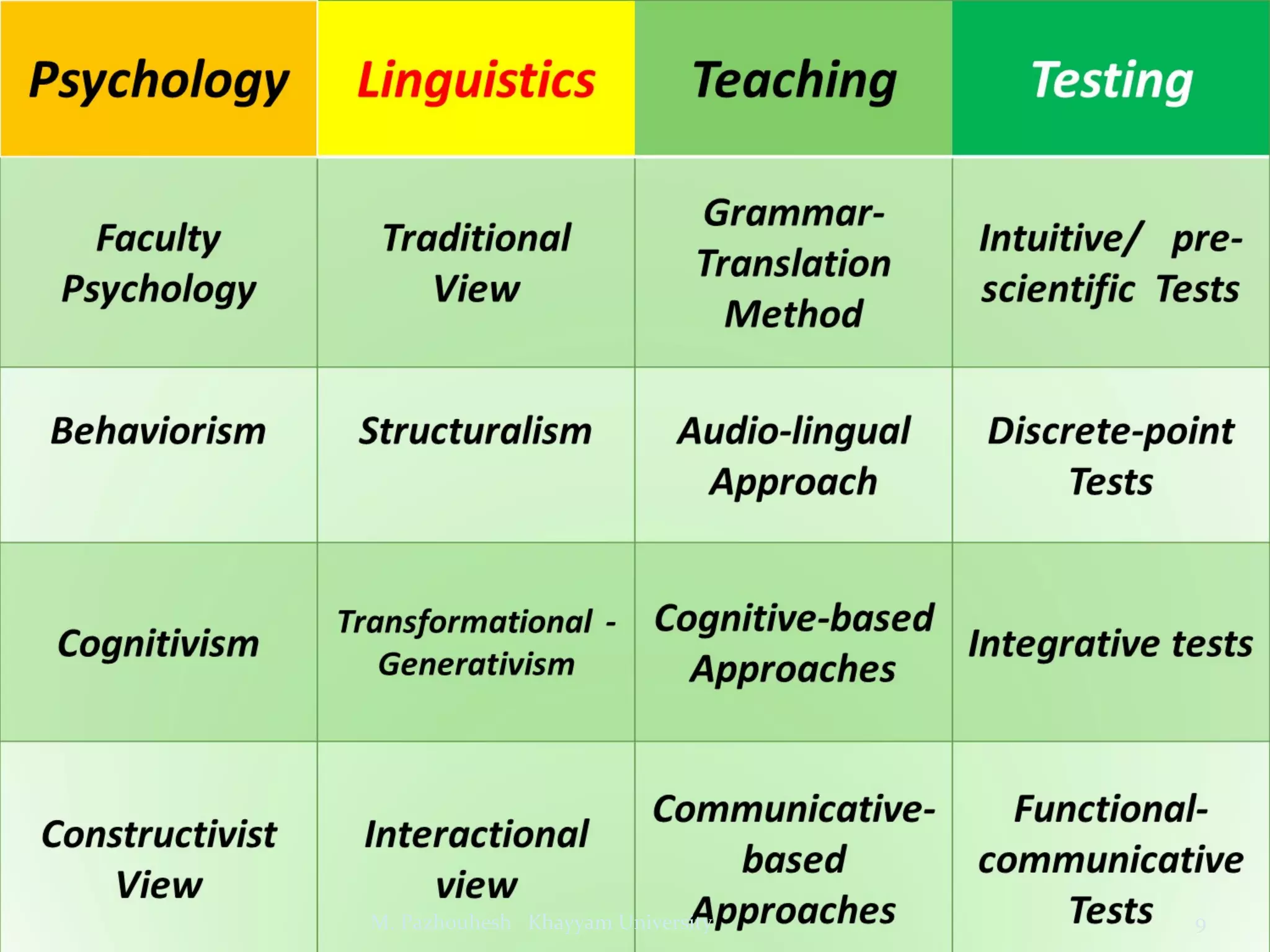
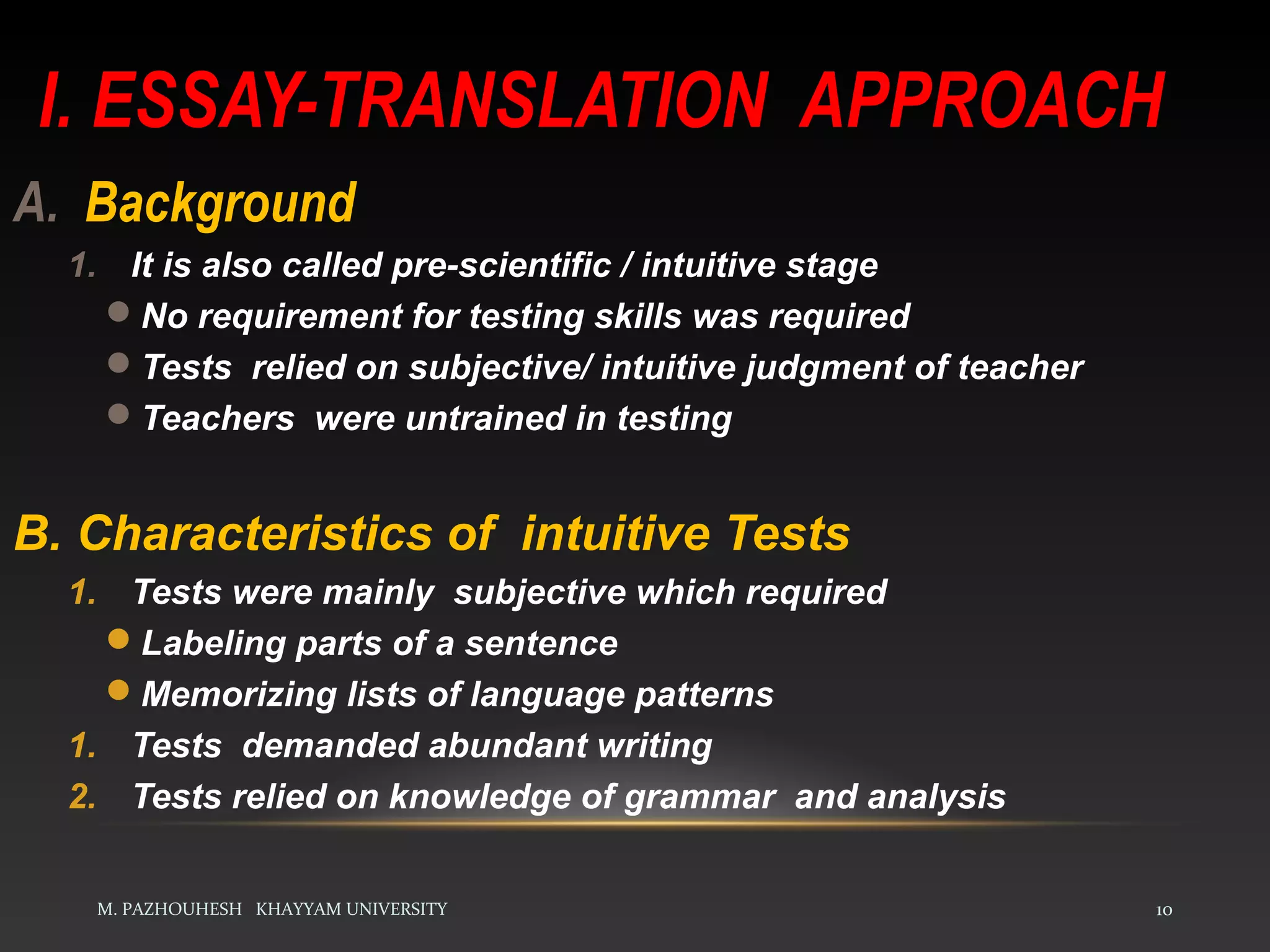
The document discusses the relationship between teaching and testing in language education, outlining various historical trends and approaches to language testing, including intuitive, structuralist, integrative, pragmatic, and communicative approaches. Each approach's characteristics, development, and key principles are analyzed, emphasizing their impact on language assessment. The importance of context, reliability, and the relevance of communicative competence in testing is also highlighted.














![ Characteristics of a communicative test
It should be interactive.
It should be direct in nature with tasks reflecting
realistic discourse processing activities.
Texts and tasks should be relevant to the intended
situation.
Ability should be sampled within meaningful and
developing contexts.
The test should be based on an a priori specification, so
what is to be tested and how it is to be tested should be
laid down at the test design stage. [Adapted from Weir, 1993]
22M. Pazhouhesh Khayyam University](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approaches-151217192211/75/Approaches-to-Language-Testing-22-2048.jpg)