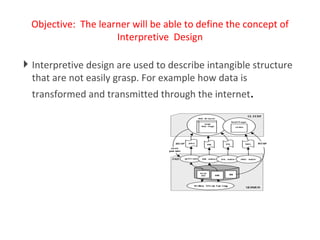
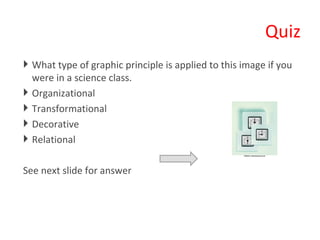
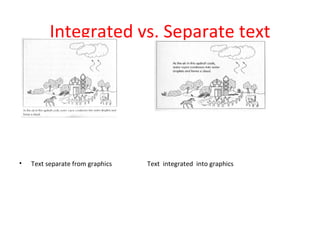
The document discusses principles of multimedia and contiguity in e-learning. It defines multimedia as using words and graphics rather than just words alone. Different types of graphics are described like static illustrations, organizational graphics, relational designs, and transformational designs. Contiguity principles emphasize aligning words with corresponding graphics, whether printed or spoken, to facilitate active learning and reduce cognitive load. Learners should not have to search for related words and graphics in e-learning materials.