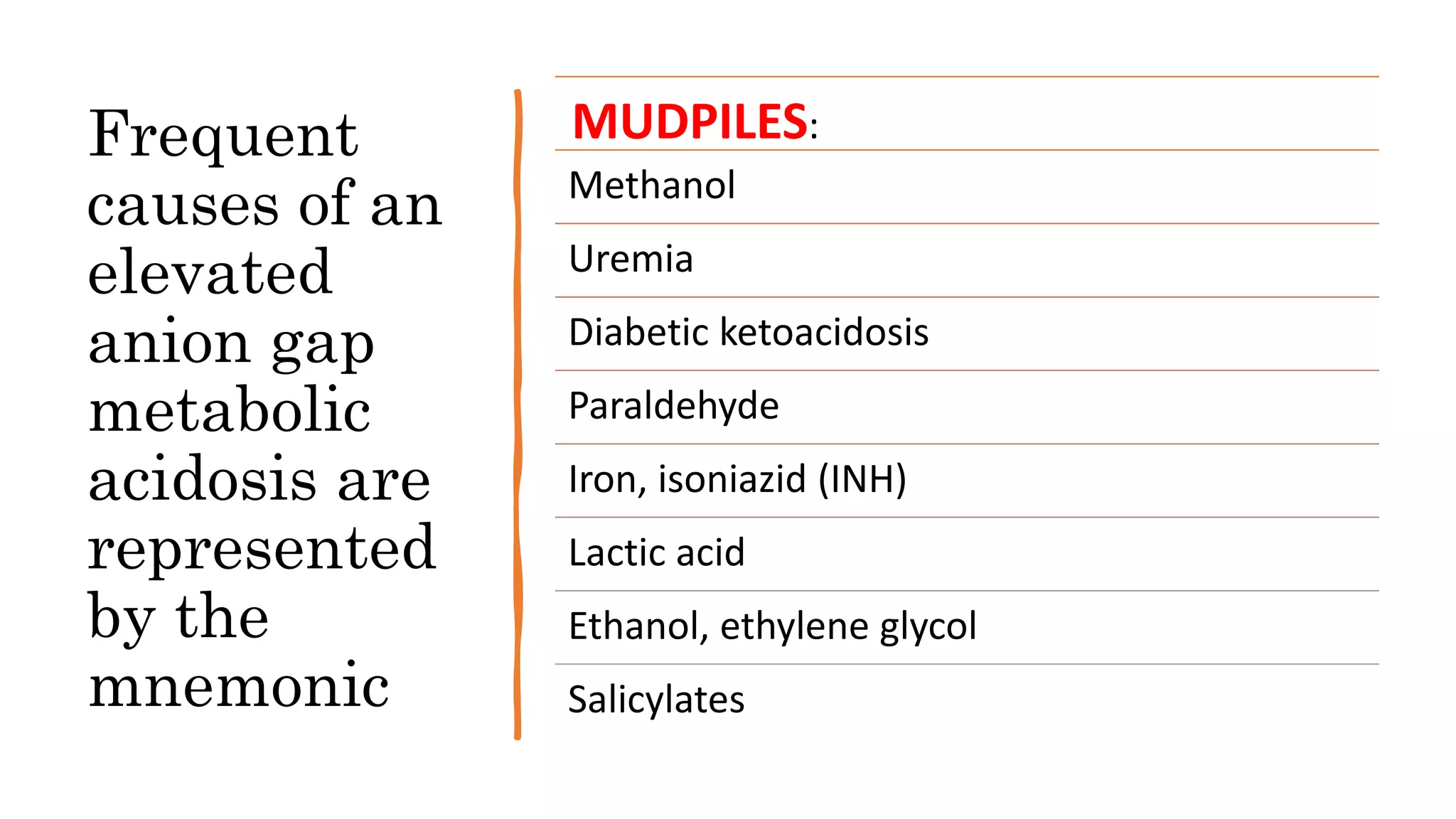
Metabolic acidosis is characterized by a decrease in serum pH caused by a decrease in bicarbonate or increase in hydrogen ions. It can be caused by increased acid production, decreased acid excretion, or alkali loss. The kidneys help eliminate daily acid load from metabolism by reclaiming bicarbonate and removing acids. Metabolic acidosis is categorized as normal or elevated anion gap based on the difference between measured cations and anions. Elevated anion gap acidosis involves unmeasured anions like in ketoacidosis, while normal anion gap involves chloride replacing depleted bicarbonate. Common causes of each type are represented by the mnemonics MUDPILES and USEDC

![Metabolic acidosis is an acid-base
disorder characterized by a decrease in
serum pH that results from either a
primary decrease in plasma
bicarbonate concentration ([HCO3-]) or
an increase in hydrogen ion
concentration ([H+])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approachtometabolicacidosis-210705154829/75/Approach-to-metabolic-acidosis-2-2048.jpg)