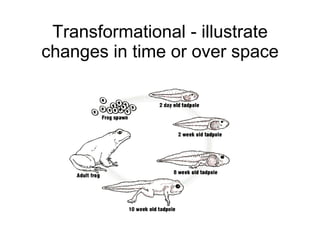
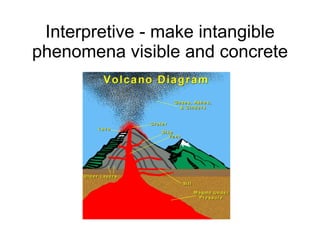
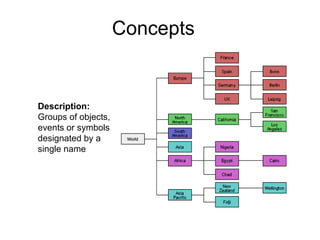
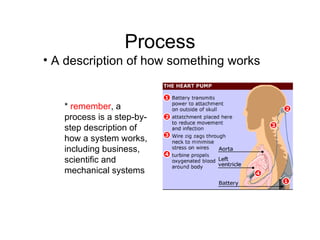
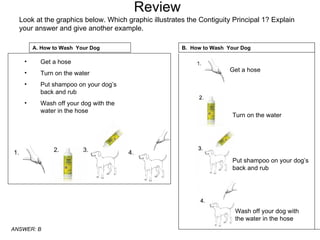
The document discusses principles of effective multimedia instruction, including the multimedia principle (using words and graphics rather than just words) and the contiguity principle (embedding words near corresponding graphics). It defines different types of graphics and explains how each can be used to teach different types of content. It also discusses cognitive load and how graphics can help engage learners and facilitate knowledge construction.