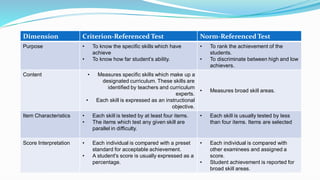
This document discusses language testing and evaluation. It defines formative and summative evaluation, with formative used to provide feedback during instruction and summative used to assess learning after instruction. Examples of evaluation include textbook, materials, course, and instructional evaluations. The purpose of evaluation is to improve teaching and learning, assess student progress, and identify weaknesses. Evaluation methods can be norm-referenced, comparing students, or criterion-referenced, assessing specific skills. Testing can directly assess skills or indirectly measure underlying abilities. Objective testing uses multiple choice while subjective uses human judgment. Proper testing is crucial for the teaching-learning process and provides feedback to improve curriculum and instruction.